Growing Membranes, Sustaining Cells
... cells. (A) The synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis) in liver cells depends on three metabolic compartments: the cytoplasm, mitochondrial matrix, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen. Three key kinases in glycolysis—hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase—catalyze nonreversible reactio ...
... cells. (A) The synthesis of glucose (gluconeogenesis) in liver cells depends on three metabolic compartments: the cytoplasm, mitochondrial matrix, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen. Three key kinases in glycolysis—hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase—catalyze nonreversible reactio ...
Review: can diet influence the selective advantage of mitochondrial
... mitohormesis [7]. Although varied, this response appears to induce a wide-ranging cytoprotective state resulting in long lasting metabolic and biochemical changes. Remarkably, rather than being harmful, these changes may increase evolutionary potential and decrease susceptibility for disease. Althou ...
... mitohormesis [7]. Although varied, this response appears to induce a wide-ranging cytoprotective state resulting in long lasting metabolic and biochemical changes. Remarkably, rather than being harmful, these changes may increase evolutionary potential and decrease susceptibility for disease. Althou ...
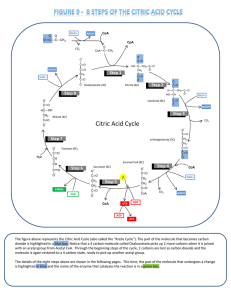
Citric Acid Cycle - BYU
... dioxide is highlighted in a blue box. Notice that a 4 carbon molecule called Oxaloacetate picks up 2 more carbons when it is joined with an acetyl group from Acetyl CoA. Through the beginning steps of the cycle, 2 carbons are lost as carbon dioxide and the molecule is again restored to a 4 carbon ...
... dioxide is highlighted in a blue box. Notice that a 4 carbon molecule called Oxaloacetate picks up 2 more carbons when it is joined with an acetyl group from Acetyl CoA. Through the beginning steps of the cycle, 2 carbons are lost as carbon dioxide and the molecule is again restored to a 4 carbon ...
Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism - Rose
... possible for the pyruvate concentration inside the mitochondria to be higher than outside. The energy for the pump comes from a proton gradient, in which the proton concentration outside the mitochondria is higher than it is inside. Many other molecules are present only on one side of the membrane, ...
... possible for the pyruvate concentration inside the mitochondria to be higher than outside. The energy for the pump comes from a proton gradient, in which the proton concentration outside the mitochondria is higher than it is inside. Many other molecules are present only on one side of the membrane, ...
Peroxidases and Catalases. Biochemistry, Biophysics, Biotechnology and Physiology Brochure
... and Catalases: Biochemistry, Biophysics, Biotechnology and Physiology provides a much–needed systematic, up–to–date treatment of peroxidases and catalases. From the structure and properties of the various superfamilies to current applications of peroxidases, the book consolidates vast amounts of inf ...
... and Catalases: Biochemistry, Biophysics, Biotechnology and Physiology provides a much–needed systematic, up–to–date treatment of peroxidases and catalases. From the structure and properties of the various superfamilies to current applications of peroxidases, the book consolidates vast amounts of inf ...
The Citric acid cycle - University of Houston
... majority of carbohydrate, fatty acid and amino acid oxidation. It also accounts for a majority of the generation of these compounds and others as well. Amphibolic - acts both catabolically and anabolically ...
... majority of carbohydrate, fatty acid and amino acid oxidation. It also accounts for a majority of the generation of these compounds and others as well. Amphibolic - acts both catabolically and anabolically ...
McFil: metabolic carbon flow in leaves
... Caputo C. & Barneix A.J. (1997) Export of amino acids to the phloem in relation to N supply in wheat. Physiologia Plantarum, 101, 853-860. Karley A.J., Douglas A.E. & Parker W.E. (2002) Amino acid composition and nutritional quality of potato leaf phloem sap for aphids. The Journal of Experimental B ...
... Caputo C. & Barneix A.J. (1997) Export of amino acids to the phloem in relation to N supply in wheat. Physiologia Plantarum, 101, 853-860. Karley A.J., Douglas A.E. & Parker W.E. (2002) Amino acid composition and nutritional quality of potato leaf phloem sap for aphids. The Journal of Experimental B ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint File
... • Chloroplasts rearrange the atoms of these ingredients to produce sugars (glucose) and other organic molecules. – Oxygen gas is a by-product of photosynthesis. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Chloroplasts rearrange the atoms of these ingredients to produce sugars (glucose) and other organic molecules. – Oxygen gas is a by-product of photosynthesis. Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Cellular Respiration Webquest
... Cellular Respiration Webquest RESPIRATION WEBQUEST ATP: THE ENERGY OF LIFE Go to: Biology in Motion. Read & complete the activity. (http://www.biologyinmotion.com/atp/index.html) 1. What is ATP? ...
... Cellular Respiration Webquest RESPIRATION WEBQUEST ATP: THE ENERGY OF LIFE Go to: Biology in Motion. Read & complete the activity. (http://www.biologyinmotion.com/atp/index.html) 1. What is ATP? ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry
... in order to regenerate NAD+ (from NADH)—which is required for the continuity of anaerobic glycolysis—in a process known as “homolactic fermentation” ...
... in order to regenerate NAD+ (from NADH)—which is required for the continuity of anaerobic glycolysis—in a process known as “homolactic fermentation” ...
Chapter 15
... Galactosemia is a disorder that affects how the body processes a simple sugar called galactose. A small amount of galactose is present in many foods. It is primarily part of a larger sugar called lactose, which is found in all dairy products and many baby formulas. The signs and symptoms of galacto ...
... Galactosemia is a disorder that affects how the body processes a simple sugar called galactose. A small amount of galactose is present in many foods. It is primarily part of a larger sugar called lactose, which is found in all dairy products and many baby formulas. The signs and symptoms of galacto ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... million dalton. So, you can you can understand that, how complex this particular molecule is, each contain covalently linked lipoic acid. So, this is a huge enzyme and it is obviously allosteric in nature, intra cellular and it plays the different various significant roles as far as the TCA cycle i ...
... million dalton. So, you can you can understand that, how complex this particular molecule is, each contain covalently linked lipoic acid. So, this is a huge enzyme and it is obviously allosteric in nature, intra cellular and it plays the different various significant roles as far as the TCA cycle i ...
metabolic pathways - MPG Systems Biology Forum
... An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state with all irreversible reactions used in the appropriate direction All flux distributions in the living cell are non-negative linear combinations of elementary modes ...
... An elementary mode is a minimal set of enzymes that can operate at steady state with all irreversible reactions used in the appropriate direction All flux distributions in the living cell are non-negative linear combinations of elementary modes ...
Glycolysis
... The tense conformation of PFK, at high [ATP], has lower affinity for the other substrate, fructose-6-P. Sigmoidal dependence of reaction rate on [fructose-6-P] is seen. AMP, present at significant levels only when there is extensive ATP hydrolysis, antagonizes effects of high ATP. ...
... The tense conformation of PFK, at high [ATP], has lower affinity for the other substrate, fructose-6-P. Sigmoidal dependence of reaction rate on [fructose-6-P] is seen. AMP, present at significant levels only when there is extensive ATP hydrolysis, antagonizes effects of high ATP. ...
Glycolysis
... The tense conformation of PFK, at high [ATP], has lower affinity for the other substrate, fructose-6-P. Sigmoidal dependence of reaction rate on [fructose-6-P] is seen. AMP, present at significant levels only when there is extensive ATP hydrolysis, antagonizes effects of high ATP. ...
... The tense conformation of PFK, at high [ATP], has lower affinity for the other substrate, fructose-6-P. Sigmoidal dependence of reaction rate on [fructose-6-P] is seen. AMP, present at significant levels only when there is extensive ATP hydrolysis, antagonizes effects of high ATP. ...
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
... energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external environment. The green as well as non-green plants obtain oxygen from their environment and return carbon dioxide and water vapour into it. This mere exchange of gases is know ...
... energy as ATP for various cellular metabolic activities. It involves exchange of gases between the organism and the external environment. The green as well as non-green plants obtain oxygen from their environment and return carbon dioxide and water vapour into it. This mere exchange of gases is know ...
Document
... • Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol where glucose is broken down into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. • Molecules like fructose, amino acids, and free fatty acids can be used as fuel by the cells. • These molecules enter glycolysis later in the pathway or by chemical conversion to one of the ...
... • Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol where glucose is broken down into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. • Molecules like fructose, amino acids, and free fatty acids can be used as fuel by the cells. • These molecules enter glycolysis later in the pathway or by chemical conversion to one of the ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.