The first battery-powered flashlights were designed around 1899
... The first battery-powered flashlights were designed around 1899 with the new invention of the dry cell battery and miniaturized incandescent light bulbs. Flashlights today use primarily incandescent light bulbs or light-emitting diodes and operate by disposable or rechargeable batteries. In this app ...
... The first battery-powered flashlights were designed around 1899 with the new invention of the dry cell battery and miniaturized incandescent light bulbs. Flashlights today use primarily incandescent light bulbs or light-emitting diodes and operate by disposable or rechargeable batteries. In this app ...
Magnetic Fields and Electric Currents
... because a magnetic force can cause electric charges to move. ...
... because a magnetic force can cause electric charges to move. ...
Electric Charges & Current
... angle of the pipe. It also depends on the length of the pipe, diameter of the pipe and if the pipe is clogged or open. Electrical Current is measured in Amperes Amount of Electrical Current ( amps) depends on more than just Voltage, it depends on the Resistance found in the circuit. ...
... angle of the pipe. It also depends on the length of the pipe, diameter of the pipe and if the pipe is clogged or open. Electrical Current is measured in Amperes Amount of Electrical Current ( amps) depends on more than just Voltage, it depends on the Resistance found in the circuit. ...
File
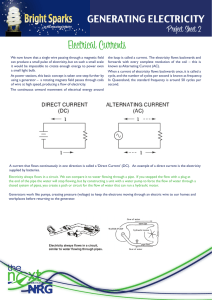
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
Deerfield High School / Homepage
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
Electricity and Magnetism - Warren County Public Schools
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
... The pressure of the water flowing through the pipes on the last slide compare to the voltage (electric potential) flowing through the wires of the circuit. The unit used to measure voltage is volts (V). The flow of charges in a circuit is called current. Current (I) is measured in Amperes (A). ...
EECS 215: Introduction to Circuits
... • The thermocouple measures the unknown temperature T2 at a junction connecting two metals with different thermal conductivities, relative to a reference temperature T1. • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circu ...
... • The thermocouple measures the unknown temperature T2 at a junction connecting two metals with different thermal conductivities, relative to a reference temperature T1. • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circu ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... for electricity to reach the ground in case of a surge (it helps to protect both the equipment and helps to prevent electrical fires within the walls of your home) ...
... for electricity to reach the ground in case of a surge (it helps to protect both the equipment and helps to prevent electrical fires within the walls of your home) ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... for electricity to reach the ground in case of a surge (it helps to protect both the equipment and helps to prevent electrical fires within the walls of your home) ...
... for electricity to reach the ground in case of a surge (it helps to protect both the equipment and helps to prevent electrical fires within the walls of your home) ...
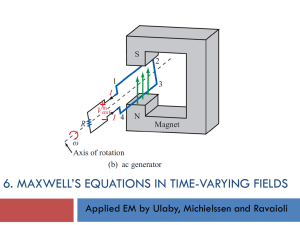
Motors and AC Generators KLT
... increase the total area of the coil. In a power station generator, an electromagnet is often used as this can provide a stronger ...
... increase the total area of the coil. In a power station generator, an electromagnet is often used as this can provide a stronger ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.