Name(s) Date_______________ Period ______ Interactive
... 4) Do the Pop-Up Questions…Good Luck!!! 5) Animal Cell Which of the following parts of an animal cell is responsible for: - giving the shape to the cell and where metabolic reactions occur ____________ - helping metabolize materials taken in __________________________ - being the site of energy meta ...
... 4) Do the Pop-Up Questions…Good Luck!!! 5) Animal Cell Which of the following parts of an animal cell is responsible for: - giving the shape to the cell and where metabolic reactions occur ____________ - helping metabolize materials taken in __________________________ - being the site of energy meta ...
Ch 12 - MsBabbey
... Cytokinesis in Plants • In plant cells, a cell plate made of vesicles filled with cellulose, forms in between the two new cells to make a new cell wall. ...
... Cytokinesis in Plants • In plant cells, a cell plate made of vesicles filled with cellulose, forms in between the two new cells to make a new cell wall. ...
Cell Structure & Function BINGO
... Contains digestive enzymes that break down many types of molecules; often called garbage ...
... Contains digestive enzymes that break down many types of molecules; often called garbage ...
Study Guide
... Chloroplast Cell wall Cilia Flagella Cell membrane Phospholipid Hydrophobic Hydrophilic ...
... Chloroplast Cell wall Cilia Flagella Cell membrane Phospholipid Hydrophobic Hydrophilic ...
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story
... Makes ATP Surrounded by two membranes Needs oxygen Liver and muscle cells have the most mitochondria Bean-shaped Breaks down food molecules to release energy ...
... Makes ATP Surrounded by two membranes Needs oxygen Liver and muscle cells have the most mitochondria Bean-shaped Breaks down food molecules to release energy ...
Cell Organelles
... double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
... double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
Ch. 1 - Cell Organelles Worksheet
... a whip-like motion to move the cell. Ex. Sperm cells have a ___ which allow them to swim in the in seminal fluid. ...
... a whip-like motion to move the cell. Ex. Sperm cells have a ___ which allow them to swim in the in seminal fluid. ...
Cell Division - Cobb Learning
... 1. Cells reproduce by splitting in half, a process called cell division. What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that they don’t just get smaller and smaller? _________________________________________________________________________ 2. The genetic information of a cell is carried in ...
... 1. Cells reproduce by splitting in half, a process called cell division. What do cells need to do between divisions to make sure that they don’t just get smaller and smaller? _________________________________________________________________________ 2. The genetic information of a cell is carried in ...
Producing new cells - Clydebank High School
... Q. What happens to the number of chromosomes during mitosis going from the parent cell to daughter cells? A. the number of chromosomes stays ...
... Q. What happens to the number of chromosomes during mitosis going from the parent cell to daughter cells? A. the number of chromosomes stays ...
We`sproutly` present
... The functionally immortalized human umbilical vein endothelial cell line CI-huVEC has just been published in the peer reviewed 'FASEB Journal'. The article describes a sophisticated three-dimensional cell culture model enabling angiogenesis studies and functional screening. The C ...
... The functionally immortalized human umbilical vein endothelial cell line CI-huVEC has just been published in the peer reviewed 'FASEB Journal'. The article describes a sophisticated three-dimensional cell culture model enabling angiogenesis studies and functional screening. The C ...
Keystone Review
... THE REGION OF THE CELL THAT IS WITHIN THE PLASMA MEMBRANE AND THAT INCLUDES THE FLUID, THE CYTOSKELETON, AND ALL ORGANELLES EXCEPT THE NUCLEUS IS CALLED THE CYTOPLASM ...
... THE REGION OF THE CELL THAT IS WITHIN THE PLASMA MEMBRANE AND THAT INCLUDES THE FLUID, THE CYTOSKELETON, AND ALL ORGANELLES EXCEPT THE NUCLEUS IS CALLED THE CYTOPLASM ...
Chapter 3
... 3. Many bacteria commonly carry extrachromosomal pieces of DNA called ___________, which are able to ___________ independently of the bacterial chromosome. 4. Protein synthesis takes place at ___________. 5. The main components of cell membranes are ___________ and ___________ 6. Gram-positive cell ...
... 3. Many bacteria commonly carry extrachromosomal pieces of DNA called ___________, which are able to ___________ independently of the bacterial chromosome. 4. Protein synthesis takes place at ___________. 5. The main components of cell membranes are ___________ and ___________ 6. Gram-positive cell ...
Ch32and33
... Binary fission – a form of asexual reproduction by which some single-celled organisms reproduce. Prokaryotes such as bacteria reproduce by binary fission Regeneration – in some organisms, the process by which certain cells produce new tissue growth at the site of a wound or lost limb; also a form of ...
... Binary fission – a form of asexual reproduction by which some single-celled organisms reproduce. Prokaryotes such as bacteria reproduce by binary fission Regeneration – in some organisms, the process by which certain cells produce new tissue growth at the site of a wound or lost limb; also a form of ...
Chapter 2 – Cell Processes and Energy
... 1. In words 2. In diagram form 3. In EQUATION form c. Photosynthesis and respiration can be thought of as opposites 1. Why? 2. What do the two processes do for the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? d. Similarities/differences between RESPIRATION and FERMENTATION e. Vocabulary – ...
... 1. In words 2. In diagram form 3. In EQUATION form c. Photosynthesis and respiration can be thought of as opposites 1. Why? 2. What do the two processes do for the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? d. Similarities/differences between RESPIRATION and FERMENTATION e. Vocabulary – ...
Eukaryotic Cells - Summit Public Schools
... Contribution to Science: Discovered microorganisms in pond water. He called them animalcules. ...
... Contribution to Science: Discovered microorganisms in pond water. He called them animalcules. ...
The Cell in Action
... • Cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. • DNA is made up of chromosomes. • Chromosomes are copied which ensures that the new cells have the exact DNA as the parent cells. • Prokaryotic cells are less complicated and may split by binary fission. The cell splits into two and each new cell has the ma ...
... • Cell cycle is the life cycle of a cell. • DNA is made up of chromosomes. • Chromosomes are copied which ensures that the new cells have the exact DNA as the parent cells. • Prokaryotic cells are less complicated and may split by binary fission. The cell splits into two and each new cell has the ma ...
All About Cells Review
... 22. What is cytosol & what does it contain? 23. Name 3 organelles found in plant, but not animal cells. 24. What is the function of mitochondria? What energy molecule is made there? 25. Describe the outer covering of the mitochondria. 26. What are cristae & what is their purpose? 27. Mitochondria ar ...
... 22. What is cytosol & what does it contain? 23. Name 3 organelles found in plant, but not animal cells. 24. What is the function of mitochondria? What energy molecule is made there? 25. Describe the outer covering of the mitochondria. 26. What are cristae & what is their purpose? 27. Mitochondria ar ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... the Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus – set of flattened membrane bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
... the Golgi Apparatus Golgi Apparatus – set of flattened membrane bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell Enzymes inside the golgi modify the proteins, which then are enclosed in new Vesicles that bud from the surface of the golgi apparatus ...
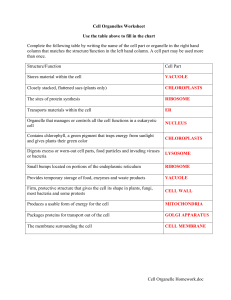
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
... column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis
... chromosomes apart (2 chromatids then called chromosomes, each with its own centromere and kinetochore) ...
... chromosomes apart (2 chromatids then called chromosomes, each with its own centromere and kinetochore) ...
Name
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
review WS
... 22. What are the 4 phases of mitosis – in order? 23. What phase of mitosis is the longest? 24. What is the first phase of mitosis where chromosomes are visible? 25. During which phase of mitosis do centrioles start to move to the poles and spindle fibers appear? 26. During which phase of mitosis do ...
... 22. What are the 4 phases of mitosis – in order? 23. What phase of mitosis is the longest? 24. What is the first phase of mitosis where chromosomes are visible? 25. During which phase of mitosis do centrioles start to move to the poles and spindle fibers appear? 26. During which phase of mitosis do ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.