The Atomic Theory of Matter
... Dalton’s theory explained: Law of constant composition: The relative kinds and numbers of atoms are constant for a given compound. Law of conservation of mass (matter): During a chemical reaction, the total mass before reaction is equal to the total mass after reaction. ...
... Dalton’s theory explained: Law of constant composition: The relative kinds and numbers of atoms are constant for a given compound. Law of conservation of mass (matter): During a chemical reaction, the total mass before reaction is equal to the total mass after reaction. ...
Chemistry Honors Unit 2 Study Guide Atomic Theory Mr. Brown Use
... ____ 2. Differentiate between the terms: mass number, atomic number, and average atomic mass. ____ 3. Differentiate and recognize examples of the terms “ion” and “isotope” ____ 4. Calculate the average atomic mass of isotopes in a given problem and/or the relative abundance of an isotope. ____ 5. Un ...
... ____ 2. Differentiate between the terms: mass number, atomic number, and average atomic mass. ____ 3. Differentiate and recognize examples of the terms “ion” and “isotope” ____ 4. Calculate the average atomic mass of isotopes in a given problem and/or the relative abundance of an isotope. ____ 5. Un ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure I. History of the Atom A. Democritus (400
... 1. Elements in groups have similar electron configurations and chemical properties 2. Periodic law: Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when elements are arranged by increasing atomic number B. Atomic Mass: Average atomic mass of isotopes found in nature, noted on periodic table a. Ca ...
... 1. Elements in groups have similar electron configurations and chemical properties 2. Periodic law: Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when elements are arranged by increasing atomic number B. Atomic Mass: Average atomic mass of isotopes found in nature, noted on periodic table a. Ca ...
Sep 2
... Rutherford's nuclear model: 1. Most of atom's mass is in a tiny dense nucleus 2. Most of the volume is empty space, with tiny electrons around the nucleus 3. In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of ...
... Rutherford's nuclear model: 1. Most of atom's mass is in a tiny dense nucleus 2. Most of the volume is empty space, with tiny electrons around the nucleus 3. In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of ...
Subatomic notes - Chemistry R: 4(AE) 5(A,C)
... the radius of the nucleus to be less than 1/10,000 of the atom. – If the nucleus were the size of a marble, the atom would be the size of a football stadium ...
... the radius of the nucleus to be less than 1/10,000 of the atom. – If the nucleus were the size of a marble, the atom would be the size of a football stadium ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
Atomic Structure Notes Atoms
... Electron cloud or energy rings -Atoms are made of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, & electrons ...
... Electron cloud or energy rings -Atoms are made of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, & electrons ...
Matter_Quiz_Topics_2017
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
... Understand what is meant by the following terms: atom, proton, neutron and electron, isotope, atomic number, mass number, matter, families, period, charge, atomic mass, ion Discuss the structure of an atom. How many electrons can each of the first three energy levels hold? Where is most of the mass ...
Subatomic Particles Do Now • What is an atom?
... the radius of the nucleus to be less than 1/10,000 of the atom. – If the nucleus were the size of a ________, the atom would be the size of a __________________ ...
... the radius of the nucleus to be less than 1/10,000 of the atom. – If the nucleus were the size of a ________, the atom would be the size of a __________________ ...
The Periodic Table - Harlan Independent Schools
... familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Chapter 3 - Vocabulary and Notes
... A. Substance – Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout B. Compound – Substance whose smallest unit is made up of more than one element 1. Chemical Formula – tells which elements make up a compound as well as how many atoms of each element are present a. The subscript number te ...
... A. Substance – Matter that has the same composition and properties throughout B. Compound – Substance whose smallest unit is made up of more than one element 1. Chemical Formula – tells which elements make up a compound as well as how many atoms of each element are present a. The subscript number te ...
Chemistry in Focus 3rd edition Tro
... electrons within a spherical region surrounding the nucleus. • Atoms can lose and gain one or more electrons. ...
... electrons within a spherical region surrounding the nucleus. • Atoms can lose and gain one or more electrons. ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
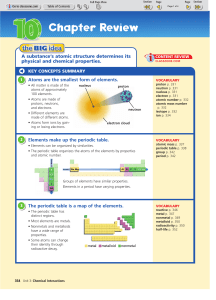
... • Elements in any group or family have similar physical and chemical properties • Groups 1A—8A elements are called the representative elements (have a wide range of physical and chemical properties) • Groups 1B—8B elements in the middle of the table are called transition elements (metals) • Bottom r ...
... • Elements in any group or family have similar physical and chemical properties • Groups 1A—8A elements are called the representative elements (have a wide range of physical and chemical properties) • Groups 1B—8B elements in the middle of the table are called transition elements (metals) • Bottom r ...
Protons, electrons and neutrons worksheet
... Atomic symbol is the symbol you find for each element shown in the periodic table. Magnesium symbol is Mg Gold symbol is Au Potassium symbol is K Phosphorous symbol is P Note: First letter of the element is not always the symbol. Atomic number is the number on the top left of atomic symbol in period ...
... Atomic symbol is the symbol you find for each element shown in the periodic table. Magnesium symbol is Mg Gold symbol is Au Potassium symbol is K Phosphorous symbol is P Note: First letter of the element is not always the symbol. Atomic number is the number on the top left of atomic symbol in period ...
There are 3 particles in an atom
... Protons have a positive charge and are found in the nucleus (center) of an atom. They are always equal to the atomic number on the periodic table (top number in the box). Neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. They are also found in the center of an atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They a ...
... Protons have a positive charge and are found in the nucleus (center) of an atom. They are always equal to the atomic number on the periodic table (top number in the box). Neutrons have no charge. They are neutral. They are also found in the center of an atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They a ...
CH 115 Fall 2014Exam I Review Brief overview of topics/concepts to
... Subatomic particles – what are they Atomic number Mass number Atomic weight Atomic mass Isotopes + calculating atomic weight of an element, vice versa Mass spectra diagram Two equations used when talking about light E = hv C = (wavelength*frequency) UNITS Bohr diagram What does it ...
... Subatomic particles – what are they Atomic number Mass number Atomic weight Atomic mass Isotopes + calculating atomic weight of an element, vice versa Mass spectra diagram Two equations used when talking about light E = hv C = (wavelength*frequency) UNITS Bohr diagram What does it ...
Atom Reading Passage and Questions File
... Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical charge. A proton always has an electrical charge of +1. An electron always has an electrical charge of -1. A neutron has no electrical charge associated with it, a charge of 0. Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the c ...
... Each type of subatomic particle has a different electrical charge. A proton always has an electrical charge of +1. An electron always has an electrical charge of -1. A neutron has no electrical charge associated with it, a charge of 0. Atoms form the building blocks of the simplest substances, the c ...
c) C2 Glossary Topic 1
... The number of objects of a particular kind in a sample (shown as a percentage of the total number of objects) ...
... The number of objects of a particular kind in a sample (shown as a percentage of the total number of objects) ...
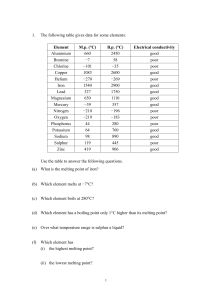
Chapter Review - BAschools.org
... 29. CALCULATE One of the more common isotopes of mercury is mercury-200. How many protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of mercury-200? 30. INFER Cadmium occupies the square directly above mercury on the periodic table. Is a cadium atom larger or smaller than a mercury atom? 31. CALCULATE An isoto ...
... 29. CALCULATE One of the more common isotopes of mercury is mercury-200. How many protons and neutrons are in the nucleus of mercury-200? 30. INFER Cadmium occupies the square directly above mercury on the periodic table. Is a cadium atom larger or smaller than a mercury atom? 31. CALCULATE An isoto ...
Chemistry - Spokane Public Schools
... portion of their electron clouds. This is called a covalent bond. The combined atoms form what is called a molecule. 12. Compound - When the atoms of different elements combine to form a substance that has different properties from the original elements this is called a compound. Example: When two a ...
... portion of their electron clouds. This is called a covalent bond. The combined atoms form what is called a molecule. 12. Compound - When the atoms of different elements combine to form a substance that has different properties from the original elements this is called a compound. Example: When two a ...
Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Atomic Theory of Matter
... o Alpha decay—a nucleus emits a clump of two protons and two neutrons o Beta decay—a nucleus changes a neutron into a proton and ejects an electron o Gamma decay—a nucleus emits high-energy electromagnetic rays ...
... o Alpha decay—a nucleus emits a clump of two protons and two neutrons o Beta decay—a nucleus changes a neutron into a proton and ejects an electron o Gamma decay—a nucleus emits high-energy electromagnetic rays ...
Study Guide Answers
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.