L18_PNdepletion
... The voltage potential across the junction is just (minus) the integral over the electric field: So the built-in voltage V0 is the area under the electric field triangle. ...
... The voltage potential across the junction is just (minus) the integral over the electric field: So the built-in voltage V0 is the area under the electric field triangle. ...
In-Class Worksheet on Displacement and Velocity
... with a large vertical drop where the skiers can build up a lot of speed, or one with a short vertical drop, where they don’t build up as much speed? ...
... with a large vertical drop where the skiers can build up a lot of speed, or one with a short vertical drop, where they don’t build up as much speed? ...
Electricity
... Physics - Students will know the definitions of electric current, voltage and voltage sources, resistance, electric shock, DC/AC current, and electrical power as well as be able to use them correctly in physical systems. Students will conceptually and mathematically understand Ohm’s Law and use the ...
... Physics - Students will know the definitions of electric current, voltage and voltage sources, resistance, electric shock, DC/AC current, and electrical power as well as be able to use them correctly in physical systems. Students will conceptually and mathematically understand Ohm’s Law and use the ...
9J Force Fields and Electromagnets
... An atom consists of a central nucleus with small particles called electrons moving around it. An atom normally has no overall charge because it has the same number of positive and negative charges. When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If t ...
... An atom consists of a central nucleus with small particles called electrons moving around it. An atom normally has no overall charge because it has the same number of positive and negative charges. When you rub two materials together, electrons may be transferred from one material to the other. If t ...
CS 436 HCI Technology Basic Electricity/Electronics Review 1 Basic Quantities and Units
... Voltage between plates is a function of charge difference between plates. Energy is stored in an electric (potential) field. Constant current causes linearly rising (or falling) charge difference, and thus a steady linearly changing voltage. ...
... Voltage between plates is a function of charge difference between plates. Energy is stored in an electric (potential) field. Constant current causes linearly rising (or falling) charge difference, and thus a steady linearly changing voltage. ...
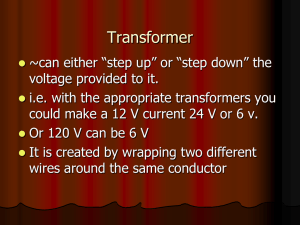
What is a transformer?
... The voltage of an alternating current can be changed using a device called a transformer. A transformer contains two coils that are wound around a soft iron core. ...
... The voltage of an alternating current can be changed using a device called a transformer. A transformer contains two coils that are wound around a soft iron core. ...
Hall Probe CYHP881
... different measuring and controlling systems for magnetic field measurement. The Hall probe is powered with a single voltage source +5VDC that can be provided in the most microprocessor controlled systems. A low-cost measuring device, which is easy to operate and convenient to handle and store. Ideal ...
... different measuring and controlling systems for magnetic field measurement. The Hall probe is powered with a single voltage source +5VDC that can be provided in the most microprocessor controlled systems. A low-cost measuring device, which is easy to operate and convenient to handle and store. Ideal ...
Chapter 8 Test Review – Electricity and Magnetism
... o Voltage = the potential energy difference needed to get current flowing (the push) o Resistance = opposition to the flow of current o Electrical power = the rate at work is done within an electrical device Know the units used to measure current, voltage, resistance, power o Current = amps (amperes ...
... o Voltage = the potential energy difference needed to get current flowing (the push) o Resistance = opposition to the flow of current o Electrical power = the rate at work is done within an electrical device Know the units used to measure current, voltage, resistance, power o Current = amps (amperes ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
... build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
Inductor Basics notes
... An inductor is a series of turns of wire around a core material. The core can be air, soft iron in solid of powdered form, graphite or alloys of different metals chosen for their magnetic properties. The inductance of a coil (inductor) is dependant on: 1. Number of turns 2. Area (How close the turns ...
... An inductor is a series of turns of wire around a core material. The core can be air, soft iron in solid of powdered form, graphite or alloys of different metals chosen for their magnetic properties. The inductance of a coil (inductor) is dependant on: 1. Number of turns 2. Area (How close the turns ...
circuits 1.notebook
... Ohms- unit of resistance resistance of wire- due to the diameter, length, material and ...
... Ohms- unit of resistance resistance of wire- due to the diameter, length, material and ...
Motors, Generators , and Transformers
... A larger current at low voltage flows in the secondary circuit ...
... A larger current at low voltage flows in the secondary circuit ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.