Reactive Oxygen Intermediates Activate NF-KB in a
... radicals, hydrated electrons, and H202. Additional H,Oz is generated in irradiated cells by the dismutation of superoxide anions that are produced by the action of hydrated electrons on oxygen molecule^.^ H202 can be converted into highly active ROI.’ Compelling evidence indicates that a cascade of ...
... radicals, hydrated electrons, and H202. Additional H,Oz is generated in irradiated cells by the dismutation of superoxide anions that are produced by the action of hydrated electrons on oxygen molecule^.^ H202 can be converted into highly active ROI.’ Compelling evidence indicates that a cascade of ...
Reactive Oxygen Intermediates Activate NF-KB in a
... radicals, hydrated electrons, and H202. Additional H,Oz is generated in irradiated cells by the dismutation of superoxide anions that are produced by the action of hydrated electrons on oxygen molecule^.^ H202 can be converted into highly active ROI.’ Compelling evidence indicates that a cascade of ...
... radicals, hydrated electrons, and H202. Additional H,Oz is generated in irradiated cells by the dismutation of superoxide anions that are produced by the action of hydrated electrons on oxygen molecule^.^ H202 can be converted into highly active ROI.’ Compelling evidence indicates that a cascade of ...
C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of anaerobic
... pyruvate and glycerol are produced (12,14), reservations have been expressed as to the validity of this pathway (15,16). Aerobically, pyruvate is considered to be the exclusive end-product of glycolysis (1%17) as it cannot be further metabolized, due to the absence of both a functional tricarboxylic ...
... pyruvate and glycerol are produced (12,14), reservations have been expressed as to the validity of this pathway (15,16). Aerobically, pyruvate is considered to be the exclusive end-product of glycolysis (1%17) as it cannot be further metabolized, due to the absence of both a functional tricarboxylic ...
Overview of Metabolism Chapter
... the type of exercise underway, aerobic or anaerobic activity. First Stage of Glucose Metabolism: Glycolysis The first stage in the breakdown of glucose to produce ATP is glycolysis (from the Greek words glykys, meaning “sweet“ and lysis meaning “splitting”). In this metabolic pathway, the six-carbon ...
... the type of exercise underway, aerobic or anaerobic activity. First Stage of Glucose Metabolism: Glycolysis The first stage in the breakdown of glucose to produce ATP is glycolysis (from the Greek words glykys, meaning “sweet“ and lysis meaning “splitting”). In this metabolic pathway, the six-carbon ...
Chapter 9
... drive phosphorylation of ATP This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work ...
... drive phosphorylation of ATP This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work ...
Cellular Respiration
... Process by which cells convert the energy in food (usually glucose) into usable ATP. ...
... Process by which cells convert the energy in food (usually glucose) into usable ATP. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Process by which cells convert the energy in food (usually glucose) into usable ATP. ...
... Process by which cells convert the energy in food (usually glucose) into usable ATP. ...
Cellular Respiration
... 2. H+ them moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase 3. ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP 4. This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work 5. The energy stored in a H+ gradient acr ...
... 2. H+ them moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase 3. ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP 4. This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work 5. The energy stored in a H+ gradient acr ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Outline Glycolysis Transition
... A cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. – Most often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. ! Energy within a glucose molecule is released slowly so that ATP can be produced gradually. ! NAD+ and FAD are oxidation-reduction enzymes active du ...
... A cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. – Most often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. ! Energy within a glucose molecule is released slowly so that ATP can be produced gradually. ! NAD+ and FAD are oxidation-reduction enzymes active du ...
Evolution of Cell Signaling
... • Scaffolding proteins are large relay proteins to which other relay proteins are attached • Scaffolding proteins can increase the signal transduction efficiency by grouping together different proteins involved in the same pathway • In some cases, scaffolding proteins may also help activate some of ...
... • Scaffolding proteins are large relay proteins to which other relay proteins are attached • Scaffolding proteins can increase the signal transduction efficiency by grouping together different proteins involved in the same pathway • In some cases, scaffolding proteins may also help activate some of ...
Poster
... in endocytosis by helping to determine the curvature of the formed vesicle. To do this, certain positively charged residues on the concave surface of the FBAR domain of CIP4 interact with the negatively charged membrane phospholipids. CIP4 is important to the lab we are collaborating with because th ...
... in endocytosis by helping to determine the curvature of the formed vesicle. To do this, certain positively charged residues on the concave surface of the FBAR domain of CIP4 interact with the negatively charged membrane phospholipids. CIP4 is important to the lab we are collaborating with because th ...
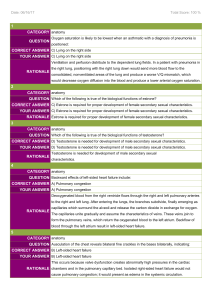
1 category question correct answer your answer
... Glycogen metabolism increases the glucose levels within cells, while decreasing glucose levels in blood. Insulin stimulates uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells and ...
... Glycogen metabolism increases the glucose levels within cells, while decreasing glucose levels in blood. Insulin stimulates uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells and ...
Biochemical studies on antioxidant
... this mixture was used for sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Oxidative protein damage was assessed as tryptophan oxidation, carbonyl, quenone and advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) generation in BSA in separate aliquots of the mixture. Results: All the pla ...
... this mixture was used for sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Oxidative protein damage was assessed as tryptophan oxidation, carbonyl, quenone and advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) generation in BSA in separate aliquots of the mixture. Results: All the pla ...
Diet for a person with a 10km run in a weeks time
... Bulk of chemical energy released = Carbohydrates The body’s principle fuel 75% of the body’s energy requirements The main and most efficient source of long lasting energy In the form of sugars and starches (simple or complex) Breakdown carbohydrates = Fuel for intensive exercise Stored in the mu ...
... Bulk of chemical energy released = Carbohydrates The body’s principle fuel 75% of the body’s energy requirements The main and most efficient source of long lasting energy In the form of sugars and starches (simple or complex) Breakdown carbohydrates = Fuel for intensive exercise Stored in the mu ...
Regulation of microtubule dynamics by microtubule
... proteins, MAP 1A and MAP 1B (Schoenfeld et al" 1989; Garner et al" 1990; Langkopf etal., 1992). MAP 1B (Bloom elal., 1985) is also known as MAP1.2 (Greene el al., 1983; Aletta et al" 1988), MAPI X (Binder et al., 1984; Calvert and Anderton, 1985) and MAP5 (Riederer el al., 1986). MAP1A has a molecul ...
... proteins, MAP 1A and MAP 1B (Schoenfeld et al" 1989; Garner et al" 1990; Langkopf etal., 1992). MAP 1B (Bloom elal., 1985) is also known as MAP1.2 (Greene el al., 1983; Aletta et al" 1988), MAPI X (Binder et al., 1984; Calvert and Anderton, 1985) and MAP5 (Riederer el al., 1986). MAP1A has a molecul ...
Pancréas et cellules bêta
... Pancreas and beta cells Focus on C. Wollheims’ lecture during SFD meeting (Geneva, 22-25 March 2011): “The Langerhans islet at the heart of Diabetes” Key role of Langerhans islets in pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes (T2D) has been highlighted in different models. Indeed, as well described, T2D is ...
... Pancreas and beta cells Focus on C. Wollheims’ lecture during SFD meeting (Geneva, 22-25 March 2011): “The Langerhans islet at the heart of Diabetes” Key role of Langerhans islets in pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes (T2D) has been highlighted in different models. Indeed, as well described, T2D is ...
Impaired overload-induced muscle growth is associated with
... proteins and elongation factors (including eEF2), presumably via phosphorylation of rpS6 (Terada et al. 1994; Jefferies et al. 1997), and also promotes a general increase in protein elongation by an indirect activation of eEF2 (Wang et al. 2001). On the other hand, mTOR phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 pro ...
... proteins and elongation factors (including eEF2), presumably via phosphorylation of rpS6 (Terada et al. 1994; Jefferies et al. 1997), and also promotes a general increase in protein elongation by an indirect activation of eEF2 (Wang et al. 2001). On the other hand, mTOR phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 pro ...
Brachmann et al., 2005 Mol Cell Biol. 25, 2593
... probability of being in the active conformation (~1%). Despite this low activity, when brought in proximity with a another low activity Tyr kinase (due to growth factor binding), crossphosphorylation of respective activation loops can occur. Phosphorylation of the residues on this loop stabilizes th ...
... probability of being in the active conformation (~1%). Despite this low activity, when brought in proximity with a another low activity Tyr kinase (due to growth factor binding), crossphosphorylation of respective activation loops can occur. Phosphorylation of the residues on this loop stabilizes th ...
... B2: (6 pts) Answer ONE of the following two questions, please indicate which one you are answering i) The principle component of margarine or butter are triglycerides. Both margarine and butter melt on hot summer days. Suggest a way of altering the triglyceride composition to prevent melting in the ...
15.3 Homeostasis - Liver Functions
... undergo deamination and are also converted into glucose and triglycerides Transamination reactions occur in the liver; this involves the conversion of one amino acid into another and is the process by which non-essential amino acids are synthesised ...
... undergo deamination and are also converted into glucose and triglycerides Transamination reactions occur in the liver; this involves the conversion of one amino acid into another and is the process by which non-essential amino acids are synthesised ...
21. glycolysis
... activity. The 2 lobes of hexokinase remain separate in the absence of its substrate molecule, i.e., glucose. However, the conformation changes markedly on binding with glucose and the 2 lobes of the enzyme come together Glucose and surround the substrate. This induced fit is shown in Fig, 21–5. Hexo ...
... activity. The 2 lobes of hexokinase remain separate in the absence of its substrate molecule, i.e., glucose. However, the conformation changes markedly on binding with glucose and the 2 lobes of the enzyme come together Glucose and surround the substrate. This induced fit is shown in Fig, 21–5. Hexo ...
Aluminum stress and its role in the phospholipid signaling pathway
... growth inhibition that results from Al-mediated toxicity. Al Effect on Phospholipid Signaling In coffee cells, Al is known to produce growth inhibition at different concentrations. Al has also been related to different biochemical processes involving membrane phospholipids as well as several enzymes ...
... growth inhibition that results from Al-mediated toxicity. Al Effect on Phospholipid Signaling In coffee cells, Al is known to produce growth inhibition at different concentrations. Al has also been related to different biochemical processes involving membrane phospholipids as well as several enzymes ...
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain)
... Citrate cycle (CC) and the RCH are interconnected a) by CO2 (produced by CC, used by RCH) b) by NADH (produced by CC, used by RCH) c) an enzyme succinate dehydrogenase d) ATP (produced by RCH, used by CC) ...
... Citrate cycle (CC) and the RCH are interconnected a) by CO2 (produced by CC, used by RCH) b) by NADH (produced by CC, used by RCH) c) an enzyme succinate dehydrogenase d) ATP (produced by RCH, used by CC) ...
word
... ER Associated Degradation: Pedro Carvalho Retro-translocation of a Misfolded Luminal ER Protein by the Ubiquitin-ligase Hrd1p Authors: Pedro Carvalho, Ann Marie Stanley, Tom Rapoport Glycosylation Veit Goder Protein O-mannosyltransferases participate in ER protein quality control by diverting protei ...
... ER Associated Degradation: Pedro Carvalho Retro-translocation of a Misfolded Luminal ER Protein by the Ubiquitin-ligase Hrd1p Authors: Pedro Carvalho, Ann Marie Stanley, Tom Rapoport Glycosylation Veit Goder Protein O-mannosyltransferases participate in ER protein quality control by diverting protei ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).