Multiple Choice Questions_1
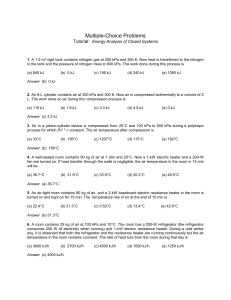
... 3. Air in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 25C and 100 kPa to 500 kPa during a polytropic process for which Pv1.3 = constant. The air temperature after compression is (a) 33C ...
... 3. Air in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 25C and 100 kPa to 500 kPa during a polytropic process for which Pv1.3 = constant. The air temperature after compression is (a) 33C ...
18. Weather – Recap - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The transfer of thermal energy from one object to ...
... The transfer of thermal energy from one object to ...
14_Water Cooling System
... Narrow spaces are chemically cleaned. Limestone deposits can be cleaned with acid solution. ...
... Narrow spaces are chemically cleaned. Limestone deposits can be cleaned with acid solution. ...
Thermodynamics
... If all 6 billion people on Earth dropped balls every second for the entire age of the universe they would be very unlikely to get 100 on one side You are very likely to get about half on each side ...
... If all 6 billion people on Earth dropped balls every second for the entire age of the universe they would be very unlikely to get 100 on one side You are very likely to get about half on each side ...
Tarea III
... 6–76 In tropical climates, the water near the surface of the ocean remains warm throughout the year as a result of solar energy absorption. In the deeper parts of the ocean, however, the water remains at a relatively low temperature since the sun’s rays cannot penetrate very far. It is proposed to ...
... 6–76 In tropical climates, the water near the surface of the ocean remains warm throughout the year as a result of solar energy absorption. In the deeper parts of the ocean, however, the water remains at a relatively low temperature since the sun’s rays cannot penetrate very far. It is proposed to ...
Heat Transfer (ME-345) - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... Spring 2014-2015 Closed Book Quiz. Name: ...
... Spring 2014-2015 Closed Book Quiz. Name: ...
Heat, land and ai.. - Hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Warm air above ground, rises up, while the warming air above the sea replaces it. The wind blows in from water to the land. ...
... Warm air above ground, rises up, while the warming air above the sea replaces it. The wind blows in from water to the land. ...
Structural analysis of piston Piston is a part of engine which converts
... Piston is a part of engine which converts pressure and heat energy into mechanical energy, by mixing of air and fuel. It transfers force\energy from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crank shaft with connecting rod. When engine at higher speed it has high pressure ratio and energy improves consta ...
... Piston is a part of engine which converts pressure and heat energy into mechanical energy, by mixing of air and fuel. It transfers force\energy from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crank shaft with connecting rod. When engine at higher speed it has high pressure ratio and energy improves consta ...
Understanding Heat Transfers Conduction, Convection and Radiation
... •Cold objects in a warmer room will •heat up to room temperature. ...
... •Cold objects in a warmer room will •heat up to room temperature. ...
Entropy - Dordt College Homepages
... ball bouncing - forward direction is one where successive bounces get smaller S > 0 same as t > 0 (tautology) no ...
... ball bouncing - forward direction is one where successive bounces get smaller S > 0 same as t > 0 (tautology) no ...
Automobiles
... the fuel and air mixture becomes extremely hot and that mixture can ignite spontaneously in a process called “knocking” or “preignition” the car can reduce its compression ratio or increase the ignition resistance of its fuel ...
... the fuel and air mixture becomes extremely hot and that mixture can ignite spontaneously in a process called “knocking” or “preignition” the car can reduce its compression ratio or increase the ignition resistance of its fuel ...
Slide 1
... equilibrium and can return to its initial conditions along the same path Most natural processes are irreversible Sets an upper limit on efficiency of heat engines ...
... equilibrium and can return to its initial conditions along the same path Most natural processes are irreversible Sets an upper limit on efficiency of heat engines ...
Consider a rigid tank with a movable piston
... 2) All the processes that make up the cycle are internally reversible. 3) The combustion process is replaced by a heat-addition process from an external source. 4) The exhaust process is replaced by a heat rejection process that restores the working fluid to its initial state Also, it is common to a ...
... 2) All the processes that make up the cycle are internally reversible. 3) The combustion process is replaced by a heat-addition process from an external source. 4) The exhaust process is replaced by a heat rejection process that restores the working fluid to its initial state Also, it is common to a ...
thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
... Latent heat of ice = 336 kJ/kg, cP for water = 4.2 kJ/kg K. 7. Air initially at 155.50C and 1 bar, is composed reversibly and isothermally to a state where the specific volume is 0.28 m3/kg. Find the change in internal energy, change of entropy, and heat and work transfers per kg of air 8. A mass of ...
... Latent heat of ice = 336 kJ/kg, cP for water = 4.2 kJ/kg K. 7. Air initially at 155.50C and 1 bar, is composed reversibly and isothermally to a state where the specific volume is 0.28 m3/kg. Find the change in internal energy, change of entropy, and heat and work transfers per kg of air 8. A mass of ...
10.213 Recitation April 8, 2002 A heat pump is used to heat a house
... (1 mole)(CV = 2.5R)(353 K – 523 K) = Q + (-1.8 kJ) gives Q = -1.73 kJ For the second law balance, we have two effects: Change in state: n∆S = nCPln(T2/T1) – Rnln(P2/P1) = -2.3 J/K Heat transfer: n∆S = -Q/Tres = -1.73 kJ/303K = 5.7 J/K ...
... (1 mole)(CV = 2.5R)(353 K – 523 K) = Q + (-1.8 kJ) gives Q = -1.73 kJ For the second law balance, we have two effects: Change in state: n∆S = nCPln(T2/T1) – Rnln(P2/P1) = -2.3 J/K Heat transfer: n∆S = -Q/Tres = -1.73 kJ/303K = 5.7 J/K ...
I. POLYTROPIC RELATIONS (25 points)
... POLYTROPIC RELATIONS (25 points) 400 ml of air at standard conditions (25 C, 1 atm) is compressed adiabatically and reversibly while its volume is reduced by a factor of ten. Assume that this occurs in a piston/cylinder apparatus and that the ratio of Cp/Cv for air is 1.4 throughout the entire proce ...
... POLYTROPIC RELATIONS (25 points) 400 ml of air at standard conditions (25 C, 1 atm) is compressed adiabatically and reversibly while its volume is reduced by a factor of ten. Assume that this occurs in a piston/cylinder apparatus and that the ratio of Cp/Cv for air is 1.4 throughout the entire proce ...
document The Latent Heat Quiz
... Latent heat is the term used to describe the quantity of heat either absorbed or _____________by a substance as it changes ______. Melting and _______________ are processes that require heat to be added. __________ and condensing are processes that release heat. ...
... Latent heat is the term used to describe the quantity of heat either absorbed or _____________by a substance as it changes ______. Melting and _______________ are processes that require heat to be added. __________ and condensing are processes that release heat. ...
6–18 A steam power plant receives heat from a furnace at a rate of
... rate of 280 GJ/h. Heat losses to the surrounding air from the steam as it passes through the pipes and other components are estimated to be about 8 GJ/h. If the waste heat is transferred to the cooling water at a rate of 145 GJ/h, determine (a) net power output and (b) the thermal efficiency of this ...
... rate of 280 GJ/h. Heat losses to the surrounding air from the steam as it passes through the pipes and other components are estimated to be about 8 GJ/h. If the waste heat is transferred to the cooling water at a rate of 145 GJ/h, determine (a) net power output and (b) the thermal efficiency of this ...
KS4 Energy Transfers 1
... Water, air, granite– which is the worst heat conductor? Why is a duvet a good insulator? What is the main method of heat transfer within a liquid? How does heat energy reach Jupiter from the Sun? What speed do infra-red waves travel at? A black and a silver car are parked outside on a sunny day for ...
... Water, air, granite– which is the worst heat conductor? Why is a duvet a good insulator? What is the main method of heat transfer within a liquid? How does heat energy reach Jupiter from the Sun? What speed do infra-red waves travel at? A black and a silver car are parked outside on a sunny day for ...
Intercooler

An intercooler is any mechanical device used to cool a fluid, including liquids or gases, between stages of a multi-stage heating process, typically a heat exchanger that removes waste heat in a gas compressor. They are used in many applications, including air compressors, air conditioners, refrigerators, and gas turbines, and are widely known in automotive use as an air-to-air or air-to-liquid cooler for forced induction (turbocharged or supercharged) internal combustion engines to improve their volumetric efficiency by increasing intake air charge density through nearly isobaric (constant pressure) cooling.




















