Atoms - misshoughton.net
... cannot be broken down into simpler parts by a chemical change. Compounds: pure substances made of more than one type of atom. Compounds are made of elements. NaCl (sodium chloride) is an example of a compound. ...
... cannot be broken down into simpler parts by a chemical change. Compounds: pure substances made of more than one type of atom. Compounds are made of elements. NaCl (sodium chloride) is an example of a compound. ...
Atoms - Science with Mrs. Schulte
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
... Atomic mass The average mass of all the isotopes (different types) of an element ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
... The periodic table is a chart containing information about the atoms that make up all matter. An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal ...
Salesian High School Elements and atoms Chemistry quiz The
... a) radioactive elements b) alpha particles c) thermometers d) cathode ray tubes ...
... a) radioactive elements b) alpha particles c) thermometers d) cathode ray tubes ...
Introduction to Atomic Theory
... Noted that the masses of the reactants before a chemical reaction was equal to the masses of the products after the reaction was completed. This became known as the Law of Conservation of Matter ...
... Noted that the masses of the reactants before a chemical reaction was equal to the masses of the products after the reaction was completed. This became known as the Law of Conservation of Matter ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... Fill in the number of each term next to its closest definition. ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as group ...
... Fill in the number of each term next to its closest definition. ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as group ...
Atomic Mass
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
... Atomic masses can be different for atoms of the same element if they have different numbers of neutrons Atoms with different masses are called Isotopes or Nuclides ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... 10. Atomic mass is measured in ____________________________11. How do the isotopes of an element differ?_________________________________ How are they alike? ______________________________________________ 12. The number 37 in the name chlorine-37 represents __________________ 13. What does each numb ...
... 10. Atomic mass is measured in ____________________________11. How do the isotopes of an element differ?_________________________________ How are they alike? ______________________________________________ 12. The number 37 in the name chlorine-37 represents __________________ 13. What does each numb ...
Chemical reactions revision
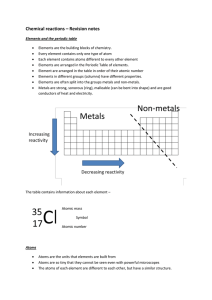
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Atomic Crossword Name: Period: ____
... 3. Two neutrons and two protons 5. Smallest piece of matter that still retains the properties of an element 6. Came up with the orbital model of atoms 9. "Plum pudding model" scientist 10. A man just full of "uncertainty" 13. This element makes up most of the atmosphere 16. We need this gas to keep ...
... 3. Two neutrons and two protons 5. Smallest piece of matter that still retains the properties of an element 6. Came up with the orbital model of atoms 9. "Plum pudding model" scientist 10. A man just full of "uncertainty" 13. This element makes up most of the atmosphere 16. We need this gas to keep ...
Chemical Bonding
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
... • The subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. • Protons=Positive charge • Neutrons=Neutral charge • Electrons=Negative charge ...
Atomic Structure - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Within atoms of the same element, the number of ________________will vary from one atom to the next. These various form of the element are called ___________________. 3. All the isotopes of a particular element have the same ___________________ but they have different ____________________________ ...
... 2. Within atoms of the same element, the number of ________________will vary from one atom to the next. These various form of the element are called ___________________. 3. All the isotopes of a particular element have the same ___________________ but they have different ____________________________ ...
Earth`s Chemistry
... protons in the atom. An uncharged atom has the same amount of protons & electrons so there’s no charge. It’s said to be neutral Example --- Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 so it has 8 protons & 8 ...
... protons in the atom. An uncharged atom has the same amount of protons & electrons so there’s no charge. It’s said to be neutral Example --- Oxygen has an atomic number of 8 so it has 8 protons & 8 ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in compounds. ...
... everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in compounds. ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
Chem vocab quiz definitons
... neutrons in the nucleus. This number is an average of the masses of all isotopes of that element and therefore a decimal. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the com ...
... neutrons in the nucleus. This number is an average of the masses of all isotopes of that element and therefore a decimal. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the com ...
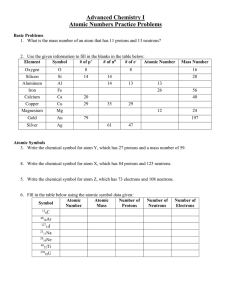
Atomic Numbers Practice Problems
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
... 3. Write the chemical symbol for atom Y, which has 27 protons and a mass number of 59. ...
Elements Unit Test
... 2. It wasn’t until an English scientist by the name of Robert Boyle came along, that the world finally accepted the fact that there are more than the original four elements of; a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. It wasn’t until an English scientist by the name of Robert Boyle came along, that the world finally accepted the fact that there are more than the original four elements of; a. b. c. d. ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... pH scale - what is it and what does it tell us – tells how strongly acidic ...
... pH scale - what is it and what does it tell us – tells how strongly acidic ...
Atomic Theory - rlhonorschem4
... Aerostatale 500 BC. »Matter=Atoms »Learned multiple elements are an atom »Matter made up of 4 elements ...
... Aerostatale 500 BC. »Matter=Atoms »Learned multiple elements are an atom »Matter made up of 4 elements ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.