Cell Standards
... interaction with their surroundings. The plasma membrane consists of two layers of lipid molecules organized with the polar (globular) heads of the molecules forming the outside of the membrane and the nonpolar (straight) tails forming the interior of the membrane. Protein molecules embedded within ...
... interaction with their surroundings. The plasma membrane consists of two layers of lipid molecules organized with the polar (globular) heads of the molecules forming the outside of the membrane and the nonpolar (straight) tails forming the interior of the membrane. Protein molecules embedded within ...
The Stages of Cellular RespiraWon
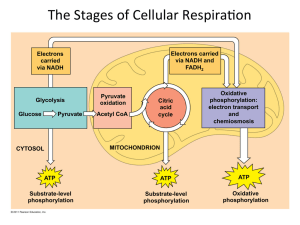
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
... Citric acid cycle and oxida3ve phosphoryla3on in mitochondria ...
8.2 HL Respiration pPractice Questions
... o The remaining two-carbon molecule (acetyl group) reacts with reduced coenzyme A, and, at the same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. o This is known as the link reaction. o In the Krebs cycle, each acetyl group (CH3CO) formed in the link reaction yields two CO2. o The names of the intermediate compoun ...
... o The remaining two-carbon molecule (acetyl group) reacts with reduced coenzyme A, and, at the same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. o This is known as the link reaction. o In the Krebs cycle, each acetyl group (CH3CO) formed in the link reaction yields two CO2. o The names of the intermediate compoun ...
Name: Date: Concept Check Questions Chapter 9 Cellular
... 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
... 9.3 The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules ...
MCB Lecture 9 – Mitchondria – Van Oost
... What are the three major types of mutations in Mitochondrial DNA? o Rearrangements that generate deletions o Point mutations o Missense mutations When mutations happen in Mitochondrial DNA, what types of tissues are affected first? What do those tissues do as a result? o Tissues with high-energy dem ...
... What are the three major types of mutations in Mitochondrial DNA? o Rearrangements that generate deletions o Point mutations o Missense mutations When mutations happen in Mitochondrial DNA, what types of tissues are affected first? What do those tissues do as a result? o Tissues with high-energy dem ...
Mitochondria and Cellular Respiration
... glucose is described in Glycolysis and in Cellular Respiration. But glucose is not the only fuel on which cells depend. Other carbohydrates, fats and even proteins may in certain cells or at certain times be used as a source of ATP. The complexity of the mechanism by which cells use glucose may make ...
... glucose is described in Glycolysis and in Cellular Respiration. But glucose is not the only fuel on which cells depend. Other carbohydrates, fats and even proteins may in certain cells or at certain times be used as a source of ATP. The complexity of the mechanism by which cells use glucose may make ...
4 Cell Resp Part 2 NT
... What is evidence of endosymbiosis? __________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ What is the advantage of the highly folded inner membrane? ___________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... What is evidence of endosymbiosis? __________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ What is the advantage of the highly folded inner membrane? ___________________ _______________________________________________ ...
BY 330 Summer 2015Mock Exam 2 Ten molecules of
... molecules of NADH are produced? How many molecules of CO2 are produced? How many molecules of pyruvate are formed? Show the pathway for this conversion, including all intermediates and energy production sites. (I won’t show the pathway for the conversion, but it is the process of glycolysis starting ...
... molecules of NADH are produced? How many molecules of CO2 are produced? How many molecules of pyruvate are formed? Show the pathway for this conversion, including all intermediates and energy production sites. (I won’t show the pathway for the conversion, but it is the process of glycolysis starting ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... This means that mutations of mtDNA are passed from mother to child. It also has implications for the cloning of mammals with the use of somatic cells. The nuclear DNA would be from the donor cell, but the mtDNA would be from the host cell. This is how Dolly the sheep was cloned. In plants, the cytop ...
... This means that mutations of mtDNA are passed from mother to child. It also has implications for the cloning of mammals with the use of somatic cells. The nuclear DNA would be from the donor cell, but the mtDNA would be from the host cell. This is how Dolly the sheep was cloned. In plants, the cytop ...
Ch9 Review Sheet - Canvas by Instructure
... 19. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria. Which stage or stages of sugar breakdown can take place in these cells? Explain your answer. 20. How is the process by which your body extracts energy from food similar to how a car's engine extracts energy from fuel? How is it different? 21. Explain ...
... 19. Red blood cells do not contain mitochondria. Which stage or stages of sugar breakdown can take place in these cells? Explain your answer. 20. How is the process by which your body extracts energy from food similar to how a car's engine extracts energy from fuel? How is it different? 21. Explain ...
Bio426Lecture25Apr3 - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... pyruvate (organic acid) producing some ATP and NADH. Can happen in presence or absence of O2 If O2, then pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA and into the citric acid cycle. ...
... pyruvate (organic acid) producing some ATP and NADH. Can happen in presence or absence of O2 If O2, then pyruvate converted to acetyl CoA and into the citric acid cycle. ...
MERRF
... reduced presence of SSV, can help distinguish MERRF from other mitochondrial myopathies (Lorenzoni et al., 2011). An elevated serum lactate level is an important MERRF indicator because it may indicate mitochondrial dysfunction (DiMauro et al., 2002; Ozawa et al., 1995) Creatine kinase levels in ...
... reduced presence of SSV, can help distinguish MERRF from other mitochondrial myopathies (Lorenzoni et al., 2011). An elevated serum lactate level is an important MERRF indicator because it may indicate mitochondrial dysfunction (DiMauro et al., 2002; Ozawa et al., 1995) Creatine kinase levels in ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... C) NADH has more energy than NAD+. D) NADH can transfer electrons into the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 8. Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following? A) glycolysis B) fermentation C) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the mitochondrial electro ...
... C) NADH has more energy than NAD+. D) NADH can transfer electrons into the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 8. Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following? A) glycolysis B) fermentation C) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the mitochondrial electro ...
Overview of mitochondria and plastids function in energy conversion
... (plural mitochondria)) ((from g greek μ μιτοςς or mitos,, thread + κουδριον or khondrion, granule) is a membrane-enclosed organelle, found in most eukaryotes. Amitochondriate eukaryotes have a related organelle called hydrogenosome or mitosome The primary function of mitochondria is the oxidative ph ...
... (plural mitochondria)) ((from g greek μ μιτοςς or mitos,, thread + κουδριον or khondrion, granule) is a membrane-enclosed organelle, found in most eukaryotes. Amitochondriate eukaryotes have a related organelle called hydrogenosome or mitosome The primary function of mitochondria is the oxidative ph ...
Biology Reading Guide 6 Where all energy ultimately come from Sun
... v Glycolysis Ø Initial # glucose molecules: 1 Ø # ATP molecules invested: 2 Ø # ATP molecules produced: 4 Ø # Net ATP molecules: 2 Ø # NADH produced: 2 Ø # Pyruvate molecules/glucose: 2 ...
... v Glycolysis Ø Initial # glucose molecules: 1 Ø # ATP molecules invested: 2 Ø # ATP molecules produced: 4 Ø # Net ATP molecules: 2 Ø # NADH produced: 2 Ø # Pyruvate molecules/glucose: 2 ...
GLYCOLYSIS and respiration review worksheet
... Glycolysis, the breakdown of carbon-containing molecules, is common to all organisms and occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. It may occur in the presence or absence of oxygen and yields a small amount of energy in the form of ATP. 1. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis ...
... Glycolysis, the breakdown of carbon-containing molecules, is common to all organisms and occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. It may occur in the presence or absence of oxygen and yields a small amount of energy in the form of ATP. 1. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis ...
Chapter 3 Exam
... separates two solutions. Solution A contains 0.9% NaCl and solution B contains 9.0 % NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution ...
... separates two solutions. Solution A contains 0.9% NaCl and solution B contains 9.0 % NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution ...
Khan Academy 15min cell respiration
... (a) In the presence of excess phosphate and substrate and intact mitochondria, oxygen is consumed only when ADP is added. When all of the added ADP has been convertedinto ATP, electron transport stops and oxygenconsumption ceases. (b) The addition of 2,4-dintrophenol uncouples electron transfer from ...
... (a) In the presence of excess phosphate and substrate and intact mitochondria, oxygen is consumed only when ADP is added. When all of the added ADP has been convertedinto ATP, electron transport stops and oxygenconsumption ceases. (b) The addition of 2,4-dintrophenol uncouples electron transfer from ...
G:\CLASSES\BI 205\Biol205_S10\exams\Final_S10.wpd
... considering aerobic respiration with optimal conditions? (B) How many ATP-equivalents does it take to build a glucose from scratch using optimal “light-independent” methods? (C) Why is there such a large difference between these two numbers? ...
... considering aerobic respiration with optimal conditions? (B) How many ATP-equivalents does it take to build a glucose from scratch using optimal “light-independent” methods? (C) Why is there such a large difference between these two numbers? ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... • The _____________is the innermost compartment, which is filled with a ____________________. • _________________________________________________of the mitochondria. • Pyruvic acid enters the _________________________. • Pyruvic acid is converted into an intermediate ___________________ ____________ ...
... • The _____________is the innermost compartment, which is filled with a ____________________. • _________________________________________________of the mitochondria. • Pyruvic acid enters the _________________________. • Pyruvic acid is converted into an intermediate ___________________ ____________ ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS – The anabolic reduction of CO2 to form sugar.
... CHAIN – NADH and FADH2 provide the electrons, and O2 ...
... CHAIN – NADH and FADH2 provide the electrons, and O2 ...
print last name first name
... 14. a. It is difficult to prevent cancer because cancer is caused by _________________________, which may result randomly from radiation, chemical, and viruses. b. Every time a normal cell divides, the __________________________ shorten, but this does not happen in cancer cells, which is why they a ...
... 14. a. It is difficult to prevent cancer because cancer is caused by _________________________, which may result randomly from radiation, chemical, and viruses. b. Every time a normal cell divides, the __________________________ shorten, but this does not happen in cancer cells, which is why they a ...
Title of project: Combating Inheritable heart disease: Functional and
... thanks to their ability to export matrix ATP, synthesised by the respiratory chain, and import cytosolic ADP, thus providing new substrate for the ATP synthase. Three tissue specific isoforms exist in humans. Point mutations in the human cardiac isoform (hANC1) have been shown to be involved in two ...
... thanks to their ability to export matrix ATP, synthesised by the respiratory chain, and import cytosolic ADP, thus providing new substrate for the ATP synthase. Three tissue specific isoforms exist in humans. Point mutations in the human cardiac isoform (hANC1) have been shown to be involved in two ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.