Atomic Structure and Periodic Table PPT
... c. Atoms of different elements can mix physically or combine chemically in whole number ratios to form compounds d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, combined or rearranged however, atoms are never changed into another atom because of a chemical reaction. ...
... c. Atoms of different elements can mix physically or combine chemically in whole number ratios to form compounds d. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, combined or rearranged however, atoms are never changed into another atom because of a chemical reaction. ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 4
... Atomic mass of elements (mass number) It is defined as the average relative mass of one atom of the element, compared to the mass of a C12 isotope (C12 isotope with atomic mass of 12 amu is taken as the standard one). The unit of atomic mass is amu. The instrument used to determine mass number is th ...
... Atomic mass of elements (mass number) It is defined as the average relative mass of one atom of the element, compared to the mass of a C12 isotope (C12 isotope with atomic mass of 12 amu is taken as the standard one). The unit of atomic mass is amu. The instrument used to determine mass number is th ...
Know (main topic)
... -demonstrate ability to use scientific notation to multiply, divide, add, and subtract, very large and very small numbers. -describe the difference bet. the four states of matter. ...
... -demonstrate ability to use scientific notation to multiply, divide, add, and subtract, very large and very small numbers. -describe the difference bet. the four states of matter. ...
The Structure of the Atom 1 Philosophers And Early Scientists
... Chemists often write out isotopes using a shortened type of notation using only the chemical symbol, atomic number, and mass number. ...
... Chemists often write out isotopes using a shortened type of notation using only the chemical symbol, atomic number, and mass number. ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... The electrons are arranged in a particular order. The electrons fill the energy shells closest to the nucleus first and then fill outward: ...
... The electrons are arranged in a particular order. The electrons fill the energy shells closest to the nucleus first and then fill outward: ...
History of the Atom - Oak Park Unified School District
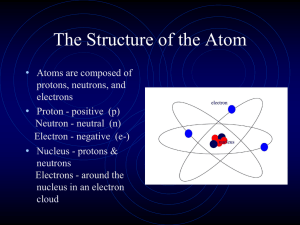
... > Mass of 1.0073 amu (2000x bigger than electron) > Atomic number: (Z) # of protons in nucleus, identifies elements • Neutron: neutral particle found in the nucleus > Mass of 1.0087 amu (about the same as a proton) > Number of neutrons determines isotopes ...
... > Mass of 1.0073 amu (2000x bigger than electron) > Atomic number: (Z) # of protons in nucleus, identifies elements • Neutron: neutral particle found in the nucleus > Mass of 1.0087 amu (about the same as a proton) > Number of neutrons determines isotopes ...
Entry Task
... – Their properties vary more from element to element than the properties of metals – All are gas in their natural state at room temperature except for bromine which is a liquid – Poor conductors of heat and electric current ...
... – Their properties vary more from element to element than the properties of metals – All are gas in their natural state at room temperature except for bromine which is a liquid – Poor conductors of heat and electric current ...
File
... • The electrons weigh almost nothing. • They are held by the nucleus by electrical attraction. • Atoms are electrically neutral, which means that the number of electrons in a neutral atom must be the same as the atomic number: number of electrons = number of protons ...
... • The electrons weigh almost nothing. • They are held by the nucleus by electrical attraction. • Atoms are electrically neutral, which means that the number of electrons in a neutral atom must be the same as the atomic number: number of electrons = number of protons ...
Unit #3: Atomic Structure Exam Review
... 31) An element’s ______Average Atomic Mass_________ is an average mass of the different isotopes of an element. 32) _______Isotopes________ are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. 33) ______Atomic Number_____ refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 34) De ...
... 31) An element’s ______Average Atomic Mass_________ is an average mass of the different isotopes of an element. 32) _______Isotopes________ are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. 33) ______Atomic Number_____ refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 34) De ...
Atom
... any amount of a compound contains the same element in the same proportions by mass No matter where the copper carbonate is used, it still has the same composition ...
... any amount of a compound contains the same element in the same proportions by mass No matter where the copper carbonate is used, it still has the same composition ...
key
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
- Triumph Learning
... Since that time, scientists have developed many different models of the atom as they have learned more about matter. A model is a representation of something that can be used to study, show, or explain how it functions. A model may be a diagram, a three-dimensional object, or a computer simulation. ...
... Since that time, scientists have developed many different models of the atom as they have learned more about matter. A model is a representation of something that can be used to study, show, or explain how it functions. A model may be a diagram, a three-dimensional object, or a computer simulation. ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 2 Chemistry
... In many ways, life can be viewed as a complicated chemical reaction. Modern models of how life works at all levels typically have at least some aspect of chemistry as a major ...
... In many ways, life can be viewed as a complicated chemical reaction. Modern models of how life works at all levels typically have at least some aspect of chemistry as a major ...
Chp 12 Lecture 2: The Atom!!! (stu copy)
... Mass number can vary for the same element, if the element has different numbers of neutrons. When this happens, these forms of an element are called _________. Chemical properties of isotopes are the same, although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. Some isotopes are radioact ...
... Mass number can vary for the same element, if the element has different numbers of neutrons. When this happens, these forms of an element are called _________. Chemical properties of isotopes are the same, although the physical properties of some isotopes may be different. Some isotopes are radioact ...
09/11/03 lecture
... of neutrons and protons present in an atom…but how much does an atom weigh? What units do we describe the mass of an atom in? • The atomic mass unit (amu): defined explicitly in terms of the 12C atom--the mass of 1 12C atom = 12 amu. • All other atomic masses are defined relative to the 12C atom. ...
... of neutrons and protons present in an atom…but how much does an atom weigh? What units do we describe the mass of an atom in? • The atomic mass unit (amu): defined explicitly in terms of the 12C atom--the mass of 1 12C atom = 12 amu. • All other atomic masses are defined relative to the 12C atom. ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... Which group of elements do not normally form chemical bonds? Based on the number of valence electrons, which of the following elements is the most reactive: Li, Be, B, Ne? How many electrons does a nitrogen (N) atom contain? How many protons does an argon (Ar) atom contain? How many neutrons does th ...
... Which group of elements do not normally form chemical bonds? Based on the number of valence electrons, which of the following elements is the most reactive: Li, Be, B, Ne? How many electrons does a nitrogen (N) atom contain? How many protons does an argon (Ar) atom contain? How many neutrons does th ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... f. ___C7H16 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O g. ___C3H5OH + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O 4. Write and balance the following reactions: a. Zinc Carbonate can be heated to form Zinc Oxide and Carbon Dioxide ...
... f. ___C7H16 + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O g. ___C3H5OH + ___O2 ___CO2 + ___H2O 4. Write and balance the following reactions: a. Zinc Carbonate can be heated to form Zinc Oxide and Carbon Dioxide ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • They are shiny, reactive metals that are often used to make alloys. • Actinide Series: (also called the Actinoid series) -- atomic #90 – 103 • Have unstable arrangements or protons and neutrons • All are radioactive and most are man-made ...
... • They are shiny, reactive metals that are often used to make alloys. • Actinide Series: (also called the Actinoid series) -- atomic #90 – 103 • Have unstable arrangements or protons and neutrons • All are radioactive and most are man-made ...
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number of
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
CP NT Ch. 4 and 25 v2
... C. He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced artificially. D. Induced transmutation can occur by bombarding an atom with _______ particles, protons or neutrons. III. Transuranium Elements A. Elements with atomic number above _______. B. All transuranium elements undergo transmutation C. None ...
... C. He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced artificially. D. Induced transmutation can occur by bombarding an atom with _______ particles, protons or neutrons. III. Transuranium Elements A. Elements with atomic number above _______. B. All transuranium elements undergo transmutation C. None ...
Bohr Diagrams, Metals, Non-Metals, and Metalloids
... to show the number and arrangement of electrons in each shell/energy level. ...
... to show the number and arrangement of electrons in each shell/energy level. ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... Democritus (2500 yrs ago) he said everything is made of small particles He called them atoms from atomos “uncut” or “indivisible” (undevideable) He thought there were different types of atoms with different properties Aristotle thought there was no limit to the number of times atoms could be divided ...
... Democritus (2500 yrs ago) he said everything is made of small particles He called them atoms from atomos “uncut” or “indivisible” (undevideable) He thought there were different types of atoms with different properties Aristotle thought there was no limit to the number of times atoms could be divided ...
The Material World: An Introduction to Chemistry 1. Modern Model of
... explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and they had to include the discovery of neutrons into their model. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that still behaves like the entire element, but that's not to say that the smaller parts do ...
... explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and they had to include the discovery of neutrons into their model. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that still behaves like the entire element, but that's not to say that the smaller parts do ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.