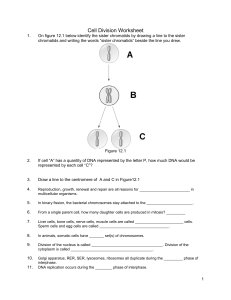
Cell Division Worksheet PDF
... 1. Synthesis of DNA takes place ____________________ 2. Division of cytoplasm and organelles _______________ 3. Cell grows in size following division ______________ 4. Cell has twice as much DNA as parent cell _________ 5. Division of chromosomes _________________ ...
... 1. Synthesis of DNA takes place ____________________ 2. Division of cytoplasm and organelles _______________ 3. Cell grows in size following division ______________ 4. Cell has twice as much DNA as parent cell _________ 5. Division of chromosomes _________________ ...
HW 11/3 Mitosis
... Directions: Read and Highlight then answer the questions. At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resu ...
... Directions: Read and Highlight then answer the questions. At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resu ...
HW 10/29 Mitosis
... Directions: Read and Highlight then answer the questions. At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resu ...
... Directions: Read and Highlight then answer the questions. At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resu ...
iscience life science unit 1 chapter 2 study guide
... d. The difference between active and passive transport: Examples of each and how this is important to the cell. T/F: 10pts M.C: 15pts Short Answer/Application: 20pts Total Points: 45pts ...
... d. The difference between active and passive transport: Examples of each and how this is important to the cell. T/F: 10pts M.C: 15pts Short Answer/Application: 20pts Total Points: 45pts ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum - Brandywine School District
... •Has openings where items may enter and exit cell (aided by ...
... •Has openings where items may enter and exit cell (aided by ...
organelles - GEOCITIES.ws
... Produce most of the energy needed for cell functions Muscle cells have lots of these ...
... Produce most of the energy needed for cell functions Muscle cells have lots of these ...
Biology Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Notes
... nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic (water loving) and interacts with the watery external environment so the cell can get the nutrients it needs. The phospholipids form a bilayer (2 laye ...
... nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic (water loving) and interacts with the watery external environment so the cell can get the nutrients it needs. The phospholipids form a bilayer (2 laye ...
biology a2
... number of chromosome as parent is formed; It involves behavior of chromosome which occur in various stages The first stage is interphase; here there is multiplication of genetic material (so that daughter cells have the same number as parent cell); there is also synthesis of new cell organelle; and ...
... number of chromosome as parent is formed; It involves behavior of chromosome which occur in various stages The first stage is interphase; here there is multiplication of genetic material (so that daughter cells have the same number as parent cell); there is also synthesis of new cell organelle; and ...
Common Assessment #3 Review Sheet Why is the plasma
... If a plasma membrane was twice as thick as normal, would it be easier or more difficult for the molecules to move across the membrane of a cell? ...
... If a plasma membrane was twice as thick as normal, would it be easier or more difficult for the molecules to move across the membrane of a cell? ...
Cell Cycle Internet Activity.2
... ONION ROOT TIPS AND THE CELL CYCLE When you have completed the activity, answer the questions that follow. Interphase Number of cells Percent of cells ...
... ONION ROOT TIPS AND THE CELL CYCLE When you have completed the activity, answer the questions that follow. Interphase Number of cells Percent of cells ...
Rebel Academy – Khan Academy Review
... Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, _________________________, ____________________________ and also Protists. ( not mentioned in the video) mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. T ...
... Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, _________________________, ____________________________ and also Protists. ( not mentioned in the video) mRNA is translated into ______________________ at the ribosome. Ribosomes are the sites where information is converted into ______________________________. T ...
Sep 52:43 PM Sep 81:29 PM Sep 52:53 PM Sep 53:37 PM Sep 54
... organize the spindle, a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes. During prophase, the condensed chromosomes becomes attached to fibers in the spindle at a point near the centromere of each chromatid. Interestingly, plant cells do not have centrioles, but still organiz ...
... organize the spindle, a fanlike microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes. During prophase, the condensed chromosomes becomes attached to fibers in the spindle at a point near the centromere of each chromatid. Interestingly, plant cells do not have centrioles, but still organiz ...
File - Coach Nowell
... 1.To make new cells (if you are injured or growing) 2.Pass on your genes to next generation (sex) ...
... 1.To make new cells (if you are injured or growing) 2.Pass on your genes to next generation (sex) ...
Cell Structures (chapter 7-1, 7-2)
... What is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? nucleus What is the cells boundary from its environment? cell membrane What contains DNA, is the control center, and is found in eukaryotes? nucleus What type of cells has chloroplasts? plants What organelle is responsible for digesting and recycli ...
... What is found in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes? nucleus What is the cells boundary from its environment? cell membrane What contains DNA, is the control center, and is found in eukaryotes? nucleus What type of cells has chloroplasts? plants What organelle is responsible for digesting and recycli ...
Cell Organelles BioH
... What is the difference between the two parts of the ER? Rough ER – has ribosomes and process proteins Smooth ER – no ribosomes, makes lipids ...
... What is the difference between the two parts of the ER? Rough ER – has ribosomes and process proteins Smooth ER – no ribosomes, makes lipids ...
The Characteristics of Cells
... Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? ...
... Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. What term describes the smallest unit that can perform all of the functions necessary for life? ...
A1979HZ27200001
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
Module map - Nuffield Foundation
... A zygote divides to form unspecialized stem cells which can develop into any type of cell in the body. After early development, human cells are differentiated. Unspecialized plant cells (meristem tissue) remain throughout the plant’s life cycle. Unlike animals, most plants continue to grow in height ...
... A zygote divides to form unspecialized stem cells which can develop into any type of cell in the body. After early development, human cells are differentiated. Unspecialized plant cells (meristem tissue) remain throughout the plant’s life cycle. Unlike animals, most plants continue to grow in height ...
7.2 Organelles
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.























