* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
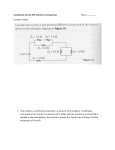
PHYS 222 Exam 1 Study Guide Concepts covered: - Superposition: Electric and potential fields do not interact with one another, they only interact with the particles. - Rules for drawing and interpreting electric field diagrams: Lines cannot intersect, correct directions of arrows, perpendicular to conductors, don’t interact with neutral insulators, etc… - Relationship between Electric field lines and equi-potential lines. - Potential Energy vs. Potential: Potential energy exists between two particles, potential is a measure of how much potential energy a particle would have if it were there. - Work done by electric field is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the change in potential energy of the particle in question. - Potential everywhere inside a conductor is the same. - Electric field everywhere inside a conductor is zero. - Capacitors: Parallel plate, spherical, cylindrical, don’t need to memorize equations, but you should understand how to setup the problems. - Charge on one plate of a capacitor is equal to charge on the other. - Equivalent capacitance - The charge distribution on a capacitor plate is not necessarily uniform. - Circuits: Emfs, resistors, resistance, parallel vs. series, Kirchoff’s Loop-rule, junctions, etc… - Understand how resistivity changes as the dimensions of the resistor change. - Voltage difference across resistors in series is equal to the sum of the voltage differences across each, while the voltage difference across each resistor which is in parallel with each other is the same. - Setting up equivalent resistors - Power output of resistors and emfs - Generating equations for a circuit using Kirchoff’s Loop rule and the junction rule