PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB QUESTIONS Laboratory
... Evaluation of the plasma proteins of a 50yearold male patient gives the following results: total serum protein: 90 g/l, A/G quotient: 0.40, albumin: 27%, gamma globulin: 55% with an intense, narrowbased peak. Acute phase reactants are normal. Serum Ca++ and uric acid are elevated. Erythrocyte sed ...
... Evaluation of the plasma proteins of a 50yearold male patient gives the following results: total serum protein: 90 g/l, A/G quotient: 0.40, albumin: 27%, gamma globulin: 55% with an intense, narrowbased peak. Acute phase reactants are normal. Serum Ca++ and uric acid are elevated. Erythrocyte sed ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam III - S2014 Name:________________________
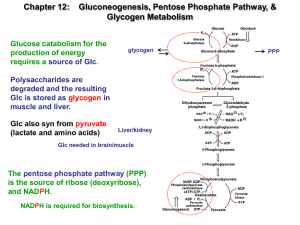
... the three pathways and describe: i) the step that is regulated (1 pt). ii) the compounds that regulate that step, and whether they activate or inhibit the step (4 pts). iii) why this regulation is useful to the cell (1 pts). Choice B: The liver cell responds to a number of different hormones, includ ...
... the three pathways and describe: i) the step that is regulated (1 pt). ii) the compounds that regulate that step, and whether they activate or inhibit the step (4 pts). iii) why this regulation is useful to the cell (1 pts). Choice B: The liver cell responds to a number of different hormones, includ ...
Common Docking Domain in Progesterone Receptor
... interaction domains [ERIDs (22)] and a poly-proline-rich (p-Pro) domain that is required for interaction between PR and the SH3-domain of c-Src (23). PR interacts with many other proteins via unknown domains (i.e. MEK1, FGFR2, STAT5) (21,24–26). In a recent in silico analysis of the PR amino acid se ...
... interaction domains [ERIDs (22)] and a poly-proline-rich (p-Pro) domain that is required for interaction between PR and the SH3-domain of c-Src (23). PR interacts with many other proteins via unknown domains (i.e. MEK1, FGFR2, STAT5) (21,24–26). In a recent in silico analysis of the PR amino acid se ...
Ch 9 and 11 Review Slides
... • 4 ATP via substratelevel phosphorylation • NAD+ is reduced to NADH. • Net Production? • 2 ATP + 2 NADH • 2 pyruvate ...
... • 4 ATP via substratelevel phosphorylation • NAD+ is reduced to NADH. • Net Production? • 2 ATP + 2 NADH • 2 pyruvate ...
Regulation of cellular homoeostasis by reversible lysine acetylation
... (transactivator of transcription)-interactive protein 60 kDa], MOZ (monocytic leukaemic zinc-finger protein), HBO1 (histone acetyltransferase binding to Orc1), MORF (MOZ-related factor) and MOF (male absent on first). These proteins have a wide range of acetylation substrates, and regulate pathways ...
... (transactivator of transcription)-interactive protein 60 kDa], MOZ (monocytic leukaemic zinc-finger protein), HBO1 (histone acetyltransferase binding to Orc1), MORF (MOZ-related factor) and MOF (male absent on first). These proteins have a wide range of acetylation substrates, and regulate pathways ...
Chemiluminescent and Fluorescent Westerns
... on a membrane. The method relies on an enzyme-substrate reaction that emits light, which is traditionally detected on x-ray film. Chemiluminescent Westerns are widely used across a variety of laboratories, and many facilities provide the necessary darkroom and developer for documentation with x-ray ...
... on a membrane. The method relies on an enzyme-substrate reaction that emits light, which is traditionally detected on x-ray film. Chemiluminescent Westerns are widely used across a variety of laboratories, and many facilities provide the necessary darkroom and developer for documentation with x-ray ...
PINdb: a database of nuclear protein complexes from human and
... assemblies. How a protein functions in vivo also appears to be dependent on its macromolecular environment: in uncomplexed forms, many of the purified proteins exhibit either altered or no enzymatic activities. To understand fundamental processes going on in the cell, it is therefore important to ma ...
... assemblies. How a protein functions in vivo also appears to be dependent on its macromolecular environment: in uncomplexed forms, many of the purified proteins exhibit either altered or no enzymatic activities. To understand fundamental processes going on in the cell, it is therefore important to ma ...
travel cards B4
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food/glucose • By combining carbon dioxide from the air; • With water obtained from the soil • Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves; • In structures called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll • Light is absorbed by chlorophyll • Light is use ...
... Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make food/glucose • By combining carbon dioxide from the air; • With water obtained from the soil • Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves; • In structures called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll • Light is absorbed by chlorophyll • Light is use ...
Campbell`s Biology, 9e (Reece et al.)
... A) substrate-level phosphorylation. B) electron transport. C) photophosphorylation. D) chemiosmosis. E) oxidation of NADH to NAD+. Answer: A 11) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) glycolysis B) accepting electrons at the end of the elec ...
... A) substrate-level phosphorylation. B) electron transport. C) photophosphorylation. D) chemiosmosis. E) oxidation of NADH to NAD+. Answer: A 11) The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event? A) glycolysis B) accepting electrons at the end of the elec ...
Cardiac glycogen accumulation after dexamethasone is regulated
... Downloaded from http://ajpheart.physiology.org/ by 10.220.32.246 on June 17, 2017 ...
... Downloaded from http://ajpheart.physiology.org/ by 10.220.32.246 on June 17, 2017 ...
09LecturePresentation
... • NADH passes the electrons to the electron transport chain • Unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction • O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energyyielding tumble • The energy yielded is used to regener ...
... • NADH passes the electrons to the electron transport chain • Unlike an uncontrolled reaction, the electron transport chain passes electrons in a series of steps instead of one explosive reaction • O2 pulls electrons down the chain in an energyyielding tumble • The energy yielded is used to regener ...
NCBI%20Sequence%20Analysis[1]
... 3. For each tree determine if there are any groupings – if so circle them and label them (ie mammals, primates, tetrapods, vertebrates etc.) 4. Analyze the trees – is their an overall pattern that emerges from the trees (provide examples) and are their any glaring surprises (provide examples). 5. Bu ...
... 3. For each tree determine if there are any groupings – if so circle them and label them (ie mammals, primates, tetrapods, vertebrates etc.) 4. Analyze the trees – is their an overall pattern that emerges from the trees (provide examples) and are their any glaring surprises (provide examples). 5. Bu ...
Enzyme changes in malnutrition - Journal of Clinical Pathology
... liver may be low without any other evidence of abnormal liver function. It seems, therefore, that these reductions in the activity of enzymes in the serum may be regarded as metabolic effects which precede functional impairment. Therefore they might be regarded as sensitive indicators of protein mal ...
... liver may be low without any other evidence of abnormal liver function. It seems, therefore, that these reductions in the activity of enzymes in the serum may be regarded as metabolic effects which precede functional impairment. Therefore they might be regarded as sensitive indicators of protein mal ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... Oxaloacetate is a component of . . . . A. the malate-aspartate shuttle B. gluconeogenesis C. the citric acid cycle D. A, B, and C above E. A and B above ...
... Oxaloacetate is a component of . . . . A. the malate-aspartate shuttle B. gluconeogenesis C. the citric acid cycle D. A, B, and C above E. A and B above ...
Regulation of Muscle Protein Synthesis and
... skeletal muscle disorders, including cachexia, muscular dystrophy, and pediatric muscle cancer rhabdomyosarcoma. Past studies have alluded to the involvement of NF-κB by demonstrating its activation in response to several factors that are themselves tightly linked to muscle wasting. Inflammatory cy ...
... skeletal muscle disorders, including cachexia, muscular dystrophy, and pediatric muscle cancer rhabdomyosarcoma. Past studies have alluded to the involvement of NF-κB by demonstrating its activation in response to several factors that are themselves tightly linked to muscle wasting. Inflammatory cy ...
intermediary metabolism
... Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone adrenalin, secreted by the medulla of the adrenal gland, is carried by the blood to the li ...
... Hormones are chemical menagers secreted by different endocrine glands and carried by blood to other tissues or organs, where they may stimulate or inhibit some specific metabolic activity. For e.g. the hormone adrenalin, secreted by the medulla of the adrenal gland, is carried by the blood to the li ...
CDPKs – a kinase for every Ca signal?
... calmodulin, and calmodulin stimulates the activity of these kinases. A third type of calcium-regulated protein kinases, the CaMKs, is well characterized from animals and yeast, but only one putative representative is known in plants7. The plant CaMK is more similar in sequence to CCaMKs than to anim ...
... calmodulin, and calmodulin stimulates the activity of these kinases. A third type of calcium-regulated protein kinases, the CaMKs, is well characterized from animals and yeast, but only one putative representative is known in plants7. The plant CaMK is more similar in sequence to CCaMKs than to anim ...
Xu-7-integration
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
... high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. In people with diabetes, blood sugar levels remain high. This may be because insulin is not being produced at all, not made at sufficient levels, not as effective as it should be. The most common forms of diabetes are type 1 diabetes (5%), which is an aut ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
... ETC accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first 2 stages - the energy released at each step of the chain is used to make ATP (oxidative phosphorylation); through redox rxns. oxidative phosphorylation accounts for 90% of generated ATP ...
UCLA Bioinformatics - Cal State LA
... Why glutaredoxin-like protein? • Only present among hyperthermophiles. • Operates in thiol-disulfide reaction via CXXC motif which either form a disulfide (oxidized form) or a dithiol (reduced form). • Requires for many functions including electron and proton transport to essential enzymes like rib ...
... Why glutaredoxin-like protein? • Only present among hyperthermophiles. • Operates in thiol-disulfide reaction via CXXC motif which either form a disulfide (oxidized form) or a dithiol (reduced form). • Requires for many functions including electron and proton transport to essential enzymes like rib ...
electron transport
... ATP production in the presence of a proton gradient and ATP/ADP exchange in the absence of a proton gradient. Exchange leads to incorporation of 18O in phosphate as shown. ...
... ATP production in the presence of a proton gradient and ATP/ADP exchange in the absence of a proton gradient. Exchange leads to incorporation of 18O in phosphate as shown. ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).











![NCBI%20Sequence%20Analysis[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009693178_1-3bb30000688a2f74739466a9a62c6c68-300x300.png)