Hall Effect
... The aim of the manipulation: Transport property investigations The Hall effect is a conduction phenomenon, which is different for different charge carriers. In most common electrical applications, the conventional current is used partly because it makes no difference whether you consider positive or ...
... The aim of the manipulation: Transport property investigations The Hall effect is a conduction phenomenon, which is different for different charge carriers. In most common electrical applications, the conventional current is used partly because it makes no difference whether you consider positive or ...
The mistery of magnetic voltage generation and Kirchhoff`s voltage law
... I was asking myself for a long time how we could use any generalized power source in the equivalent models even if there is a high probability that the voltage provided comes from a magnetic induction device. From Faraday’s law we know that Kirchhoff’s voltage law doesn’t hold any more as soon as a ...
... I was asking myself for a long time how we could use any generalized power source in the equivalent models even if there is a high probability that the voltage provided comes from a magnetic induction device. From Faraday’s law we know that Kirchhoff’s voltage law doesn’t hold any more as soon as a ...
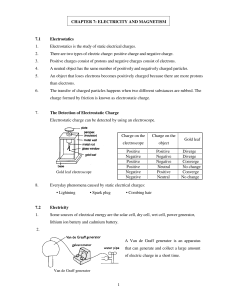
Electricity & Magnetism
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
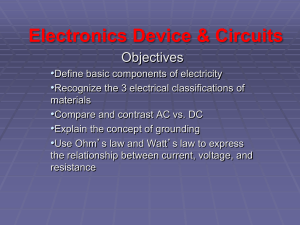
BASIC INDUSTRIAL ELECTRICITY
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
Basic Electrical Quantities - Pojęcia
... central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Hydrogen is the simplest atom.  atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus.  atomic weight – approximately the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.  copper – the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.  sh ...
... central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Hydrogen is the simplest atom.  atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus.  atomic weight – approximately the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.  copper – the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.  sh ...
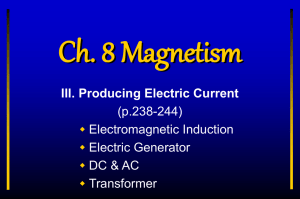
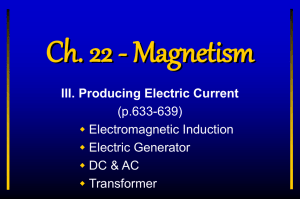
Electromagnetic Induction Notes
... wrapped and a secondary coil is wrapped • Step up transformer – secondary has more loops than primary so voltage increased in secondary (increases voltage) • Step down transformer – secondary has less loops than primary so voltage decreased in secondary (decreases voltage) ...
... wrapped and a secondary coil is wrapped • Step up transformer – secondary has more loops than primary so voltage increased in secondary (increases voltage) • Step down transformer – secondary has less loops than primary so voltage decreased in secondary (decreases voltage) ...
GENERATORS AND TRANSFORMERS
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, ...
... • A transformer can change electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
High voltage

The term high voltage usually means electrical energy at voltages high enough to inflict harm on living organisms. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant particular safety requirements and procedures. In certain industries, high voltage means voltage above a particular threshold (see below). High voltage is used in electrical power distribution, in cathode ray tubes, to generate X-rays and particle beams, to demonstrate arcing, for ignition, in photomultiplier tubes, and in high power amplifier vacuum tubes and other industrial and scientific applications.