Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Review Sheet - Phillips Scientific Methods
... Beta sheet has more hydrogen bonds An enzyme with beta sheets would be more difficult to denature Alpha helixes are easier to denature Structural properties due to the sheets Also have random coils o Tertiary structure Overall 3d shape due to the interaction of R groups. May have disulfi ...
... Beta sheet has more hydrogen bonds An enzyme with beta sheets would be more difficult to denature Alpha helixes are easier to denature Structural properties due to the sheets Also have random coils o Tertiary structure Overall 3d shape due to the interaction of R groups. May have disulfi ...
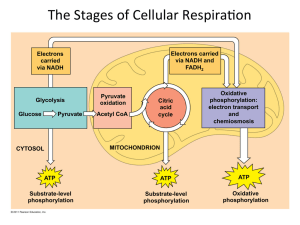
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... all the energy they were carrying from C-C bonds in glycolysis and Krebs The H+ can not accumulate indefinitely btwn membranes (high acidity) H+ flows through protein pump called ATP synthase toward e- and their acceptor (OXYGEN) This creates water and also Is used to generated energy to add P to AD ...
... all the energy they were carrying from C-C bonds in glycolysis and Krebs The H+ can not accumulate indefinitely btwn membranes (high acidity) H+ flows through protein pump called ATP synthase toward e- and their acceptor (OXYGEN) This creates water and also Is used to generated energy to add P to AD ...
Oligonucleotide 5` End Labeling with Radiochemicals
... The techniques for end labeling oligonucleotides with radioisotopes have driven nucleic acid probe technology. Oligonucleotide probes can be custom made based on sequence information of the target DNA or RNA in several hours on a DNA synthesizer. Use of a DNA synthesizer eliminates the usual cumbers ...
... The techniques for end labeling oligonucleotides with radioisotopes have driven nucleic acid probe technology. Oligonucleotide probes can be custom made based on sequence information of the target DNA or RNA in several hours on a DNA synthesizer. Use of a DNA synthesizer eliminates the usual cumbers ...
Cellular respiration includes three pathways
... oxidation-reduction reactions, or _________________________________________. 6. The loss of electrons from a substance is called _________________________. 7. The addition of electrons to another substance is called __________________________. 8. Respiration, the oxidation of glucose and other molec ...
... oxidation-reduction reactions, or _________________________________________. 6. The loss of electrons from a substance is called _________________________. 7. The addition of electrons to another substance is called __________________________. 8. Respiration, the oxidation of glucose and other molec ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Must-Knows: Unit 6 (Enzymes and Cell
... C. The rate of product formation ...
... C. The rate of product formation ...
Cellular_Respiration_overviewap
... Overview of Cellular Respiration The general equation for cellular respiration is as follows: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36-38ATP Glycolysis: In the cytoplasm The first step of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. It is when glucose is broken down into 2 pyruvic acids. To start the reaction ...
... Overview of Cellular Respiration The general equation for cellular respiration is as follows: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36-38ATP Glycolysis: In the cytoplasm The first step of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. It is when glucose is broken down into 2 pyruvic acids. To start the reaction ...
PART 1: TRUE OR FALSE (1 point each)
... which a molecule of water is generated. 2. In living organisms, the majority of proteins found exist in only one isomeric form. 3. Within a single protein, both alpha helices and beta sheets can be present. 4. Noncovalent bonds are the main determinant of protein tertiary structure. 5. According to ...
... which a molecule of water is generated. 2. In living organisms, the majority of proteins found exist in only one isomeric form. 3. Within a single protein, both alpha helices and beta sheets can be present. 4. Noncovalent bonds are the main determinant of protein tertiary structure. 5. According to ...
ATP - Mhanafi123`s Blog
... Pyruvate is the end product of Glycolysis with 7 ATP as high energy phosphate. ( older textbook still counting as 8 ATP). In unaerobic Glycolysis of certain type of muscle for sprinters, lack of oxygen cause inactive respiratory chain. NADH will reduces Pyruvate, and Lactate is the final product of ...
... Pyruvate is the end product of Glycolysis with 7 ATP as high energy phosphate. ( older textbook still counting as 8 ATP). In unaerobic Glycolysis of certain type of muscle for sprinters, lack of oxygen cause inactive respiratory chain. NADH will reduces Pyruvate, and Lactate is the final product of ...
3. Related Pathways
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
File
... • Starting point for respiration in aerobic AND anaerobic conditions – Aerobic with oxygen – Anaerobic no oxygen present ...
... • Starting point for respiration in aerobic AND anaerobic conditions – Aerobic with oxygen – Anaerobic no oxygen present ...
Problem Set 5 (Due February 25th) 1. Show how glucose can be
... Fat cannot be converted to glucose and can therefore not maintain blood glucose levels 10. Glycogen Phosphorylase uses inorganic phosphate to generate glucose-1-phosphate (G1P) from glycogen a. How does G1P enter glycolysis? It’s converted to G6P by Phosphoglucomutase. b. Why is it significant that ...
... Fat cannot be converted to glucose and can therefore not maintain blood glucose levels 10. Glycogen Phosphorylase uses inorganic phosphate to generate glucose-1-phosphate (G1P) from glycogen a. How does G1P enter glycolysis? It’s converted to G6P by Phosphoglucomutase. b. Why is it significant that ...
Slide 1
... – Occurs during starvation to keep the brain and red blood cells supplied with glucose, and occurs following exercise (Cori Cycle: lactate converted to glucose, which is re-supplied to muscle tissue) – Occurs in the mammalian liver; other starting materials include glycerol, and most amino acids ...
... – Occurs during starvation to keep the brain and red blood cells supplied with glucose, and occurs following exercise (Cori Cycle: lactate converted to glucose, which is re-supplied to muscle tissue) – Occurs in the mammalian liver; other starting materials include glycerol, and most amino acids ...
The Protoeomics and Lipidomics Center Mass Spectrometer Facility
... state of the art mass spectrometers to the University of Miami community. This facility provides various types of techniques such as proteomics and metabolomics (especially lipidomics). The facility provides hands on training on sample preparation and manipulation in proteomics and lipidomics for in ...
... state of the art mass spectrometers to the University of Miami community. This facility provides various types of techniques such as proteomics and metabolomics (especially lipidomics). The facility provides hands on training on sample preparation and manipulation in proteomics and lipidomics for in ...
Document
... Example: glucose and fructose both have chemical formulas of C6 H12 O6 BUT their shapes are different! ...
... Example: glucose and fructose both have chemical formulas of C6 H12 O6 BUT their shapes are different! ...
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid
... medium in which they lived as they shifted the nutrients into the components of their own bodies. This hypothetical situation would have resulted in natural selection favoring those organisms that could exist by using the nutrients that remained in their environment and by manipulating these nutrien ...
... medium in which they lived as they shifted the nutrients into the components of their own bodies. This hypothetical situation would have resulted in natural selection favoring those organisms that could exist by using the nutrients that remained in their environment and by manipulating these nutrien ...
key - Scioly.org
... Biological components- lactobacilli and yeast, enzymes i.e. amylase Biochemical components- starch into the sugars such as glucose, sucrose, galactose, etc 19. Draw the biochemical pathway for conversion of lactose to lactic acid? ...
... Biological components- lactobacilli and yeast, enzymes i.e. amylase Biochemical components- starch into the sugars such as glucose, sucrose, galactose, etc 19. Draw the biochemical pathway for conversion of lactose to lactic acid? ...
Structure Reveals How Cells `Sugar
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
... Biologists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory, Stony Brook University, and the University of Wurzburg, Germany, have deciphered the structure of a large protein complex responsible for adding sugar molecules to newly formed proteins - a process essential to many protei ...
CHAPTER-III CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... The citriic acid cyclle — also knnown as thee tricarboxyylic acid cyycle (TCA cycle), c the Krebs K cycle, or the Szent-G Györgyi–Krrebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions ussed by all aeerobic ...
... The citriic acid cyclle — also knnown as thee tricarboxyylic acid cyycle (TCA cycle), c the Krebs K cycle, or the Szent-G Györgyi–Krrebs cycle — is a series of chemical reactions ussed by all aeerobic ...
Ans
... molecules of pyruvic acid (3C). It occurs in cytoplasm outside the mitochondria. It is anaerobic phase so is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Q2. What is the difference between oxidative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation? Ans: Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs ...
... molecules of pyruvic acid (3C). It occurs in cytoplasm outside the mitochondria. It is anaerobic phase so is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Q2. What is the difference between oxidative phosphorylation and substrate level phosphorylation? Ans: Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs ...
Transport
... o Energy in the form of ATP is required o Movement from low to high areas of concentration o Examples are: 1. Primary active transport Phosphorylation occurs (from ATP hydrolysis)- to transport protein allowing it to change shape Na+K+ pump is an example (page 76) 2. Secondary active transpo ...
... o Energy in the form of ATP is required o Movement from low to high areas of concentration o Examples are: 1. Primary active transport Phosphorylation occurs (from ATP hydrolysis)- to transport protein allowing it to change shape Na+K+ pump is an example (page 76) 2. Secondary active transpo ...
amino acid - proffittscience
... Fatty acid chains can be of many lengths, extended by adding CH2 units. They are an efficient store of energy and bond with glycerol (a simple sugar alcohol) to make triglycerides – lipids. ...
... Fatty acid chains can be of many lengths, extended by adding CH2 units. They are an efficient store of energy and bond with glycerol (a simple sugar alcohol) to make triglycerides – lipids. ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).