lec4.Respiratory chain.mac2010-09
... membrane مهمهand is the final common pathway by which electrons derived from different fuels of the body flow to oxygen. ...
... membrane مهمهand is the final common pathway by which electrons derived from different fuels of the body flow to oxygen. ...
The efficiency of the isolation procedure is determined by
... fraction with respect to the enzyme activity in initial homogenate. We found that only 0.16+0.03 % of the homogenate lactate dehydrogenase activity is found in the mitochondria-enriched fraction, indicating a very low cytoplasmic contamination of the final mitochondrial preparation. There is also a ...
... fraction with respect to the enzyme activity in initial homogenate. We found that only 0.16+0.03 % of the homogenate lactate dehydrogenase activity is found in the mitochondria-enriched fraction, indicating a very low cytoplasmic contamination of the final mitochondrial preparation. There is also a ...
Respiration
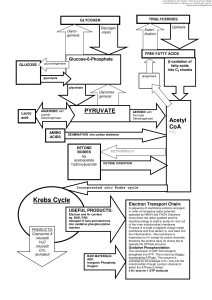
... matrix. Some ATP and other energy carrying molecules are produced here. The gas carbon dioxide is a byproduct of this process. The Electron Transport Chain Most of the ATP is produced in this last step of cellular respiration. Electron transport takes place in the infoldings of the inner-membrane of ...
... matrix. Some ATP and other energy carrying molecules are produced here. The gas carbon dioxide is a byproduct of this process. The Electron Transport Chain Most of the ATP is produced in this last step of cellular respiration. Electron transport takes place in the infoldings of the inner-membrane of ...
File
... • Aerobic oxidation – Cells use a four-stage process to convert energy released by the of glucose/fatty acid oxidation into ATP terminal phosphoanhydride bond. • Glycolysis – Stage 1: Cytosolic enzymes convert glucose to two molecules of pyruvate and generate two molecules each of NADH and ATP. • In ...
... • Aerobic oxidation – Cells use a four-stage process to convert energy released by the of glucose/fatty acid oxidation into ATP terminal phosphoanhydride bond. • Glycolysis – Stage 1: Cytosolic enzymes convert glucose to two molecules of pyruvate and generate two molecules each of NADH and ATP. • In ...
protein - Hagan Bayley
... Golgi- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Endosomes- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Lysosomes- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Peroxisomes- Single membrane. Thought to divide by enlargement and division, but recent results suggest peroxisomes are derived from ...
... Golgi- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Endosomes- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Lysosomes- Single membrane. No DNA or internal ribosomes Peroxisomes- Single membrane. Thought to divide by enlargement and division, but recent results suggest peroxisomes are derived from ...
p134
... removed from pyruvate using pyruvate decarboxylase. This produces ATP, ethanol, and carbon dioxide. 13. Muscle cells produce lactate from pyruvate when there is no oxygen available to accept electrons from the cytochrome oxidase complex. 20. A: inner mitochondrial membrane B: cristae C: mitochondria ...
... removed from pyruvate using pyruvate decarboxylase. This produces ATP, ethanol, and carbon dioxide. 13. Muscle cells produce lactate from pyruvate when there is no oxygen available to accept electrons from the cytochrome oxidase complex. 20. A: inner mitochondrial membrane B: cristae C: mitochondria ...
Section 7-1
... VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Aerobic respiration is the set of pathways in cellular respiration that require oxygen to break down pyruvic acid. 2. The mitochondrial matrix is the space inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. 3. The Krebs cycle is a biochemical pathway that breaks down acetyl coenzyme ...
... VOCABULARY REVIEW 1. Aerobic respiration is the set of pathways in cellular respiration that require oxygen to break down pyruvic acid. 2. The mitochondrial matrix is the space inside the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. 3. The Krebs cycle is a biochemical pathway that breaks down acetyl coenzyme ...
If you did a 10 minute wall sit, what would your muscles start to feel
... Input: pyruvate Output: CO2, NADH, FADH2 Location: Happens in the mitochondria Main Players: Carbon, NADH, FADH2 Significance: Makes 2 more ATPs and creates lots of positive and negatives charges for the ...
... Input: pyruvate Output: CO2, NADH, FADH2 Location: Happens in the mitochondria Main Players: Carbon, NADH, FADH2 Significance: Makes 2 more ATPs and creates lots of positive and negatives charges for the ...
BIOL 101 Cellular Respiration I. Organic Molecules A. Energy input
... B. Krebs cycle/citric acid cycle (in the matrix) 1. acetyl-CoA stuck onto 4-C sugar 2. enzyme-catalyzed metabolic pathway 3. net results a. ____ CO2 ...
... B. Krebs cycle/citric acid cycle (in the matrix) 1. acetyl-CoA stuck onto 4-C sugar 2. enzyme-catalyzed metabolic pathway 3. net results a. ____ CO2 ...
Introduction to Cell Symbiosis Therapy
... HAT DO we really know about the mitochondria? Well, most of us, not being cell biologists, probably know them as powerhouses of the cell. They are tiny bodies, generally termed organelles, that have the ability to convert oxygen and various nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used ...
... HAT DO we really know about the mitochondria? Well, most of us, not being cell biologists, probably know them as powerhouses of the cell. They are tiny bodies, generally termed organelles, that have the ability to convert oxygen and various nutrients into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used ...
File - Ms. Daley Science
... Refer to the information above. Do the plants produce carbon dioxide? a) Yes, but only at night when the plants can no longer early on photosynthesis. 42) Yes, carbon dioxide is produced all the time as a result of cell respiration. c) No, carbon dioxide is a waste product of animals only. d) No, pl ...
... Refer to the information above. Do the plants produce carbon dioxide? a) Yes, but only at night when the plants can no longer early on photosynthesis. 42) Yes, carbon dioxide is produced all the time as a result of cell respiration. c) No, carbon dioxide is a waste product of animals only. d) No, pl ...
Cellular Respiration
... used by humans and other organisms to release the energy stored in the food they consume ...
... used by humans and other organisms to release the energy stored in the food they consume ...
Document
... Glucose (C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ (cytoplasm) + 8 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 2 GDP + 2Pi + 2 H2O (mitochondria) ...
... Glucose (C6H12O6) + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ (cytoplasm) + 8 NAD+ + 2 FAD + 2 GDP + 2Pi + 2 H2O (mitochondria) ...
Key Terms:
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
... pyruvate CO2 and reduced coenzymes 3. Electron Transport red. coenzymes are re-ox.; e- passed to O2; H+ gradient 4. Chemiosmosis H+ gradient drives ATP synthesis Glycolysis is universal, anaerobic and cytosolic 2 ATP in; 4 ATP out & 2 reduced coenzymes glucose (six carbons, C6) 2 moleucles of py ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... some is kept in the body for blood pH (carbon dioxide) and hydrolysis reactions (water). - The most important product of respiration is the production of ATP (stored chemical potential energy). - Cell respiration occurs in your mitochondria (remember). - There are actually three stages to respiratio ...
... some is kept in the body for blood pH (carbon dioxide) and hydrolysis reactions (water). - The most important product of respiration is the production of ATP (stored chemical potential energy). - Cell respiration occurs in your mitochondria (remember). - There are actually three stages to respiratio ...
1 Which of the following are the smallest cells? A) human ovum B
... 23 The following molecules freely pass through a cell membrane except which one? A) ...
... 23 The following molecules freely pass through a cell membrane except which one? A) ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... Similarities and differences between aerobic cellular respiration, anaerobic lactic acid (lactate) production, anaerobic alcohol production, general reaction of each pathway Describe the process for carbohydrates, fats and proteins to enter the cellular respiration process. Be prepared to name some ...
... Similarities and differences between aerobic cellular respiration, anaerobic lactic acid (lactate) production, anaerobic alcohol production, general reaction of each pathway Describe the process for carbohydrates, fats and proteins to enter the cellular respiration process. Be prepared to name some ...
Glycolysis Animation
... • Acetyl CoA intermediate in all catabolism (esp. fats & proteins) • Surplus of ATP acetyl-CoA gets stored as lipid • Little ATP acetyl-CoA enters Krebs cycle & makes ATP ...
... • Acetyl CoA intermediate in all catabolism (esp. fats & proteins) • Surplus of ATP acetyl-CoA gets stored as lipid • Little ATP acetyl-CoA enters Krebs cycle & makes ATP ...
Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain
... Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain - ETC Interconnected proteins - named by Roman numerals (on large graphic on back of page) - embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ETC Jobs 1. Dehydrogenases: Removal of H from NADH and FADH Separation into a high energy electron e- & H+ 2. Proton p ...
... Stage 4 Digestion: Electron Transport Chain - ETC Interconnected proteins - named by Roman numerals (on large graphic on back of page) - embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane ETC Jobs 1. Dehydrogenases: Removal of H from NADH and FADH Separation into a high energy electron e- & H+ 2. Proton p ...
Cell Resp. Power Point Brief SV
... Outer Membrane: ____________________________________________ Inner Membrane: ____________________________________________ Intermembrane Space: _________________________________________ Crista: ______________________________________________________ Matrix: ___________________________________________ ...
... Outer Membrane: ____________________________________________ Inner Membrane: ____________________________________________ Intermembrane Space: _________________________________________ Crista: ______________________________________________________ Matrix: ___________________________________________ ...
Answers to exam 1 review #2
... 29. Mitochondria doesn't have which of the following: a. inner matrix b. adenosine triphosphate c. acetyl coA d. inner membrane e. guanine 30. Mitochondria doesn't do which of the following. a. cellular respiration b. formation of energy intermediates c. breakdown of glucose d. glycolysis e. citric ...
... 29. Mitochondria doesn't have which of the following: a. inner matrix b. adenosine triphosphate c. acetyl coA d. inner membrane e. guanine 30. Mitochondria doesn't do which of the following. a. cellular respiration b. formation of energy intermediates c. breakdown of glucose d. glycolysis e. citric ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.