Cell Respiration - South Sevier High School
... cell than inside the cell, causing water to move into the cell and swell? 5. What is the name of a solution where the concentration of dissolved substances is higher outside the cell than inside the cell, causing water to move out of the cell and shrink? 6. What is passive transport? 7. What is acti ...
... cell than inside the cell, causing water to move into the cell and swell? 5. What is the name of a solution where the concentration of dissolved substances is higher outside the cell than inside the cell, causing water to move out of the cell and shrink? 6. What is passive transport? 7. What is acti ...
Limit to Cell Growth Notes Which turtle has bigger cells?
... Waste products leave in the same way ...
... Waste products leave in the same way ...
Animal and Plant Mitosis Microviewer Questions
... 15. What is happening to the cell membrane and cytoplasm at this stage? Late Telophase 16. How many cells are there now? 17. How many chromosomes are in each cell? 18. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? ...
... 15. What is happening to the cell membrane and cytoplasm at this stage? Late Telophase 16. How many cells are there now? 17. How many chromosomes are in each cell? 18. How many chromosomes are in a human cell? ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... (charged particles), nutrients and wastes (Plant cells have one large vacuole/Animal cells have many small vacuoles.) Lysosomes – vesicles that contain digestive enzymes; digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria ...
... (charged particles), nutrients and wastes (Plant cells have one large vacuole/Animal cells have many small vacuoles.) Lysosomes – vesicles that contain digestive enzymes; digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria ...
AP Biology
... 3) Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion into the cell? 4) Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion out of the cell? 5) Which solution – the cell contents or the environment – is hypertonic to the other? 6) In which direction will there be a net osmotic movement of water? 7) After the cel ...
... 3) Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion into the cell? 4) Which solute(s) will exhibit a net diffusion out of the cell? 5) Which solution – the cell contents or the environment – is hypertonic to the other? 6) In which direction will there be a net osmotic movement of water? 7) After the cel ...
Slide 1
... white, pink, red due to blood no chloroplasts can be any shape (rounded) Many , small vacuoles ...
... white, pink, red due to blood no chloroplasts can be any shape (rounded) Many , small vacuoles ...
The Cell Theory
... All Cells Have Three Basic Features: Cell Membrane, Genetic Material, Cytoplasm Plasma Membrane (aka Cell Membrane) 1. Isolates cytoplasm from external environment 2. regulates flow or material into and out of the cell 3. allows interaction with other cells Genetic Material 1. provides cellular "blu ...
... All Cells Have Three Basic Features: Cell Membrane, Genetic Material, Cytoplasm Plasma Membrane (aka Cell Membrane) 1. Isolates cytoplasm from external environment 2. regulates flow or material into and out of the cell 3. allows interaction with other cells Genetic Material 1. provides cellular "blu ...
Organelle that uses energy to make sugar in plant cells Chloroplast
... responsible for plants standing up straight. ...
... responsible for plants standing up straight. ...
How do cells move? Mathematical modelling of cytoskeletal
... How do cells move? Mathematical modelling of cytoskeletal dynamics and cell migration ...
... How do cells move? Mathematical modelling of cytoskeletal dynamics and cell migration ...
Document
... Mitochondrion:It is made up of a bi-layer membrane; the outer membrane is smooth and the inner membrane protrudes inwards to form many infoldings. These infoldings are involved in cell respiration and act as a generator to produce ATP(energy) for cell operation. Endoplasmic reticulum:They are classi ...
... Mitochondrion:It is made up of a bi-layer membrane; the outer membrane is smooth and the inner membrane protrudes inwards to form many infoldings. These infoldings are involved in cell respiration and act as a generator to produce ATP(energy) for cell operation. Endoplasmic reticulum:They are classi ...
Cell
... These are the extensions of the cell membrane. Microvilli are common along the surface of absorptive cell. They increase the surface area for absorption. Pseudopodia are outgrowth from phagocytic cell to enclose and swallow the foreign materials. ...
... These are the extensions of the cell membrane. Microvilli are common along the surface of absorptive cell. They increase the surface area for absorption. Pseudopodia are outgrowth from phagocytic cell to enclose and swallow the foreign materials. ...
Name Date ________Block
... How does the number of chromosomes in newly divided cells compare with the number of chromosomes in the original cell? ...
... How does the number of chromosomes in newly divided cells compare with the number of chromosomes in the original cell? ...
3. Mitosis
... The chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle, which is made of microtubules. The spindle fibers are attached to each centromere(which is part of the chromosome), and anchored on the other end to a centrosome( centriole). There are 2 centrosomes, one at each end of the spindle. The Chromosomes are ...
... The chromosomes are pulled apart by the spindle, which is made of microtubules. The spindle fibers are attached to each centromere(which is part of the chromosome), and anchored on the other end to a centrosome( centriole). There are 2 centrosomes, one at each end of the spindle. The Chromosomes are ...
Cells Structure and Functions
... provide shape and allow the plant to store water and food for future use), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles,if any are ...
... provide shape and allow the plant to store water and food for future use), while animal cells have smaller vacuoles,if any are ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... 10. Describe the nuclear membrane. Give two traits that differ from the cell membrane. What is an example of a molecule that exits the nucleus? What is an example of something that enters the nucleus? 11. Describe the role of a ribosome, where they are found, and what they are made of. How does the ...
... 10. Describe the nuclear membrane. Give two traits that differ from the cell membrane. What is an example of a molecule that exits the nucleus? What is an example of something that enters the nucleus? 11. Describe the role of a ribosome, where they are found, and what they are made of. How does the ...
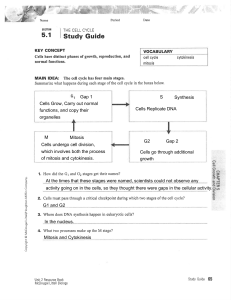
5.1 Study Guide KEY
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Breaks down high-energy organic molecules (cellular respiration) to store in chemical bonds as chemical potential energy. • In addition to glucose, it can also use lipids and proteins • The released energy is stored in the form of ATP ...
... • Breaks down high-energy organic molecules (cellular respiration) to store in chemical bonds as chemical potential energy. • In addition to glucose, it can also use lipids and proteins • The released energy is stored in the form of ATP ...
Specialised cells worksheet.
... • Large surface area, for ________ to pass through. • Contains haemoglobin, which joins with oxygen. • Has no _________. ...
... • Large surface area, for ________ to pass through. • Contains haemoglobin, which joins with oxygen. • Has no _________. ...
Ranking-of-Cell
... your ranking. Therefore, as you do your ranking you should be thinking about the principles that inform your ranking and how you’ll explain and defend them to others. Consider WHAT job is performed by each cell part and HOW each job is contributing to the overall performance of the cell. ______ A. A ...
... your ranking. Therefore, as you do your ranking you should be thinking about the principles that inform your ranking and how you’ll explain and defend them to others. Consider WHAT job is performed by each cell part and HOW each job is contributing to the overall performance of the cell. ______ A. A ...
cell division: mitosis - College of the Atlantic
... – Chromosone replicates into identical loops, each attached to the plasma membrane at adjacent sites – Between attachment sites the membrane grows and separates the two copies of the chromosone – Bacterium grows to twice its size and cleavage furrow develops – Cell wall develops across bacterium bet ...
... – Chromosone replicates into identical loops, each attached to the plasma membrane at adjacent sites – Between attachment sites the membrane grows and separates the two copies of the chromosone – Bacterium grows to twice its size and cleavage furrow develops – Cell wall develops across bacterium bet ...
Michael A. Henderson
... M. SCHLEIDEN (1804 - 1881) All organisms consist of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms All cells arise from preexisting cells ...
... M. SCHLEIDEN (1804 - 1881) All organisms consist of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms All cells arise from preexisting cells ...
SW Science 10 Unit 1 Mitosis Worksheet
... 5. The drawing below has been made from a photograph showing a cell undergoing mitosis. Based on the drawing, in what stage of mitosis must the cell have been in? ______________________ ...
... 5. The drawing below has been made from a photograph showing a cell undergoing mitosis. Based on the drawing, in what stage of mitosis must the cell have been in? ______________________ ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes ...
... Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.