Part a
... coenzymes are transferred to the electron transport chain, built into the cristae membrane. The electron transport chain ...
... coenzymes are transferred to the electron transport chain, built into the cristae membrane. The electron transport chain ...
BCH 301 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... Fructose – 6 – PO4 ½ fructose 1, 6- di PO4 Glucose 6 – P ½ glucose GLUCONEOGENESIS This is the way in which the body meets its needs of glucose when carbohydrate is not available in sufficient amounts from the diet. The body then converts non glucose substances into glucose. Site:- Major site is the ...
... Fructose – 6 – PO4 ½ fructose 1, 6- di PO4 Glucose 6 – P ½ glucose GLUCONEOGENESIS This is the way in which the body meets its needs of glucose when carbohydrate is not available in sufficient amounts from the diet. The body then converts non glucose substances into glucose. Site:- Major site is the ...
PEPTIDE HORMONES
... Sizes, origins and fate: Due to the force of custom, “peptide hormones” is a collective name that has been applied to peptides, polypeptides and proteins that all function as hormones. The name “factor” has also been given to some of these peptides and originates from a time when their peptide/prot ...
... Sizes, origins and fate: Due to the force of custom, “peptide hormones” is a collective name that has been applied to peptides, polypeptides and proteins that all function as hormones. The name “factor” has also been given to some of these peptides and originates from a time when their peptide/prot ...
Metabolism
... • Glucose and galactose are absorbed very rapidly and hence it has been suggested that they are absorbed actively and it requires energy. • Fructose absorption is also rapid but not so much as compared to glucose and galactose but it is definitely faster than pentoses. Hence fructose is not absorbed ...
... • Glucose and galactose are absorbed very rapidly and hence it has been suggested that they are absorbed actively and it requires energy. • Fructose absorption is also rapid but not so much as compared to glucose and galactose but it is definitely faster than pentoses. Hence fructose is not absorbed ...
Work and Energy in Muscles
... we see that fatty acids and blood glucose take over as major energy sources since muscle glycogen stores have become depleted. Glucose continues as an important energy source throughout the experimental period. Remember that muscle must have some degree of anaerobic flux (are always dependent upon s ...
... we see that fatty acids and blood glucose take over as major energy sources since muscle glycogen stores have become depleted. Glucose continues as an important energy source throughout the experimental period. Remember that muscle must have some degree of anaerobic flux (are always dependent upon s ...
Proteogest - User`s Guide - A-Z Directory
... acid(s) to be modified and the modification (weight differential) to be used. Proteogest will modify the specified amino acid(s) according to the weight specified. These modifications can be carried out in two ways, one is ‘complete’ and the other is ‘incomplete’. If you choose ‘complete’, then al ...
... acid(s) to be modified and the modification (weight differential) to be used. Proteogest will modify the specified amino acid(s) according to the weight specified. These modifications can be carried out in two ways, one is ‘complete’ and the other is ‘incomplete’. If you choose ‘complete’, then al ...
Cell respiration powerpoint animation
... Glycolysis Glucose Only 2 ATP are made. If NO O2 ATP Glycolysis ...
... Glycolysis Glucose Only 2 ATP are made. If NO O2 ATP Glycolysis ...
Gene Section HSPA5 (heat shock 70kDa protein 5 (glucose regulated protein, 78kDa)) -
... carboxyterminal substrate (poly)peptide binding domain. Its functional cycle involves an ATP-form with low affinity for substrate (poly)peptides and an ADP-form with high substrate affinity and is regulated by Hsp40-type co-chaperones and nucleotide exchange factors. Molecular chaperones of the Hsp7 ...
... carboxyterminal substrate (poly)peptide binding domain. Its functional cycle involves an ATP-form with low affinity for substrate (poly)peptides and an ADP-form with high substrate affinity and is regulated by Hsp40-type co-chaperones and nucleotide exchange factors. Molecular chaperones of the Hsp7 ...
Gene Section STK11 (serine/threonine kinase 11) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Most mutations are null alleles; they are dispersed through the entire gene. ...
... Most mutations are null alleles; they are dispersed through the entire gene. ...
Carbohydrates and diabetes - Sheffield Teaching Hospital
... Carbohydrates are important to all of us. They are our body's main source of energy. It is important to include these foods every day to fuel your body. Your insulin, diabetes treatment and any physical activity you do will help control the rise in your blood glucose levels after you eat carbohydrat ...
... Carbohydrates are important to all of us. They are our body's main source of energy. It is important to include these foods every day to fuel your body. Your insulin, diabetes treatment and any physical activity you do will help control the rise in your blood glucose levels after you eat carbohydrat ...
Dr. Walaa AL - Jedda – 2016 Metabolism of Glycogen Glycogen: is
... 2-Muscle glycogen on the other hand, is to act as readily available source of intermediates of glycolysis for provision of energy within the muscle itself. Muscle glycogen cannot directly contribute to blood glucose level. 3-Inherited deficiency of enzymes in the pathway of glycogen metabolism produ ...
... 2-Muscle glycogen on the other hand, is to act as readily available source of intermediates of glycolysis for provision of energy within the muscle itself. Muscle glycogen cannot directly contribute to blood glucose level. 3-Inherited deficiency of enzymes in the pathway of glycogen metabolism produ ...
Ch36-Integration of Carbohydrate and Lipid
... eat and to use these stores when we are fasting. Regulatory mechanisms direct compounds through the pathways of metabolism involved in the storage and utilization of fuels. These mechanisms are controlled by hormones, by the concentration of available fuels, and by the energy needs of the body. Chan ...
... eat and to use these stores when we are fasting. Regulatory mechanisms direct compounds through the pathways of metabolism involved in the storage and utilization of fuels. These mechanisms are controlled by hormones, by the concentration of available fuels, and by the energy needs of the body. Chan ...
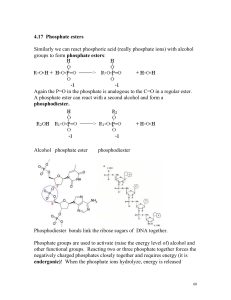
4.17 Phosphate esters Similarly we can react phosphoric acid (really
... The estrogens with sulfate covalently attached are collectively referred to as conjugated estrogens. This is analogous to the term conjugated bilirubin which is used to describe a bilirubin molecule in which glucuronic acid has been covalently attached. Indeed the active ingredients of Premarin are ...
... The estrogens with sulfate covalently attached are collectively referred to as conjugated estrogens. This is analogous to the term conjugated bilirubin which is used to describe a bilirubin molecule in which glucuronic acid has been covalently attached. Indeed the active ingredients of Premarin are ...
Document
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
How Cells Release Chemical Energy
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
... ATP-Generating Steps C Enzymes attach a phosphate to the two PGAL, and transfer two electrons and a hydrogen ion from each PGAL to NAD+. Two PGA (phosphoglycerate) and two NADH are the result. D Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from each PGA to ADP. Thus, two ATP have formed by substratelevel phos ...
Bio 6B Lecture Slides - R1
... macromolecules. Releases energy which may be used to produce ATP. • Anabolic pathway (anabolism): building up of macromolecules. Requires energy from ATP. • Metabolism: the balance of catabolism and anabolism in the body. ...
... macromolecules. Releases energy which may be used to produce ATP. • Anabolic pathway (anabolism): building up of macromolecules. Requires energy from ATP. • Metabolism: the balance of catabolism and anabolism in the body. ...
week 5_carbohydrates cont
... • Long, unbranched chains of D-glucose residues. • Linked by α-(1,4) glycosidic bonds • Amylose has one reducing end in which ring can open to form a free aldehyde group with reducing properties. • The internal anomeric carbon- involved in acetal lingkages and not free to act as reducing agents. • L ...
... • Long, unbranched chains of D-glucose residues. • Linked by α-(1,4) glycosidic bonds • Amylose has one reducing end in which ring can open to form a free aldehyde group with reducing properties. • The internal anomeric carbon- involved in acetal lingkages and not free to act as reducing agents. • L ...
L26_Adv06
... B liver glycolysis lactate is a product of rapid glycolysis C muscle glycolysis D muscle PDH activity lactate is a substrate E All of the above ...
... B liver glycolysis lactate is a product of rapid glycolysis C muscle glycolysis D muscle PDH activity lactate is a substrate E All of the above ...
chapter 14
... Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic condition it forms a. Lactic acid b. CO2 + H2O c. Acetyl CoA + CO2 ...
... Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic condition it forms a. Lactic acid b. CO2 + H2O c. Acetyl CoA + CO2 ...
PDF Format - Kinexus Bioinformatics Corporation
... communications networks of living cells for biomedical research into the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases. In particular, we track enzymes called protein kinases that control other proteins by carrying out their phosphorylation at regulatory sites known as phosphosites. Phosphosi ...
... communications networks of living cells for biomedical research into the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of human diseases. In particular, we track enzymes called protein kinases that control other proteins by carrying out their phosphorylation at regulatory sites known as phosphosites. Phosphosi ...
Isoforms of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
... difference between the two ACC isoforms is that ACC-2 appears to be a far better substrate for PKA in vitro than ACC-1. This was first observed for the rat liver ACC preparation [3S] and has been confirmed using preparations of ACC-2 from rat heart and skeletal muscle [SO]. Is the phosphorylation of ...
... difference between the two ACC isoforms is that ACC-2 appears to be a far better substrate for PKA in vitro than ACC-1. This was first observed for the rat liver ACC preparation [3S] and has been confirmed using preparations of ACC-2 from rat heart and skeletal muscle [SO]. Is the phosphorylation of ...
6- Fed Fast Cycle- ENDO
... The liver can synthesize & release ketone bodies from fatty acids to tissues for use as a fuel. (BUT: liver cannot use ketone bodies as a fuel). Ketone bodies formation is favored by the availability of fatty acids obtained from adipose tissue (fatty acids are degraded to acetyl CoA, the precursor o ...
... The liver can synthesize & release ketone bodies from fatty acids to tissues for use as a fuel. (BUT: liver cannot use ketone bodies as a fuel). Ketone bodies formation is favored by the availability of fatty acids obtained from adipose tissue (fatty acids are degraded to acetyl CoA, the precursor o ...
fed fast cycle
... The liver can synthesize & release ketone bodies from fatty acids to tissues for use as a fuel. (BUT: liver cannot use ketone bodies as a fuel). Ketone bodies formation is favored by the availability of fatty acids obtained from adipose tissue (fatty acids are degraded to acetyl CoA, the precursor o ...
... The liver can synthesize & release ketone bodies from fatty acids to tissues for use as a fuel. (BUT: liver cannot use ketone bodies as a fuel). Ketone bodies formation is favored by the availability of fatty acids obtained from adipose tissue (fatty acids are degraded to acetyl CoA, the precursor o ...
Metabolic Integration during the Postprandial, Fasting and Feedback
... and adipose tissue that accompany fasting [1,3,4,6,8]. It is needed to remember that the synthesis of glucose that occurs in the liver during periods of fasting the main precursors are amino acids, skeletal muscle, glycerol, resulting from the mobilization of adipose tissue triglycerides and Lactate ...
... and adipose tissue that accompany fasting [1,3,4,6,8]. It is needed to remember that the synthesis of glucose that occurs in the liver during periods of fasting the main precursors are amino acids, skeletal muscle, glycerol, resulting from the mobilization of adipose tissue triglycerides and Lactate ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).