ENGINEERING PHYSICS II SEMICONDUCTING MATERIALS
... field is produced inside the conductor in a direction normal to both the current and the magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as Hall effect and the generated voltage is called “Hall voltage”. Hall effect in n-type semiconductor Let us consider an n type material to which the current is allowe ...
... field is produced inside the conductor in a direction normal to both the current and the magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as Hall effect and the generated voltage is called “Hall voltage”. Hall effect in n-type semiconductor Let us consider an n type material to which the current is allowe ...
Charge to mass ratio of electron
... the tube. (CAUTION: All exposed anode connections should be taped for your protection. Anode voltage should not exceed 300 V.) When a magnetic field is applied, the electrons will begin to curve around in a helix. Rotate the tube so that the electrons are launched perpendicular to the field, and th ...
... the tube. (CAUTION: All exposed anode connections should be taped for your protection. Anode voltage should not exceed 300 V.) When a magnetic field is applied, the electrons will begin to curve around in a helix. Rotate the tube so that the electrons are launched perpendicular to the field, and th ...
Lecture 23 - UConn Physics
... • A circuit consisting of capacitor C and voltage source is constructed as shown. The graph shows the voltage presented to the capacitor as a function of time. – Which of the following graphs best represents the time dependence of the current i in the circuit? ...
... • A circuit consisting of capacitor C and voltage source is constructed as shown. The graph shows the voltage presented to the capacitor as a function of time. – Which of the following graphs best represents the time dependence of the current i in the circuit? ...
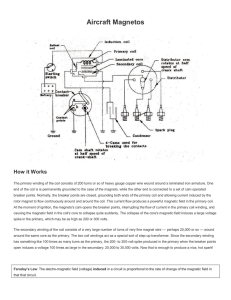
Magneto Diagram - Take Flight San Diego
... The primary winding of the coil consists of 200 turns or so of heavy gauge copper wire wound around a laminated iron armature. One end of the coil is is permanently grounded to the case of the magneto, while the other end is connected to a set of cam operated breaker points. Normally, the breaker po ...
... The primary winding of the coil consists of 200 turns or so of heavy gauge copper wire wound around a laminated iron armature. One end of the coil is is permanently grounded to the case of the magneto, while the other end is connected to a set of cam operated breaker points. Normally, the breaker po ...
are conductors (metals). Insulators (rubber,
... (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet ...
... (The manipulated variable could be the number of coils of wire and the responding variable could be the number of paperclips the magnet ...
engineering physics ii semiconducting materials
... field is produced inside the conductor in a direction normal to both the current and the magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as Hall effect and the generated voltage is called “Hall voltage”. Hall effect in n-type semiconductor Let us consider an n type material to which the current is allowe ...
... field is produced inside the conductor in a direction normal to both the current and the magnetic field. This phenomenon is known as Hall effect and the generated voltage is called “Hall voltage”. Hall effect in n-type semiconductor Let us consider an n type material to which the current is allowe ...
Department of Natural Sciences
... Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a certain distance R. If the magnitudes of the charges are doubled, and their separation is halved, then what happens to the electrical force between these charges? a. It increases by a factor of 16. b. It increases by a factor of 8. c. It is doubled. d. It r ...
... Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a certain distance R. If the magnitudes of the charges are doubled, and their separation is halved, then what happens to the electrical force between these charges? a. It increases by a factor of 16. b. It increases by a factor of 8. c. It is doubled. d. It r ...
Electric Potential Difference
... 4. Write an equation for each of the following: (a) electric current in terms of energy used, voltage, and time interval (b) voltage in terms of electric current, energy used, and time interval (c) time interval the device is used in terms of current, voltage, and energy used 5. A 120-V electric san ...
... 4. Write an equation for each of the following: (a) electric current in terms of energy used, voltage, and time interval (b) voltage in terms of electric current, energy used, and time interval (c) time interval the device is used in terms of current, voltage, and energy used 5. A 120-V electric san ...
rain drops as an alternative electrical energy source
... hydrologic cycle. The cycle starts from the evaporation of water in the earth's surface by the heat of the sun, the condensation of water vapor to form clouds, until the clouds become saturated and eventually become rain. Rain water that absorb by the soil is very useful, such as ground water. Moreo ...
... hydrologic cycle. The cycle starts from the evaporation of water in the earth's surface by the heat of the sun, the condensation of water vapor to form clouds, until the clouds become saturated and eventually become rain. Rain water that absorb by the soil is very useful, such as ground water. Moreo ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.