Chapter 4 Presentation - Spearfish School District
... 1. The different colors that were created by using different gases showed that atoms of different elements possessed different energies. 2. The cast shadow was thought to be due to the beam of light created by the cathode-ray. However, the experiment made with the spinning paddle-wheel showed that t ...
... 1. The different colors that were created by using different gases showed that atoms of different elements possessed different energies. 2. The cast shadow was thought to be due to the beam of light created by the cathode-ray. However, the experiment made with the spinning paddle-wheel showed that t ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... alkenes by decolourisation of manganate (VII) ions and of bromine in an inert solvent. Catalytic hydrogenation to alkanes. Arenes – Characterised by electrophilic substitution, e.g. AlBr3/Br2, conc. HNO3/H2SO4. (Monosubstitution only). ...
... alkenes by decolourisation of manganate (VII) ions and of bromine in an inert solvent. Catalytic hydrogenation to alkanes. Arenes – Characterised by electrophilic substitution, e.g. AlBr3/Br2, conc. HNO3/H2SO4. (Monosubstitution only). ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled ...
... Electrons in the highest occupied energy level D. What do elements that belong to the same group have in common? They have the same number of valence electrons; similar chemical properties E. What is the “octet rule”? Atoms are most stable if they have filled or empty outer shell of electrons Filled ...
Section 1 The Development of Atomic Theory
... > What is the difference between protons, neutrons, and electrons? > The three main subatomic particles are distinguished by mass, charge, and location in the atom. • Each element has a unique number of protons. • Unreacted atoms have no overall charge. – Because there is an equal number of protons ...
... > What is the difference between protons, neutrons, and electrons? > The three main subatomic particles are distinguished by mass, charge, and location in the atom. • Each element has a unique number of protons. • Unreacted atoms have no overall charge. – Because there is an equal number of protons ...
Chapter 2 – Elements
... Many properties of the elements are periodic in nature. That means that it has a property that repeats itself at regular intervals. There are 4 periodic properties that we will study. 1)Atomic radii 2) Ionic radii 3) Ionization energy and 4) Electronegativity An elements position on the periodic tab ...
... Many properties of the elements are periodic in nature. That means that it has a property that repeats itself at regular intervals. There are 4 periodic properties that we will study. 1)Atomic radii 2) Ionic radii 3) Ionization energy and 4) Electronegativity An elements position on the periodic tab ...
isotopes - LCC1050
... was a good thing it took a long time for the discovery of the neutron as it was essential for the development of the atomic bomb. ...
... was a good thing it took a long time for the discovery of the neutron as it was essential for the development of the atomic bomb. ...
Match the person / institution with the concept / discovery
... c. The ratio between the mass and charge of every cathode ray particle was identical. d. All of the above. 23. What is the name of Thomson’s atomic model? a. Wave model b. Planetary model Page 1 of 4 ...
... c. The ratio between the mass and charge of every cathode ray particle was identical. d. All of the above. 23. What is the name of Thomson’s atomic model? a. Wave model b. Planetary model Page 1 of 4 ...
Questions - SMK Raja Perempuan Ipoh
... 3.4 Number of Moles and Volume of gas 1. Molar volume of a gas : Volume occupied by one mole of any gas. 2. The molar volume of any gas is 24 dm3 at room conditions and 22.4 dm3 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) 3. generalization : One mole of any gas always occupies the same volume under t ...
... 3.4 Number of Moles and Volume of gas 1. Molar volume of a gas : Volume occupied by one mole of any gas. 2. The molar volume of any gas is 24 dm3 at room conditions and 22.4 dm3 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) 3. generalization : One mole of any gas always occupies the same volume under t ...
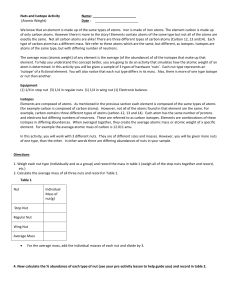
Nuts,Bolts and Isotopes- Average Atomic Mass Activity
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
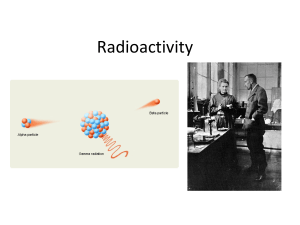
... 1. Write the nuclear symbol that represents alpha, beta and gamma decay? 2. a. Which of the 3 types of decay is the most harmful? b. Which one is the heaviest? c. Which one is a high speed electron? d. Which one(s) can be blocked by paper? 3. Define radioactive decay. Do all nuclei undergo this proc ...
... 1. Write the nuclear symbol that represents alpha, beta and gamma decay? 2. a. Which of the 3 types of decay is the most harmful? b. Which one is the heaviest? c. Which one is a high speed electron? d. Which one(s) can be blocked by paper? 3. Define radioactive decay. Do all nuclei undergo this proc ...
Atomic Structure The Nucleus The Electrons Atomic Theory
... century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called "indivisible atom" ...
... century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called "indivisible atom" ...
Radioactivity2015
... • The discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel and the Curies showed that one of Dalton’s ideas, that matter is indestructible and indivisible, is not always true. • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons, are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energ ...
... • The discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel and the Curies showed that one of Dalton’s ideas, that matter is indestructible and indivisible, is not always true. • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons, are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energ ...
Atoms and Integers Classwork
... Exploring Integers through Atoms Do Now: What is the periodic table? List 3 elements that you recognize from everyday life. Where do you recognize them from? ...
... Exploring Integers through Atoms Do Now: What is the periodic table? List 3 elements that you recognize from everyday life. Where do you recognize them from? ...
Unit 4: History of the Atom
... • Matter is indestructible and made up of atoms • Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of a specific element • Atoms of the same element can vary in mass • Atoms are divisible, into smaller subatomic particles – protons, neutrons, ...
... • Matter is indestructible and made up of atoms • Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of a specific element • Atoms of the same element can vary in mass • Atoms are divisible, into smaller subatomic particles – protons, neutrons, ...
File
... into different kinds of matter by physical means and are made up of one single chemical throughout 2) Mixtures are made up of multiple substances Most matter in the world around us are mixtures ...
... into different kinds of matter by physical means and are made up of one single chemical throughout 2) Mixtures are made up of multiple substances Most matter in the world around us are mixtures ...
2.1 Atomic Theory
... into subshells of four different types, identified as s, p, d, and f in order of increasing energy. The first shell has only an s subshell; the second shell has an s and a p subshell; the third shell has s, p, and d subshells, and the fourth has s, p, d and f subshells. The number of subshells is eq ...
... into subshells of four different types, identified as s, p, d, and f in order of increasing energy. The first shell has only an s subshell; the second shell has an s and a p subshell; the third shell has s, p, and d subshells, and the fourth has s, p, d and f subshells. The number of subshells is eq ...
Ch. 10: States of Matter Solids
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from another element. Atoms of different elements can chemically combine to form compounds Any chemical reaction is simply a re-arrangement of atoms ...
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from another element. Atoms of different elements can chemically combine to form compounds Any chemical reaction is simply a re-arrangement of atoms ...
atoms
... • Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons – How then are atoms of one element different from another element? ...
... • Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons – How then are atoms of one element different from another element? ...
Atomic Structure
... a) Three isotopes of sulfur are sulfur-32, sulfur33, and sulfur-34. Write the complete symbol for each isotope, including the atomic number and the mass number. b) How many neutrons, protons, and electrons are in Na+ with a mass number of 24? What is its atomic number? ...
... a) Three isotopes of sulfur are sulfur-32, sulfur33, and sulfur-34. Write the complete symbol for each isotope, including the atomic number and the mass number. b) How many neutrons, protons, and electrons are in Na+ with a mass number of 24? What is its atomic number? ...
Ms - cloudfront.net
... 13. Which atom has a greater ionization energy, nitrogen or bismuth? 14. Which atom has a larger atomic radius, fluorine or barium? 15. Which element is more like lithium in terms of properties, sodium or beryllium? 16. Which element has more electrons in its valence shell, sodium or magnesium? 17. ...
... 13. Which atom has a greater ionization energy, nitrogen or bismuth? 14. Which atom has a larger atomic radius, fluorine or barium? 15. Which element is more like lithium in terms of properties, sodium or beryllium? 16. Which element has more electrons in its valence shell, sodium or magnesium? 17. ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... Electron brother is balanced out by one positive Proton sister. The number of residents in Matterville depends on the Proton and Neutron families. Challenge: What would happen to the morale of Matterville if one Elliott Electron was kidnapp ...
... Electron brother is balanced out by one positive Proton sister. The number of residents in Matterville depends on the Proton and Neutron families. Challenge: What would happen to the morale of Matterville if one Elliott Electron was kidnapp ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.