* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How electricity is made
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
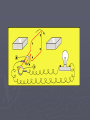
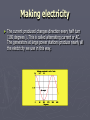
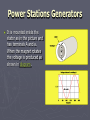
How electricity is made Electricity can be made or generated by moving a wire (conductor) through a magnetic field. Magnetism ► A bar magnet has a north and south pole. If it is placed under a sheet of paper and iron filings are sprinkled over the top of the paper, these iron filings will arrange themselves into a pattern of lines that link the north pole with the south pole of the magnet. These lines show the magnetic field around the magnet. Making electricity ► If a coil of wire is moved within a magnetic field so that it passes through the magnetic field, electrons in the wire are made to move. When the coil of wire is connected into an electric circuit (at the terminals A and a) the electrons get energy to move in a certain direction and a current will flow. This electrical energy is called voltage. Making electricity ► The amount of energy or voltage depends on the strength and position of the magnetic field relative to the coil, as well as the speed at which the coil is turning. As the amount of electricity changes so does its voltage. Making electricity ► In the adjacent diagram, the coil of wire is rotating in a clockwise direction. When the coil of wire is in the horizontal position the voltage is greatest (diagram), because the coil is passing through the strongest part of the magnetic field. At this stage the current flows from 1 to 2 to 3 to 4, out through terminal a, through the globe and back into terminal a. Making electricity ► When the coil of wire is in the vertical position, no electricity is produced because the coil does not cut the magnetic field, and no current flows. Making electricity ► When the coil of wire is in the horizontal position again, the voltage is at its maximum (diagram), however the current flows in the opposite direction 4 to 3 to 2 to 1, out through terminal a, through the globe, and back into terminal A. Making electricity ► The current produced changes direction every half turn (180 degrees ). This is called alternating current or AC. The generators at large power stations produce nearly all the electricity we use in this way. Power Stations Generators ► ► With large power station generators, the coils actually remain stationary, and the magnetic field rotates. This still produces the same effect as described above. The magnet rotates as the turbine to which it is attached rotates. When only one of the coils of wire is connected in the stationary part of the generator (known as the stator), the electricity circuit is said to be one phase (or one circuit). shows what a rectangular coil or winding may look like Power Stations Generators ► It is mounted inside the stator as in the picture and has terminals A and a. When the magnet rotates the voltage is produced as shown in diagram. Power Stations Generators ► ► It is more cost efficient and technically better to connect three sets of coils in the stator. The picture shows how these coils are mounted. Each of these coils will be connected as separate electrical circuits. When the magnet rotates an identical voltage is produced in each coil and circuit, but each is staggered or delayed from one another (see diagram). The electricity circuit is said to be three phase.