Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... The results show voltage is stepped (up, down) from primary to secondary, and that the current is stepped (up, down) to compensate. For a step-up transformer, there are (more, fewer) turns in the secondary coil than the primary coil. For such a transformer, there is (more, less) current in the secon ...
... The results show voltage is stepped (up, down) from primary to secondary, and that the current is stepped (up, down) to compensate. For a step-up transformer, there are (more, fewer) turns in the secondary coil than the primary coil. For such a transformer, there is (more, less) current in the secon ...
document
... magnets or can be made into permanent magnets. Magnetic domains – group of atoms with aligned magnetic poles (too small to be seen with eye) Permanent magnets are made by placing a magnetic material in a strong magnetic field, forcing magnetic domains to line up. ...
... magnets or can be made into permanent magnets. Magnetic domains – group of atoms with aligned magnetic poles (too small to be seen with eye) Permanent magnets are made by placing a magnetic material in a strong magnetic field, forcing magnetic domains to line up. ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... B. Air is fair insulator but not when ARCING occurs: 1. Arcing – electrons break free and create a conducting path. 2. Examples: a. Getting “shocked” by doorknob: the potential difference between hand / knob is large and the electrons arc across air space. b. Lightning. How potential difference, cur ...
... B. Air is fair insulator but not when ARCING occurs: 1. Arcing – electrons break free and create a conducting path. 2. Examples: a. Getting “shocked” by doorknob: the potential difference between hand / knob is large and the electrons arc across air space. b. Lightning. How potential difference, cur ...
Voltage Lab
... Voltage (Electric Potential) of a Dipole Introduction The space around a positive or negative source charge is filled with a web of influence called the electric field. Another way of looking at the space around sources charges is through the eyes of voltage. Voltage (electric potential) at a point ...
... Voltage (Electric Potential) of a Dipole Introduction The space around a positive or negative source charge is filled with a web of influence called the electric field. Another way of looking at the space around sources charges is through the eyes of voltage. Voltage (electric potential) at a point ...
PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide
... - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to conductors, don’t interact with neutral insulat ...
... - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to conductors, don’t interact with neutral insulat ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... • Secondary – output, reacts to changes in the magnetic field intensity of the primary coil and voltage can be induced ...
... • Secondary – output, reacts to changes in the magnetic field intensity of the primary coil and voltage can be induced ...
R Ch 37 Electric Induction pg 1
... • Electromagnetic Waves have an magnetic half and an electric half that; • 1) move as a wave • 2) are at 90 degrees to each other • 3) they can move through a vacuum (space) ...
... • Electromagnetic Waves have an magnetic half and an electric half that; • 1) move as a wave • 2) are at 90 degrees to each other • 3) they can move through a vacuum (space) ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
What Do We Know About Stray Voltage?
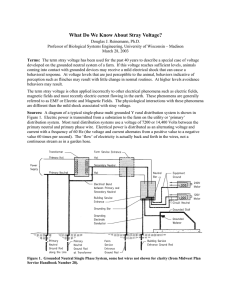
... The neutral wire on the primary distribution system is grounded 6 times per mile or more. These grounds are provided, in part, to reduce damage caused by lightening striking the power lines. The high voltage and low current carried by distribution lines is converted to lower voltage and higher curr ...
... The neutral wire on the primary distribution system is grounded 6 times per mile or more. These grounds are provided, in part, to reduce damage caused by lightening striking the power lines. The high voltage and low current carried by distribution lines is converted to lower voltage and higher curr ...
forcibly push - Cloudfront.net
... Imagine a large coil with a current running through it. Things are normal. The current is steady and creating a large magnetic field. ...
... Imagine a large coil with a current running through it. Things are normal. The current is steady and creating a large magnetic field. ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.