Civil War Study Guide KEY
... Abraham Lincoln – president of the Union; freed the slaves with the Emancipation Proclamation; wanted to restore the Union; South Carolina seceded after he was elected. Robert E. Lee – overall commander of the Confederacy; brilliant military mind; West Point graduate; surrendered to Grant at Appomat ...
... Abraham Lincoln – president of the Union; freed the slaves with the Emancipation Proclamation; wanted to restore the Union; South Carolina seceded after he was elected. Robert E. Lee – overall commander of the Confederacy; brilliant military mind; West Point graduate; surrendered to Grant at Appomat ...
Civil War Layered Book Foldable
... of Richmond, Virginia failed as the Confederacy won. The Union would continue to try to capture Richmond for over three years. At this early battle, both sides realized that their armies needed to be well trained and equipped. The Union’s other strategy was to capture the Mississippi River. This wou ...
... of Richmond, Virginia failed as the Confederacy won. The Union would continue to try to capture Richmond for over three years. At this early battle, both sides realized that their armies needed to be well trained and equipped. The Union’s other strategy was to capture the Mississippi River. This wou ...
total war
... After the surrender of General Lee at Appomattox Courthouse, Grant forbade his men from celebrating. He ordered his men to be silent, saying, “The war is over. The rebels are our countrymen again.” ...
... After the surrender of General Lee at Appomattox Courthouse, Grant forbade his men from celebrating. He ordered his men to be silent, saying, “The war is over. The rebels are our countrymen again.” ...
THE CIVIL WAR
... 6. Outline the 11 Confederate states in RED. 7. Outline the four border states in GREEN. 8. Outline the Union states in BLUE. 9. Show Sherman’s March to the Sea with a heavy BLUE line. 10. Which t ...
... 6. Outline the 11 Confederate states in RED. 7. Outline the four border states in GREEN. 8. Outline the Union states in BLUE. 9. Show Sherman’s March to the Sea with a heavy BLUE line. 10. Which t ...
Chapter 19, Section 1.
... The Confederacy had the advantage of having a better military tradition, and thus had better military leaders than the Union. ...
... The Confederacy had the advantage of having a better military tradition, and thus had better military leaders than the Union. ...
Early Civil War
... LEADERS • President • Abraham Lincoln – Union • Jefferson Davis – Confederate ...
... LEADERS • President • Abraham Lincoln – Union • Jefferson Davis – Confederate ...
AP US History - DavidBAPNotebook
... The North was victorious because it had a larger pool of well trained and/or experienced military leaders and larger forces in general. Union forces had Ulysses S. Grant and Sherman. On the other hand the Confederacy only had Robert E. Lee. Grant and Sherman were really important because of their fe ...
... The North was victorious because it had a larger pool of well trained and/or experienced military leaders and larger forces in general. Union forces had Ulysses S. Grant and Sherman. On the other hand the Confederacy only had Robert E. Lee. Grant and Sherman were really important because of their fe ...
Key Figures of the Civil War
... • Lost many soldiers at Gettysburg when he ordered a frontal assault • His army was almost destroyed • Surrendered to General Grant at Appomattox Courthouse ...
... • Lost many soldiers at Gettysburg when he ordered a frontal assault • His army was almost destroyed • Surrendered to General Grant at Appomattox Courthouse ...
File
... II. Civil War Sites: 1860 – 1865 Use the map “Civil War Sites 1860-1865” on the back of the Casualty Figures packet to answer the following questions. 1. Name the 4 states that had slaves but did not leave the union. 2. Sherman marched through the South destroying towns and crops. Most of the destr ...
... II. Civil War Sites: 1860 – 1865 Use the map “Civil War Sites 1860-1865” on the back of the Casualty Figures packet to answer the following questions. 1. Name the 4 states that had slaves but did not leave the union. 2. Sherman marched through the South destroying towns and crops. Most of the destr ...
tennessee - National Park Service History
... have been turned, and the entire Army would have found itself in serious danger of crushing defeat. Johnston had been sitting quietly on his horse, bareheaded, among a clump of trees some distance behind the line of battle watching the progress of the attack. At this point, as he watched the progres ...
... have been turned, and the entire Army would have found itself in serious danger of crushing defeat. Johnston had been sitting quietly on his horse, bareheaded, among a clump of trees some distance behind the line of battle watching the progress of the attack. At this point, as he watched the progres ...
What was the first battle of the Civil War? - Ms. Sims
... • Confederates met the Union north of Richmond • Stonewall Jackson gets his nickname for standing his position • Confederates defeat the Union to the surprise of everyone ...
... • Confederates met the Union north of Richmond • Stonewall Jackson gets his nickname for standing his position • Confederates defeat the Union to the surprise of everyone ...
July 1862
... Feb 9, - The Confederate States of America is formed with Jefferson Davis, a West Point graduate and former U.S. Army officer, as president. ...
... Feb 9, - The Confederate States of America is formed with Jefferson Davis, a West Point graduate and former U.S. Army officer, as president. ...
Chapter Seventeen Structured Notes
... Their was no victory at the Battle of Antietam, but 23,000 Union and Confederate soldiers died in battle President Lincoln chose Ulysses S. Grant to replace George McClellan as the General of the Union Army The Confederacy won the Battles of Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville Stone Wall Jac ...
... Their was no victory at the Battle of Antietam, but 23,000 Union and Confederate soldiers died in battle President Lincoln chose Ulysses S. Grant to replace George McClellan as the General of the Union Army The Confederacy won the Battles of Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville Stone Wall Jac ...
Civil War Review Guide
... President Davis knew the South only had to drag out the war to make North give up Had the best military leaders ...
... President Davis knew the South only had to drag out the war to make North give up Had the best military leaders ...
The War In The East: Chapter 16, Section 2
... Northern army was marching very slowly towards Manassas, Virginia under Gen. McDowell These troops ran into Gen. Beauregard’s army and began an assault but Thomas Jackson’s unit stood standing like a brick wall against the advance. The victory earned Jackson the nickname of “Stonewall” ...
... Northern army was marching very slowly towards Manassas, Virginia under Gen. McDowell These troops ran into Gen. Beauregard’s army and began an assault but Thomas Jackson’s unit stood standing like a brick wall against the advance. The victory earned Jackson the nickname of “Stonewall” ...
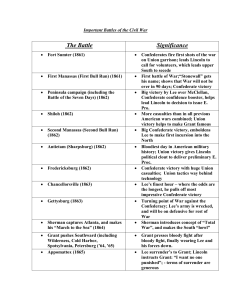
Civil War Battles and Events
... Northern victory – Ulysses S. Grant was commander of the Union army here. This was where he received his nickname “Unconditional Surrender,” after the battle of Ft. Donelson for not letting the Confederate soldiers off easy. He captured over 12,000 Confederate soldiers here. He was promoted to Major ...
... Northern victory – Ulysses S. Grant was commander of the Union army here. This was where he received his nickname “Unconditional Surrender,” after the battle of Ft. Donelson for not letting the Confederate soldiers off easy. He captured over 12,000 Confederate soldiers here. He was promoted to Major ...
21 The Furnace of the Civil War
... Civil War? 2. In which four states were the slaves all freed by state action—without and federal involvement? 3. Which two states kept slavery until it was finally abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution? 4. On what three rivers were the major Confederate strategic points that Gran ...
... Civil War? 2. In which four states were the slaves all freed by state action—without and federal involvement? 3. Which two states kept slavery until it was finally abolished by the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution? 4. On what three rivers were the major Confederate strategic points that Gran ...
Civil War Strategies
... Theaters of War Two theaters of war Eastern Theater Fought on land east of the Appalachian Mountains Fighting to control land between Washington, D.C. and Richmond, Virginia Northern Army called Army of the Potomac under the leadership of Gen. George B. McClellan responsible for defending ...
... Theaters of War Two theaters of war Eastern Theater Fought on land east of the Appalachian Mountains Fighting to control land between Washington, D.C. and Richmond, Virginia Northern Army called Army of the Potomac under the leadership of Gen. George B. McClellan responsible for defending ...
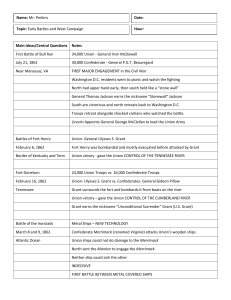
civil_war_timeline
... The Battle of Shiloh The Battle of Shiloh occurred soon after the Union had divided into the East and West. General Grant led his army through the woods only to find that the Confederates were there to attack near Shiloh. This battle lasted two days with many casualties. And even though the Union w ...
... The Battle of Shiloh The Battle of Shiloh occurred soon after the Union had divided into the East and West. General Grant led his army through the woods only to find that the Confederates were there to attack near Shiloh. This battle lasted two days with many casualties. And even though the Union w ...
Battle of Shiloh

The Battle of Shiloh, also known as the Battle of Pittsburg Landing, was a major battle in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, fought April 6–7, 1862, in southwestern Tennessee. A Union army under Major General Ulysses S. Grant had moved via the Tennessee River deep into Tennessee and was encamped principally at Pittsburg Landing, Tennessee on the west bank of the river, where Confederate forces under Generals Albert Sidney Johnston and Pierre G. T. Beauregard launched a surprise attack on Grant's army. Johnston was killed in action during the fighting; Beauregard, who thus succeeded to command of the army, decided against pressing the attack late in the evening. Overnight Grant received considerable reinforcements from another Union army under Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell, allowing him to launch an unexpected counterattack the next morning which completely reversed the Confederate gains of the previous day.On April 6, the first day of the battle, the Confederates struck with the intention of driving the Union defenders away from the river and into the swamps of Owl Creek to the west. Johnston hoped to defeat Grant's Army of the Tennessee before the anticipated arrival of General Don Carlos Buell's Army of the Ohio. The Confederate battle lines became confused during the fierce fighting, and Grant's men instead fell back to the northeast, in the direction of Pittsburg Landing. A Union position on a slightly sunken road, nicknamed the ""Hornet's Nest"", defended by the men of Brig. Gens. Benjamin M. Prentiss's and William H. L. Wallace's divisions, provided critical time for the remainder of the Union line to stabilize under the protection of numerous artillery batteries. W. H. L. Wallace was mortally wounded at Shiloh, while Prentiss was eventually surrounded and surrendered. General Johnston was shot in the leg and bled to death while personally leading an attack. Beauregard, his second in command, acknowledged how tired the army was from the day's exertions and decided against assaulting the final Union position that night.Reinforcements from Buell's army and a division of Grant's army arrived in the evening of April 6 and helped turn the tide the next morning, when the Union commanders launched a counterattack along the entire line. Confederate forces were forced to retreat from the area, ending their hopes of blocking the Union advance into northern Mississippi. The Battle of Shiloh was the bloodiest battle in American history up to that time, replaced the next year by the Battle of Chancellorsville (and, soon after, the three-day Battle of Gettysburg, which would prove to be the bloodiest of the war).