Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... Father of modern chemistry unfortunate association with a company organized to collect taxes for King Louis died at guillotine of no use to the New Republic of France headless body buried in unmarked grave Showed conservation of mass in chemical reactions invented precise scale to weigh small a ...
... Father of modern chemistry unfortunate association with a company organized to collect taxes for King Louis died at guillotine of no use to the New Republic of France headless body buried in unmarked grave Showed conservation of mass in chemical reactions invented precise scale to weigh small a ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... Father of modern chemistry unfortunate association with a company organized to collect taxes for King Louis died at guillotine of no use to the New Republic of France headless body buried in unmarked grave Showed conservation of mass in chemical reactions invented precise scale to weigh small a ...
... Father of modern chemistry unfortunate association with a company organized to collect taxes for King Louis died at guillotine of no use to the New Republic of France headless body buried in unmarked grave Showed conservation of mass in chemical reactions invented precise scale to weigh small a ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... Isotopes • Isotopes: – Atoms that have the same number to protons, but different numbers of neutrons. This will also create different mass numbers. ...
... Isotopes • Isotopes: – Atoms that have the same number to protons, but different numbers of neutrons. This will also create different mass numbers. ...
File - Ms. Gutierrez`s Chemistry Website
... • Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • The atoms of each element differ from the atom of the element before it by one proton. • In atoms that are electrically neutral, atomic number also is the number of electrons. ...
... • Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • The atoms of each element differ from the atom of the element before it by one proton. • In atoms that are electrically neutral, atomic number also is the number of electrons. ...
elements and compounds
... that carry an electric charge. So…if an atom has more protons it is??? If there are more electrons?? ...
... that carry an electric charge. So…if an atom has more protons it is??? If there are more electrons?? ...
Nickel 28 Ni 58.693
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
14_1_atoms and isotopes FPS3
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
... If you look at a periodic table, you will notice that the atomic number increases by one whole number at a time. This is because you add one proton at a time for each element. The atomic mass however, increases by amounts greater than one. This difference is due to the neutrons in the nucleus. The v ...
Key Concepts - Chemistry Classes of Professor Alba
... electrons in their chemical changes. Elements on the upper right side of the periodic table are nonmetals and tend to gain electrons in their chemical changes. Elements located on the boundary between these two classes are called metalloids. The atomic mass of an element, listed directly below its s ...
... electrons in their chemical changes. Elements on the upper right side of the periodic table are nonmetals and tend to gain electrons in their chemical changes. Elements located on the boundary between these two classes are called metalloids. The atomic mass of an element, listed directly below its s ...
Packet 5
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
... Protons – Positive charge, found in the nucleus and have a mass of 1 amu. ( Identify) Neutrons- No charge, found in the nucleus, and have a mass of 1 amu ( Isotopes) Electrons- Negative charge, found in the energy levels outside of the nucleus, have relatively no mass ( Ions) ...
ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... they are written in a very specific way. 1. Capitalize the first letter of the element name, like C for carbon. 2. Capitalize the first letter of the element name and then make the second letter of the element’s name small case, like Ca for calcium. 3. Sometimes the element’s symbol does not seem to ...
... they are written in a very specific way. 1. Capitalize the first letter of the element name, like C for carbon. 2. Capitalize the first letter of the element name and then make the second letter of the element’s name small case, like Ca for calcium. 3. Sometimes the element’s symbol does not seem to ...
CH 5 Periodic Law
... - highly reactive metallic elements in group 1 - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
... - highly reactive metallic elements in group 1 - react with water to form hydrogen and alkaline solutions; burn in air - one outer electron, by losing this electron they become a cation, and become stable - soft metals; can be cut with a knife - shiny, but dull quickly due to oxygen and water in air ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1 - Mrs. Tainter`s Physical Science Class
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
... proton, found in nuclei of atoms along with protons the center of positive charge called protons – also contains protons (with no charge) the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in a single atom. the number of protons in every atom of an element. atoms of the same element with di ...
John Dalton is known as the father of modern atomic theory because
... Definite Proportions that says pure compounds are made of elements combined in definite proportions. For instance, the smallest piece of water is always composed of 2 hydrogen pieces combined with 1 oxygen piece. In 1803 John Dalton’s combined new scientific ideas of his time along with his experime ...
... Definite Proportions that says pure compounds are made of elements combined in definite proportions. For instance, the smallest piece of water is always composed of 2 hydrogen pieces combined with 1 oxygen piece. In 1803 John Dalton’s combined new scientific ideas of his time along with his experime ...
Chapter 2 Law of Dalton`s Atomic Theory Law of Multiple
... 1. The cation name is given first followed by the anion name. 2. If the metal forms only one positive ion, the cation name is the element name. 3. If the metal forms more than one ppositive ion (transition/post-transitional elements), the cation name is the English name followed, without a space, by ...
... 1. The cation name is given first followed by the anion name. 2. If the metal forms only one positive ion, the cation name is the element name. 3. If the metal forms more than one ppositive ion (transition/post-transitional elements), the cation name is the English name followed, without a space, by ...
atomic number - Net Start Class
... •How many protons does helium have? •What element has 79 protons? •What is uranium’s atomic number? •How many electrons does a neutral atom of calcium have? ...
... •How many protons does helium have? •What element has 79 protons? •What is uranium’s atomic number? •How many electrons does a neutral atom of calcium have? ...
Fall Final Exam Review Questions
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
... 41. What are properties of metals and where are they generally located on a periodic table? 42. What are properties of nonmetals and where are they generally located? 43. What are properties of metalloids and where are they generally located? 44. Make sure you know the major groups/chemical families ...
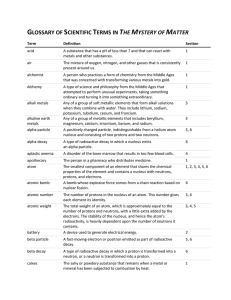
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... A unit that measures the effect of ionizing radiation upon a particular person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the si ...
... A unit that measures the effect of ionizing radiation upon a particular person. A group of two or more atoms linked together by sharing electrons in a chemical bond. A heavy, neutral particle in an atom’s nucleus that accounts for almost all of each atom’s mass, in addition to protons. Any of the si ...
Chapter 5 The Structure of the Atom
... Students should be able to: • Summarize the essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory. • Describe the particle theory of matter. • Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in an atom • Compare the Bohr atomic model to the electron cloud. ...
... Students should be able to: • Summarize the essential points of Dalton’s atomic theory. • Describe the particle theory of matter. • Use the Bohr model to differentiate among the three basic particles in an atom • Compare the Bohr atomic model to the electron cloud. ...
atomic structure (see second part of ppt)
... ·1935- Schrodinger proposed Electron Cloud Theory basic difference being that the electrons are found in "probable" locations outside the nucleus on energy levels and that the atom is mostly empty space ...
... ·1935- Schrodinger proposed Electron Cloud Theory basic difference being that the electrons are found in "probable" locations outside the nucleus on energy levels and that the atom is mostly empty space ...
2/1: Atomic Structure
... explosion has just started; surplus ships moored nearby can still be seen. ...
... explosion has just started; surplus ships moored nearby can still be seen. ...
Thomson`s Atom
... Atomic weights do not always increase with atomic number, i.e. position in Periodic table: Atomic weight of Argon (Ar) exceeds that of the succeeding element Potassium (K) Atomic weight of Cobalt (Co) exceeds that of the succeeding element Nickel (Ni) Pb from different localities has different atomi ...
... Atomic weights do not always increase with atomic number, i.e. position in Periodic table: Atomic weight of Argon (Ar) exceeds that of the succeeding element Potassium (K) Atomic weight of Cobalt (Co) exceeds that of the succeeding element Nickel (Ni) Pb from different localities has different atomi ...
Notes
... Everything in the world is made up from about 100 elements. Every element is made up of very small particles called atoms. An element is a substance in which all the atoms are of one kind only. An element is a substance which cannot be broken into any simpler substances. Elements can be classified i ...
... Everything in the world is made up from about 100 elements. Every element is made up of very small particles called atoms. An element is a substance in which all the atoms are of one kind only. An element is a substance which cannot be broken into any simpler substances. Elements can be classified i ...
Unit 1: Atomic Structure AP Chemistry
... Compounds are made when atoms combine. If elements combine in more than one whole number ratio, the resulting compound has different properties Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. ...
... Compounds are made when atoms combine. If elements combine in more than one whole number ratio, the resulting compound has different properties Chemical reactions involve the reorganization of atoms. ...
Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called
... Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called: a. classes b. periods c. groups d. families 2. As you move from left to right across the periodic table: a. atomic number decreases b. atomic number increases c. The elements become darker in color d. The elements become lighter in ...
... Chemistry and elements 1. The rows of the periodic table are called: a. classes b. periods c. groups d. families 2. As you move from left to right across the periodic table: a. atomic number decreases b. atomic number increases c. The elements become darker in color d. The elements become lighter in ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.