The Chemistry of Life ppt
... • Atoms with less than 8 valence electrons can move close to each other and share their electrons • The electrons spend their time around both atoms. ...
... • Atoms with less than 8 valence electrons can move close to each other and share their electrons • The electrons spend their time around both atoms. ...
The Chemistry of Life Chapter 2
... • Atoms with less than 8 valence electrons can move close to each other and share their electrons • The electrons spend their time around both atoms. ...
... • Atoms with less than 8 valence electrons can move close to each other and share their electrons • The electrons spend their time around both atoms. ...
Chapter 4 - H - Regional School District 17
... objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. 1. Atoms in compounds are like bricks in a wall. Explain this analogy. 2. Think of ...
... objects from one location to another. The comparison is an example of an analogy. An analogy uses a similarity to compare two objects or systems. A familiar object is often used to help explain a less familiar object. 1. Atoms in compounds are like bricks in a wall. Explain this analogy. 2. Think of ...
atomic number
... • what makes one element different from another? The proton number. • all atoms of the same element have the same proton number, and atoms of different elements have different proton numbers. • ex: all gold (Au) atoms have 79 protons. 79 ≠ 47, so all silver (Ag) atoms have 47 protons. gold ≠ silver ...
... • what makes one element different from another? The proton number. • all atoms of the same element have the same proton number, and atoms of different elements have different proton numbers. • ex: all gold (Au) atoms have 79 protons. 79 ≠ 47, so all silver (Ag) atoms have 47 protons. gold ≠ silver ...
File
... magnesium 24 with a mass of 23.9850 amu, 10.00% magnesium 25 with a mass of 24.9858 amu, and the rest magnesium 25 with a mass of 25.9826 amu. What is the atomic mass of magnesium? If not told otherwise, the mass of the isotope is the mass number in amu ...
... magnesium 24 with a mass of 23.9850 amu, 10.00% magnesium 25 with a mass of 24.9858 amu, and the rest magnesium 25 with a mass of 25.9826 amu. What is the atomic mass of magnesium? If not told otherwise, the mass of the isotope is the mass number in amu ...
All matter is made of atoms.
... they are attracted to the positively charged protons. Also, because electrical charges that are alike (such as two negative charges) repel each other, electrons remain spread out in the electron cloud. Neutral atoms have no overall electrical charge because they have an equal number of protons and e ...
... they are attracted to the positively charged protons. Also, because electrical charges that are alike (such as two negative charges) repel each other, electrons remain spread out in the electron cloud. Neutral atoms have no overall electrical charge because they have an equal number of protons and e ...
Solutions - Dynamic Science
... Atoms from element “X” will give up some of their electrons. Element “X” will react with other element to form a gas. Element “X” is a very stable substance an will not react with other elements. ...
... Atoms from element “X” will give up some of their electrons. Element “X” will react with other element to form a gas. Element “X” is a very stable substance an will not react with other elements. ...
summer learning G10
... brown nitrogen dioxide gas being produced. When a glowing splint was held at the top of the test-tube, it relit, proving that oxygen gas was also produced. A fine black solid, copper(II) oxide, was left in the test-tube. a. Assess which substances are reactants and which are products. ...
... brown nitrogen dioxide gas being produced. When a glowing splint was held at the top of the test-tube, it relit, proving that oxygen gas was also produced. A fine black solid, copper(II) oxide, was left in the test-tube. a. Assess which substances are reactants and which are products. ...
- Orangefield ISD
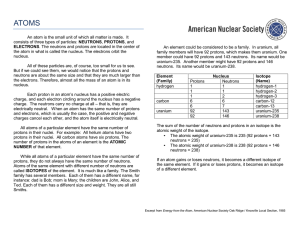
... Isotopes and Mass Number All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons and electrons but the number of neutrons in the nucleus can differ. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, most elements are found as mixtures ...
... Isotopes and Mass Number All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons and electrons but the number of neutrons in the nucleus can differ. Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. In nature, most elements are found as mixtures ...
Atomic Structure notes
... Legos can be taken apart and built into many different things. Atoms can be rearranged into different substances. ...
... Legos can be taken apart and built into many different things. Atoms can be rearranged into different substances. ...
The Chemical Earth
... chemically bonded together. They are composed of a fixed number of atoms of each component element. They can be decomposed into their component elements or into simpler compounds. ...
... chemically bonded together. They are composed of a fixed number of atoms of each component element. They can be decomposed into their component elements or into simpler compounds. ...
High School Chemistry
... Students will understand that the relationship between the transition of electrons to different energy levels in an atom and the emission or absorption of energy, and that the emission of high-energy radiation results from nuclear changes and that matter can be converted to energy in nuclear reactio ...
... Students will understand that the relationship between the transition of electrons to different energy levels in an atom and the emission or absorption of energy, and that the emission of high-energy radiation results from nuclear changes and that matter can be converted to energy in nuclear reactio ...
Chapter 2
... dealing with atoms and not molecules, required a unit that distinguished between isotopes. As early as 1927 physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scal ...
... dealing with atoms and not molecules, required a unit that distinguished between isotopes. As early as 1927 physicists were using an atomic mass unit defined as equal to one sixteenth of the mass of the oxygen-16 atom (the isotope of oxygen containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons). Thus the two amu scal ...
Atomic structure
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
Timeline Atom Theory PPT
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
HISTORY OF ATOMIC THEORY File
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of
... the electrons. Therefore, almost all the mass of an atom is in its nucleus. Each proton in an atom’s nucleus has a positive electric charge, and each electron circling around the nucleus has a negative charge. The neutrons carry no charge at all – that is, they are electrically neutral. When an atom ...
... the electrons. Therefore, almost all the mass of an atom is in its nucleus. Each proton in an atom’s nucleus has a positive electric charge, and each electron circling around the nucleus has a negative charge. The neutrons carry no charge at all – that is, they are electrically neutral. When an atom ...
chem100chapter5 - Imperial Valley College Faculty Websites
... masses using “atomic mass units” was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. ...
... masses using “atomic mass units” was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. ...
average atomic mass
... The average atomic mass of an element depends of both the mass and relative abundance of each of the element’s isotopes. Most elements occur in nature as a specific mixture of isotopes. They don’t occur equally… some are more abundant than others. ...
... The average atomic mass of an element depends of both the mass and relative abundance of each of the element’s isotopes. Most elements occur in nature as a specific mixture of isotopes. They don’t occur equally… some are more abundant than others. ...
What are elements?
... fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
... fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
Atomic structure
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
Elements & Atoms PPT
... fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
... fold the top down by 1 ½ inches. Unfold, you now have 3 columns. Label the columns: element, Bohr model, Lewis Dot. ...
Chapter 9: Understanding the Atom
... They undergo nuclear reactions that form atoms of different AN or AM. is a process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus changes into another more stable nucleus by emitting radiation. ...
... They undergo nuclear reactions that form atoms of different AN or AM. is a process that occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus changes into another more stable nucleus by emitting radiation. ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 6. Define the following: mass, volume, and matter. 7. Define pure substance. What are the two categories of pure substances? 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separati ...
... 6. Define the following: mass, volume, and matter. 7. Define pure substance. What are the two categories of pure substances? 8. What is a compound? List an example. 9. What is an element? List an example. 10. List and define the four states of matter. 11. List and define the two methods for separati ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.