Two tomato GDP-D-mannose epimerase isoforms involve in
... SlGME1 and SlGME2 allowed normal ascorbate accumulation in the leaf and fruits, thus suggesting the same function regarding ascorbate. However, SlGME1 and SlGME2 were shown to play distinct roles in cell wall biosynthesis, depending on the tissue considered. The RNAi-SlGME1 plants harbored small and ...
... SlGME1 and SlGME2 allowed normal ascorbate accumulation in the leaf and fruits, thus suggesting the same function regarding ascorbate. However, SlGME1 and SlGME2 were shown to play distinct roles in cell wall biosynthesis, depending on the tissue considered. The RNAi-SlGME1 plants harbored small and ...
compound - NWIC Blogs - Northwest Indian College
... petioles or stems) spines (usually a modified leaf, leaf portion or stipule; e.g., cacti; Opuntia also has glochids) various modifications (e.g., insectivorous ...
... petioles or stems) spines (usually a modified leaf, leaf portion or stipule; e.g., cacti; Opuntia also has glochids) various modifications (e.g., insectivorous ...
Topic 26. The Angiosperms
... The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and diverse group of plants on Earth. The earliest, unambiguous, flowering plant fossils are from the Cretaceous, the last period of the Mesozoic. The group ...
... The Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) Angiosperms were the last major clade of plants to appear in the geologic record, and are the most abundant and diverse group of plants on Earth. The earliest, unambiguous, flowering plant fossils are from the Cretaceous, the last period of the Mesozoic. The group ...
Document
... Figure 2 Phenotype of sep1 sep2 sep3 triple mutants. a, Wild-type flower consisting of four sepals, four petals, six stamens and two fused carpels. b, sep1 sep2 sep3 triple mutant flower in which the four petals and six stamens are replaced by sepaloid organs and carpels are re ...
... Figure 2 Phenotype of sep1 sep2 sep3 triple mutants. a, Wild-type flower consisting of four sepals, four petals, six stamens and two fused carpels. b, sep1 sep2 sep3 triple mutant flower in which the four petals and six stamens are replaced by sepaloid organs and carpels are re ...
The physiology of Curcuma alismatifolia Gagnep. as a
... environmental condition. The days to shoot emergence debeen observed at a shoot height of 11–15 cm when plants creased when the storage temperature increased, or longer were grown in a greenhouse under minimum temperature of storage duration (Criley, 2013). In ‘Chiangmai Pink’, plant 15°C. The devel ...
... environmental condition. The days to shoot emergence debeen observed at a shoot height of 11–15 cm when plants creased when the storage temperature increased, or longer were grown in a greenhouse under minimum temperature of storage duration (Criley, 2013). In ‘Chiangmai Pink’, plant 15°C. The devel ...
Anemone (Anomone (a·nem·o·ne) from the Latin
... Northern Hemisphere. It does not occur naturally in the Southern Hemisphere. It is grown in Australia as a cash crop. ...
... Northern Hemisphere. It does not occur naturally in the Southern Hemisphere. It is grown in Australia as a cash crop. ...
Glossary
... BROAD (= Wide) Distance across a structure (equal to diameter if CAMBIUM The thin layer of delicate,rapidly dividing,meristematic tubular);sometimes restricted to signify the width or diameter of cells that forms wood internally and bark externally; also known three-dimensional structures. as vascul ...
... BROAD (= Wide) Distance across a structure (equal to diameter if CAMBIUM The thin layer of delicate,rapidly dividing,meristematic tubular);sometimes restricted to signify the width or diameter of cells that forms wood internally and bark externally; also known three-dimensional structures. as vascul ...
QUESERIA CREEK PLANT DIRECTORY
... simple cold frame, you can extend your season by a month or more on either end—in some climates, you can grow right through the winter with one. A cold frame is an ideal place to gradually acclimate tomato or pepper seedlings grown indoors to conditions outside. What is a cold frame? Nothing more th ...
... simple cold frame, you can extend your season by a month or more on either end—in some climates, you can grow right through the winter with one. A cold frame is an ideal place to gradually acclimate tomato or pepper seedlings grown indoors to conditions outside. What is a cold frame? Nothing more th ...
Functional Analysis of the STRUBBELIG
... Initiative 2000; Campbell 2006). Sequence comparisons and homology analysis between animal genes with already known function and plant genes can be taken into consideration for first indications about the gene structure and possible functions in plants. The question about the developmental processes ...
... Initiative 2000; Campbell 2006). Sequence comparisons and homology analysis between animal genes with already known function and plant genes can be taken into consideration for first indications about the gene structure and possible functions in plants. The question about the developmental processes ...
Epidermis
... Plant Body Organization Epidermis – Hypodermis A hypodermis is a subepidermal layer similar to a multiple epidermis except that the cells are derived from ground tissue rather than protoderm or epidermis. Ontogenetic studies are necessary to differentiate between hypodermal and multiple epidermal l ...
... Plant Body Organization Epidermis – Hypodermis A hypodermis is a subepidermal layer similar to a multiple epidermis except that the cells are derived from ground tissue rather than protoderm or epidermis. Ontogenetic studies are necessary to differentiate between hypodermal and multiple epidermal l ...
Macronutrient utilization by photosynthetic eukaryotes and the fabric
... AtAmt1;3 genes all show diurnal patterns of expression, although peak levels of AtAmt1;3 mRNA best correspond to the peak of NH4+ uptake (91). The influx of NH4+ toward the end of the light period may be influenced by increased availability of sugars (91, 314), suggesting a link between NH4+ uptake, ...
... AtAmt1;3 genes all show diurnal patterns of expression, although peak levels of AtAmt1;3 mRNA best correspond to the peak of NH4+ uptake (91). The influx of NH4+ toward the end of the light period may be influenced by increased availability of sugars (91, 314), suggesting a link between NH4+ uptake, ...
table partner review
... What is the difference between a fibrous root and a taproot? • A fibrous root system consists of many similarly sized roots that form a dense, tangled mass. ...
... What is the difference between a fibrous root and a taproot? • A fibrous root system consists of many similarly sized roots that form a dense, tangled mass. ...
Ferns for NJ Gardens - pleasantrunnursery.com
... narrower – and may only function to produce spores! Spores are somewhat similar to seeds, in that they can travel about by wind or by some form of mechanical means and, depending upon the plant, can remain dormant for extended periods of time. Spores differ from seeds since they are produced through ...
... narrower – and may only function to produce spores! Spores are somewhat similar to seeds, in that they can travel about by wind or by some form of mechanical means and, depending upon the plant, can remain dormant for extended periods of time. Spores differ from seeds since they are produced through ...
Seed Plants - MUGAN`S BIOLOGY PAGE
... a dicot plant if possible! PROCEDURE: MAKE ALL OF YOUR SKETCHES ON THE BACK OF THIS PAPER 1. Examine the leaves of the live specimens! Observe the differences in the pattern of veins on the leaves! 2. Sketch each leaf, including its vein pattern (TWO SKETCHES – ONE MONOCOT, ONE DICOT) 3. Count the n ...
... a dicot plant if possible! PROCEDURE: MAKE ALL OF YOUR SKETCHES ON THE BACK OF THIS PAPER 1. Examine the leaves of the live specimens! Observe the differences in the pattern of veins on the leaves! 2. Sketch each leaf, including its vein pattern (TWO SKETCHES – ONE MONOCOT, ONE DICOT) 3. Count the n ...
The Plant Cell, Vol. 27: 1889–1906, July 2015
... the swp73a-1 or swp73a-2 allele failed to reveal any distinguishing trait compared with the wild type during germination, seedling, organ development, and detailed monitoring of leaf shape, leaf blade extension, and root elongation. By contrast, the swp73b-1 and swp73b-2 mutations caused comparably ...
... the swp73a-1 or swp73a-2 allele failed to reveal any distinguishing trait compared with the wild type during germination, seedling, organ development, and detailed monitoring of leaf shape, leaf blade extension, and root elongation. By contrast, the swp73b-1 and swp73b-2 mutations caused comparably ...
Botany Handbook IFAS - Escambia County Extension
... rootlets, and travel through the main root into the stems and leaves. Root hairs are formed in great numbers near the tips of roots. In most plants they are short-lived. If a plant is transplanted carelessly, it is the loss of many of these small root hairs with their water-absorbing cells that will ...
... rootlets, and travel through the main root into the stems and leaves. Root hairs are formed in great numbers near the tips of roots. In most plants they are short-lived. If a plant is transplanted carelessly, it is the loss of many of these small root hairs with their water-absorbing cells that will ...
Development 128, 1771-1783 - The Company of Biologists
... 1772 E. Semiarti and others architecture arises during leaf development remains at a descriptive level (see below) and the molecular and genetic basis for this phenomenon remains to be analyzed. Previous studies using Arabidopsis thaliana have focused on two aspects of leaf symmetry. It has been de ...
... 1772 E. Semiarti and others architecture arises during leaf development remains at a descriptive level (see below) and the molecular and genetic basis for this phenomenon remains to be analyzed. Previous studies using Arabidopsis thaliana have focused on two aspects of leaf symmetry. It has been de ...
F-Box Protein FBX92 Affects Leaf Size in
... In Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), >1,400 genes or approximately 5% of the proteome encode elements of the ubiquitin– proteasome pathway (Smalle and Vierstra 2004). Several mutants and plants transgenic for the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway with altered leaf size have been identified, illustratin ...
... In Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis), >1,400 genes or approximately 5% of the proteome encode elements of the ubiquitin– proteasome pathway (Smalle and Vierstra 2004). Several mutants and plants transgenic for the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway with altered leaf size have been identified, illustratin ...
博士論文 Analysis of gene function involved in plant organ
... mutant. Thus, I suspected that the chromosomes of the acl1-1 mutant might be seriously disrupted. In order to explore chromosome disruptions, approximately 260 kb of the genomic region from At4g22290, the gene nearest to MASC04642, to At4g21690 was examined by amplifying fragments covering the geno ...
... mutant. Thus, I suspected that the chromosomes of the acl1-1 mutant might be seriously disrupted. In order to explore chromosome disruptions, approximately 260 kb of the genomic region from At4g22290, the gene nearest to MASC04642, to At4g21690 was examined by amplifying fragments covering the geno ...
Genetic Regulation of Vascular Tissue Patterning in
... McHale, 1996; Przemeck et al., 1996). Although these studies clearly indicate a role for auxin in vascular tissue differentiation, it has not been demonstrated that stochastic auxin transport is the sole determinant of vascular tissue patterns during normal development. To investigate the extent of ...
... McHale, 1996; Przemeck et al., 1996). Although these studies clearly indicate a role for auxin in vascular tissue differentiation, it has not been demonstrated that stochastic auxin transport is the sole determinant of vascular tissue patterns during normal development. To investigate the extent of ...
Unit 6: Plants - davis.k12.ut.us
... Stomata Like algae, most plants carry on photosynthesis, which produces glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. The exchange of gases between plant tissues and the environment is necessary for photosynthesis to occur. If the cuticle reduces water loss, it also might prevent the exchange of ...
... Stomata Like algae, most plants carry on photosynthesis, which produces glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. The exchange of gases between plant tissues and the environment is necessary for photosynthesis to occur. If the cuticle reduces water loss, it also might prevent the exchange of ...
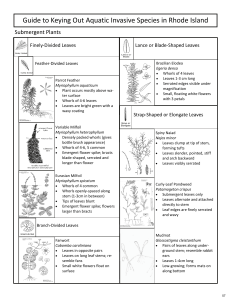
RIDEM Guide to Keying Out Plants
... ground stem; resemble rabbit ears • Leaves 1‐4cm long • Low‐growing; forms mats on along bottom ...
... ground stem; resemble rabbit ears • Leaves 1‐4cm long • Low‐growing; forms mats on along bottom ...
plant morphology
... ✧ In Eichhornia petiole swell and in citrus it is winged. ✧ Petiole is modified in tendrils in Nepenthes. ✧ In Australian acacia petiole is modified in phyllode. ✧ Long thin flexible petiole allow leaf blade to flutter in air, thereby cooling the leaf and bringing fresh air to leaf. Lamina (Epipodiu ...
... ✧ In Eichhornia petiole swell and in citrus it is winged. ✧ Petiole is modified in tendrils in Nepenthes. ✧ In Australian acacia petiole is modified in phyllode. ✧ Long thin flexible petiole allow leaf blade to flutter in air, thereby cooling the leaf and bringing fresh air to leaf. Lamina (Epipodiu ...
Plant ID Guide - New York
... alternate leaves that are minutely toothed on the edge. Swamp milkweed (Asclepias incarnata) also found in wet areas has opposite leaves but they are wider and they have a milky sap. The stem is round and not ridged. The flower is not similar. ...
... alternate leaves that are minutely toothed on the edge. Swamp milkweed (Asclepias incarnata) also found in wet areas has opposite leaves but they are wider and they have a milky sap. The stem is round and not ridged. The flower is not similar. ...
Structural Botany Laboratory 10 Cordaitales and Coniferales
... Nature of Branching and Foliage Several representative forms are present in the laboratory. These have varying types of leaves and branching patterns, and include members of several major conifer families. As you examine each specimen locate the leaves, distinguish them from the branches, and note ...
... Nature of Branching and Foliage Several representative forms are present in the laboratory. These have varying types of leaves and branching patterns, and include members of several major conifer families. As you examine each specimen locate the leaves, distinguish them from the branches, and note ...
Meristem

A meristem is the tissue in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place.Meristematic cells give rise to various organs of the plant and keep the plant growing. The shoot apical meristem (SAM) gives rise to organs like the leaves and flowers, while the root apical meristem (RAM) provides the meristematic cells for the future root growth. SAM and RAM cells divide rapidly and are considered indeterminate, in that they do not possess any defined end status. In that sense, the meristematic cells are frequently compared to the stem cells in animals, which have an analogous behavior and function.The term meristem was first used in 1858 by Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli (1817–1891) in his book Beiträge zur Wissenschaftlichen Botanik. It is derived from the Greek word merizein (μερίζειν), meaning to divide, in recognition of its inherent function.In general, differentiated plant cells cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Therefore, cell division in the meristem is required to provide new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body.Meristematic cells are incompletely or not at all differentiated, and are capable of continued cellular division (youthful). Furthermore, the cells are small and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The vacuoles are extremely small. The cytoplasm does not contain differentiated plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), although they are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together without intercellular cavities. The cell wall is a very thin primary cell wall.Maintenance of the cells requires a balance between two antagonistic processes: organ initiation and stem cell population renewal.Apical meristems are the completely undifferentiated (indeterminate) meristems in a plant. These differentiate into three kinds of primary meristems. The primary meristems in turn produce the two secondary meristem types. These secondary meristems are also known as lateral meristems because they are involved in lateral growth.At the meristem summit, there is a small group of slowly dividing cells, which is commonly called the central zone. Cells of this zone have a stem cell function and are essential for meristem maintenance. The proliferation and growth rates at the meristem summit usually differ considerably from those at the periphery.Meristems also are induced in the roots of legumes such as soybean, Lotus japonicus, pea, and Medicago truncatula after infection with soil bacteria commonly called Rhizobium. Cells of the inner or outer cortex in the so-called ""window of nodulation"" just behind the developing root tip are induced to divide. The critical signal substance is the lipo-oligosaccharide Nod-factor, decorated with side groups to allow specificity of interaction. The Nod factor receptor proteins NFR1 and NFR5 were cloned from several legumes including Lotus japonicus, Medicago truncatula and soybean (Glycine max). Regulation of nodule meristems utilizes long distance regulation commonly called ""Autoregulation of Nodulation"" (AON). This process involves a leaf-vascular tissue located LRR receptor kinases (LjHAR1, GmNARK and MtSUNN), CLE peptide signalling, and KAPP interaction, similar to that seen in the CLV1,2,3 system. LjKLAVIER also exhibits a nodule regulation phenotype though it is not yet known how this relates to the other AON receptor kinases.