E. coli
... induces the RpoS regulon associated with entry into stationary phase. Above pH 7, the favored fermentation products are acetate (with ethanol) and formate. Production of acetate and formate is maximal in the absence of oxygen or other respiratory electron acceptors, but oxygenated cultures also excr ...
... induces the RpoS regulon associated with entry into stationary phase. Above pH 7, the favored fermentation products are acetate (with ethanol) and formate. Production of acetate and formate is maximal in the absence of oxygen or other respiratory electron acceptors, but oxygenated cultures also excr ...
2. Glucogenic amino acids
... Propionyl CoA is formed either from odd chain fatty acids and carbon skeleton of some amino acids. It is converted to succinyl CoA which also enter TCAcycleto form oxaloacetate and terminate by formation of glucose. It is a minor source for glucose ...
... Propionyl CoA is formed either from odd chain fatty acids and carbon skeleton of some amino acids. It is converted to succinyl CoA which also enter TCAcycleto form oxaloacetate and terminate by formation of glucose. It is a minor source for glucose ...
Metabolic Integration during the Postprandial, Fasting and Feedback
... Copyright Rocha AJ. This book chapter is open access distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which allows users to download, copy and build upon published articles even for commercial purposes, as long as the author and publisher are properly credited. ...
... Copyright Rocha AJ. This book chapter is open access distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which allows users to download, copy and build upon published articles even for commercial purposes, as long as the author and publisher are properly credited. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 12.1 Glycolysis (Embden
... molecule taken up with three Na+ ions, one glucosemolecule enters astrocytes, two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis, and two lactate molecules are released. Within the astrocyte, one ATP fuels one “turn of the pump,” while the other provides the energy needed to convert glutamate to glut ...
... molecule taken up with three Na+ ions, one glucosemolecule enters astrocytes, two ATP molecules are produced through glycolysis, and two lactate molecules are released. Within the astrocyte, one ATP fuels one “turn of the pump,” while the other provides the energy needed to convert glutamate to glut ...
Inducible uptake and metabolism of glucose by the phosphorylative
... uptake in CSV86 is by active transport. Cells grown on succinic acid or naphthalene alone showed very low glucose uptake compared with glucose-grown cells. Similar results were observed when cells were grown on benzyl alcohol or pyruvate (data not shown). These results suggest that glucose transport ...
... uptake in CSV86 is by active transport. Cells grown on succinic acid or naphthalene alone showed very low glucose uptake compared with glucose-grown cells. Similar results were observed when cells were grown on benzyl alcohol or pyruvate (data not shown). These results suggest that glucose transport ...
Anti-beta-Galactosidase, Rabbit IgG Fraction
... Molecular Probes products are high-quality reagents and materials intended for research purposes only. These products must be used by, or directly under the supervision of, a technically qualified individual experienced in handling potentially hazardous chemicals. Please read the Material Safety Da ...
... Molecular Probes products are high-quality reagents and materials intended for research purposes only. These products must be used by, or directly under the supervision of, a technically qualified individual experienced in handling potentially hazardous chemicals. Please read the Material Safety Da ...
... 16. (8 pts) I’ve referred to the liver as a “glucose bank” because it stores excess glucose and releases glucose into the blood when there is a request for glucose. Please do one of the following two questions. Choice A: Name one hormone that is responsible for regulating glucose metabolism in the l ...
- WordPress.com
... A common way that cells capture the energy released during the breakdown of large molecules is to add electrons to smaller, specialized molecules that can accept them. This process of electron acceptance is otherwise known as A.biosynthesis B. Metabolism C. reduction D.Catalysis ...
... A common way that cells capture the energy released during the breakdown of large molecules is to add electrons to smaller, specialized molecules that can accept them. This process of electron acceptance is otherwise known as A.biosynthesis B. Metabolism C. reduction D.Catalysis ...
Application of stable isotopes and mass isotopomer distribution
... was fed to fish and chicks, appearance of [M+6] plasma glucose represented the contribution of absorbed dietary [U-13C6] glucose to plasma glucose flux. Similar precursor to product relationships can be used to determine dietary essentiality of nutrients (see below). Second, as noted above, an impor ...
... was fed to fish and chicks, appearance of [M+6] plasma glucose represented the contribution of absorbed dietary [U-13C6] glucose to plasma glucose flux. Similar precursor to product relationships can be used to determine dietary essentiality of nutrients (see below). Second, as noted above, an impor ...
Slide 1
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought o ...
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. Whether a mutation is negative or beneficial depends on how its DNA changes relative to the organism’s situation. Mutations are often thought o ...
GLUCONEOGENESIS, GLYCOGEN SYNTHESIS & DEGRADATION
... breakdown is cleaved to free glucose by glucose-6-phosphatase. The liver releases this glucose into the blood for use by needy tissues, including brain and blood cells ...
... breakdown is cleaved to free glucose by glucose-6-phosphatase. The liver releases this glucose into the blood for use by needy tissues, including brain and blood cells ...
Introduction - MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
... Circadian rhythms are cell-autonomous phenomena found throughout biology and have been shown to regulate many aspects of health and disease1. Despite this almost ubiquitous observation of cellular timekeeping, the genes generally proposed to be responsible show little or no homology between kingdoms ...
... Circadian rhythms are cell-autonomous phenomena found throughout biology and have been shown to regulate many aspects of health and disease1. Despite this almost ubiquitous observation of cellular timekeeping, the genes generally proposed to be responsible show little or no homology between kingdoms ...
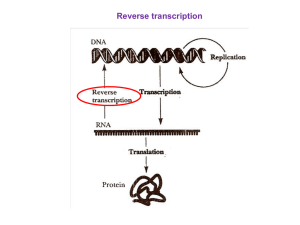
Reverse transcriptase
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
Modulation of glucokinase by glucose, small
... maintaining glucose homoeostasis and is the major glucosephosphorylating enzyme expressed in hepatocytes and pancreatic β-cells [1]. GK is unique among hexokinases in that it displays a sigmoidal substrate dose–response curve, demonstrates low affinity and positive co-operativity for substrate gluco ...
... maintaining glucose homoeostasis and is the major glucosephosphorylating enzyme expressed in hepatocytes and pancreatic β-cells [1]. GK is unique among hexokinases in that it displays a sigmoidal substrate dose–response curve, demonstrates low affinity and positive co-operativity for substrate gluco ...
2_5 Slides
... substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes. How are you going to make sure it is a fair test (control variables)? • What variables other than your independent variable could affect the results? • Why would these variables affect the results? • How will you ensure each is kept constant and mo ...
... substrate concentration on the activity of enzymes. How are you going to make sure it is a fair test (control variables)? • What variables other than your independent variable could affect the results? • Why would these variables affect the results? • How will you ensure each is kept constant and mo ...
Xu-7-integration
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
Mutations lowering the phosphatase activity of HPr kinase
... phosphorylation cascade leading to the phosphorylation of carbohydrates during their transport (Postma et al., 1993). In addition, P-Ser-HPr has been reported to inhibit the activity of several non-PTS permeases (Ye and Saier, 1995; Gauthier et al., 1997; Dossonnet et al., 2000; Viana et al., 2000), ...
... phosphorylation cascade leading to the phosphorylation of carbohydrates during their transport (Postma et al., 1993). In addition, P-Ser-HPr has been reported to inhibit the activity of several non-PTS permeases (Ye and Saier, 1995; Gauthier et al., 1997; Dossonnet et al., 2000; Viana et al., 2000), ...
B324notesTheme 2
... Decreasing cAMP (insulin) stimulates dephosphorylation, favoring PFK-2. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is strongly inhibited by fructose-6-phosphate. Glucagon represses transcription of pyruvate kinase. Glucagon activates transcription of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase Insulin represses transcriptio ...
... Decreasing cAMP (insulin) stimulates dephosphorylation, favoring PFK-2. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is strongly inhibited by fructose-6-phosphate. Glucagon represses transcription of pyruvate kinase. Glucagon activates transcription of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase Insulin represses transcriptio ...
Ammonium transport in Escherichia coli: localization and nucleotide
... mass of 27 kDa. The open reading frame is preceded by a putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence and followed by an inverted repeat which might function as a simple transcription terminator. Hydropathic analysis of the inferred amino acid sequence of the gene product predicts that umtA encodes a cytoplasmic ...
... mass of 27 kDa. The open reading frame is preceded by a putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence and followed by an inverted repeat which might function as a simple transcription terminator. Hydropathic analysis of the inferred amino acid sequence of the gene product predicts that umtA encodes a cytoplasmic ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... which can enter the glycolytic pathway as the first intermediate in that pathway. Since brain and muscle cells do not produce glucose, these cells can use glycogen for energy production only. 24.64 It enters already phosphorylated, and thus an ATP does not need to be expended to phosphorylate it. 24 ...
... which can enter the glycolytic pathway as the first intermediate in that pathway. Since brain and muscle cells do not produce glucose, these cells can use glycogen for energy production only. 24.64 It enters already phosphorylated, and thus an ATP does not need to be expended to phosphorylate it. 24 ...
Next Step Bio Supplement
... transacetylase, which is thought to inactivate thiogalactosides that are transported into the cell along with lactose by the permease enzyme. ...
... transacetylase, which is thought to inactivate thiogalactosides that are transported into the cell along with lactose by the permease enzyme. ...
gal isomer preferences of siglecs with a sialic acid microarray.
... did not show any binding while H-siglec-3 and H-siglec-10 bound to 1 and 2. Remarkably, the isomers of 1 and 2 displayed better binding to Siglec-3 and -10 than the native form (Fig. 1D and E). According to the microarray studies, compounds 1–6 sialic acid glycans possess two distinct binding patter ...
... did not show any binding while H-siglec-3 and H-siglec-10 bound to 1 and 2. Remarkably, the isomers of 1 and 2 displayed better binding to Siglec-3 and -10 than the native form (Fig. 1D and E). According to the microarray studies, compounds 1–6 sialic acid glycans possess two distinct binding patter ...
Journal of Applied Phycology
... We report the cloning and sequencing of the recA gene from Spirulinaplatensis. A genomic library of Spirulina was constructed in pUC19 and screened by PCR using oligonucleotides corresponding to the conserved amino acid sequences of Anabaena variabilisand Synechococcus RecA proteins. The Spirulina r ...
... We report the cloning and sequencing of the recA gene from Spirulinaplatensis. A genomic library of Spirulina was constructed in pUC19 and screened by PCR using oligonucleotides corresponding to the conserved amino acid sequences of Anabaena variabilisand Synechococcus RecA proteins. The Spirulina r ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... 42 base pairs downstream of this nod box is also indicated in Fig. 2. The codon usage of the indicated open reading frame is very similar to that of the nodA, nodB, and nodC genes of fast-growing rhizobia, which suggests that the open reading frame is a structural gene (data not shown). The open rea ...
... 42 base pairs downstream of this nod box is also indicated in Fig. 2. The codon usage of the indicated open reading frame is very similar to that of the nodA, nodB, and nodC genes of fast-growing rhizobia, which suggests that the open reading frame is a structural gene (data not shown). The open rea ...
Lac operon

lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes at universities for this reason.Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when lactose is required as a sugar source for the bacterium, the three genes of the lac operon can be expressed and their subsequent proteins translated: lacZ, lacY, and lacA. The gene product of lacZ is β-galactosidase which cleaves lactose, a disaccharide, into glucose and galactose. LacY encodes lactose permease, a protein which becomes embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane to enable transport of lactose into the cell. Finally, lacA encodes galactoside O-acetyltransferase. Layout of the lac operon.It would be wasteful to produce the enzymes when there is no lactose available or if there is a more preferable energy source available, such as glucose. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing the enzymes encoded by the lac operon only when necessary. In the absence of lactose, the lac repressor halts production of the enzymes encoded by the lac operon. In the presence of glucose, the catabolite activator protein (CAP), required for production of the enzymes, remains inactive, and EIIAGlc shuts down lactose permease to prevent transport of lactose into the cell. This dual control mechanism causes the sequential utilization of glucose and lactose in two distinct growth phases, known as diauxie.