Biology: Cellular Respiration Practice Problems
... 6. Where in the cell does the electron transport part of cellular respiration occur? Why? 7. How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 8. How many ATP are made in the Kreb’s cycle part of cellular respiration? 9. How many ATP are made in the electron transport part of cel ...
... 6. Where in the cell does the electron transport part of cellular respiration occur? Why? 7. How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 8. How many ATP are made in the Kreb’s cycle part of cellular respiration? 9. How many ATP are made in the electron transport part of cel ...
Overview of Aerobic Respiration
... Two ATP are used to split glucose and form 2 PGAL, each with one phosphate group Enzymes convert 2 PGAL to 2 PGA, forming 2 NADH Four ATP are formed by substrate-level phosphorylation (net 2 ATP) ...
... Two ATP are used to split glucose and form 2 PGAL, each with one phosphate group Enzymes convert 2 PGAL to 2 PGA, forming 2 NADH Four ATP are formed by substrate-level phosphorylation (net 2 ATP) ...
2 ATP
... (stored energy) called chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose and turn it into ATP. ATP is called free energy because it is available to do any type of work needed in our cells called Kinetic Energy (energy available for work) The amount of energy released is measure in calories or kilocalor ...
... (stored energy) called chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose and turn it into ATP. ATP is called free energy because it is available to do any type of work needed in our cells called Kinetic Energy (energy available for work) The amount of energy released is measure in calories or kilocalor ...
Midterm Exam Advanced Biochemistry II (Answer) 1. At equilibrium
... muscle tissue is vastly increased. In rabbit leg muscle or turkey flight muscle, the ATP is produced almost exclusively by lactic acid fermentation. ATP is formed in the payoff phase of glycolysis by two reactions, promoted by phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase. Suppose skeletal muscle were ...
... muscle tissue is vastly increased. In rabbit leg muscle or turkey flight muscle, the ATP is produced almost exclusively by lactic acid fermentation. ATP is formed in the payoff phase of glycolysis by two reactions, promoted by phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase. Suppose skeletal muscle were ...
Metabolic pathways
... Energy yields are low. Typical energy yields are 1-4 ATP per substrate molecule fermented. In the absence of oxygen, the available NAD+ is often limiting. The primary purpose is to regenerate NAD+ from NADH allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
... Energy yields are low. Typical energy yields are 1-4 ATP per substrate molecule fermented. In the absence of oxygen, the available NAD+ is often limiting. The primary purpose is to regenerate NAD+ from NADH allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
Biology 233
... occurs in mitochondrial matrix 2 (3C) pyruvic acid + 2 coenzyme A -----> 2 (2C) acetyl CoA net gain (per glucose) 2 CO2 2 NADH 3) Citric Acid Cycle (TCA cycle, Kreb’s cycle) 2 acetyl CoA enter cycle and are broken down occurs in mitochondrial matrix in one cycle: 1 (2C) acetyl CoA + (4C) molecule -- ...
... occurs in mitochondrial matrix 2 (3C) pyruvic acid + 2 coenzyme A -----> 2 (2C) acetyl CoA net gain (per glucose) 2 CO2 2 NADH 3) Citric Acid Cycle (TCA cycle, Kreb’s cycle) 2 acetyl CoA enter cycle and are broken down occurs in mitochondrial matrix in one cycle: 1 (2C) acetyl CoA + (4C) molecule -- ...
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable en ...
... central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and water to generate a form of usable en ...
video slide - Ethical Culture Fieldston School
... • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
... • NADH and FADH2 – Donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation ...
STRUCTURE OF ATP
... Under anaerobic conditions , pyruvate undergoes reductive decarboxylation to yield CO 2 and ethyl alcohol.Very less amount of energy is generated through this type of respiration in the cytoplasm of living cells. This occurs in lower organisms , such as many bacteria and some fungi. AEROBIC RESPIRAT ...
... Under anaerobic conditions , pyruvate undergoes reductive decarboxylation to yield CO 2 and ethyl alcohol.Very less amount of energy is generated through this type of respiration in the cytoplasm of living cells. This occurs in lower organisms , such as many bacteria and some fungi. AEROBIC RESPIRAT ...
Photosynthesis
... – Produces: NADH and FADH2, CO2 and 2 ATP molecules • Attaches H’s to NAD+ and FAD to create NADH and FADH2 (these will be used to make more ATP in the ETC) ...
... – Produces: NADH and FADH2, CO2 and 2 ATP molecules • Attaches H’s to NAD+ and FAD to create NADH and FADH2 (these will be used to make more ATP in the ETC) ...
Cellular Respiration - MF011 General Biology 2 (May 2011 Semester)
... Produce ATP by chemiosis (proton pumps and ATP Synthase) Oxygen serves as a final electron acceptor ...
... Produce ATP by chemiosis (proton pumps and ATP Synthase) Oxygen serves as a final electron acceptor ...
Chem464 Abrol Spring2017 FlippedReview4
... making ATP. Because ATP synthesis is much more efficient under aerobic conditions, the amount of glucose needed will decrease (the Pasteur effect). This decreased utilization of glucose in the presence of oxygen can be demonstrated in any tissue that is capable of aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis. ( ...
... making ATP. Because ATP synthesis is much more efficient under aerobic conditions, the amount of glucose needed will decrease (the Pasteur effect). This decreased utilization of glucose in the presence of oxygen can be demonstrated in any tissue that is capable of aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis. ( ...
Chapters 9-10 practice qui
... a doctor for help and is sent to the hospital for some tests. There they discover his mitochondria can use only fatty acids and amino acids for respiration, and his cells produce more lactate than normal. Of the following, which is the best explanation of his condition? a. His mitochondria lack the ...
... a doctor for help and is sent to the hospital for some tests. There they discover his mitochondria can use only fatty acids and amino acids for respiration, and his cells produce more lactate than normal. Of the following, which is the best explanation of his condition? a. His mitochondria lack the ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... phosphorylation—via the F1F0-ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial membrane d) reduction of NAD+—in both the cytosol of the cell and the matrix of the mitochondria e) reduction of oxygen gas to water—in the matrix of the mitochondria © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... phosphorylation—via the F1F0-ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial membrane d) reduction of NAD+—in both the cytosol of the cell and the matrix of the mitochondria e) reduction of oxygen gas to water—in the matrix of the mitochondria © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Metabolism of Glucose C6H12O6+6O2 1 unit of Glucose 38 ATP
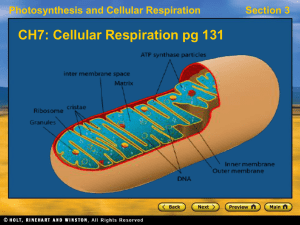
... This process enables the Glucose to pass through the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Matrix is called Matrix because it is very viscous/sticky. It’s filled with the intermediate chemicals and enzymes. At first two stages of the Kreb cycle, one CO2 is lost. It picks up 2C’s from the acetyl-c.A ...
... This process enables the Glucose to pass through the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Matrix is called Matrix because it is very viscous/sticky. It’s filled with the intermediate chemicals and enzymes. At first two stages of the Kreb cycle, one CO2 is lost. It picks up 2C’s from the acetyl-c.A ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, metabolic purpose Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only Electron transport chain: know complexes by number, mobile carrier ...
... Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex: Overall reaction, purpose of cofactors, metabolic purpose Citric acid Cycle: Structures of all intermediates, names of all intermediates, names of regulated enzymes, mechanisms presented in slides only Electron transport chain: know complexes by number, mobile carrier ...
RACC BIO Cellular respiration
... • An overview of the Citric acid cycle Pyruvate (from glycolysis, 2 molecules per glucose) This will cycle twice because 2 pyruvate molecules are formed during glycolysis ...
... • An overview of the Citric acid cycle Pyruvate (from glycolysis, 2 molecules per glucose) This will cycle twice because 2 pyruvate molecules are formed during glycolysis ...
Why ATP?
... 1. In the mitochondrion, membrane-bound enzymes couple electron flow to the production of a trans-membrane pH difference, accomplishing osmotic and electrical work. The proton gradient thus formed has potential energy (the proton-motive force). Another enzyme, ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial ...
... 1. In the mitochondrion, membrane-bound enzymes couple electron flow to the production of a trans-membrane pH difference, accomplishing osmotic and electrical work. The proton gradient thus formed has potential energy (the proton-motive force). Another enzyme, ATP synthase in the inner mitochondrial ...
Citric acid cycle
... glucose NADH electron transport chain proton-motive force ATP • About 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making about 32 ATP • There are several reasons why the number of ATP is not known exactly © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... glucose NADH electron transport chain proton-motive force ATP • About 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration, making about 32 ATP • There are several reasons why the number of ATP is not known exactly © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Cellular Respiration
... – 2 molecules NADH are created • Important because NADH are Hydrogen ion/proton and e- carriers ...
... – 2 molecules NADH are created • Important because NADH are Hydrogen ion/proton and e- carriers ...
1 Lecture 27: Metabolic Pathways Part I: Glycolysis
... How is the concentration of G-3-P reduced to insure that the aldolase reaction is spontaneous? ...
... How is the concentration of G-3-P reduced to insure that the aldolase reaction is spontaneous? ...
Unit 4 Notes - heckgrammar.co.uk
... 5. GP is converted in a series of steps to form the 3-carbon compound pyruvate. Another ATP is made during this process. Pyruvate marks the end of glycolysis, the first stage of respiration. Pyruvate can also be turned back into glucose by reversing glycolysis, and this is called gluconeogenesis. 6. ...
... 5. GP is converted in a series of steps to form the 3-carbon compound pyruvate. Another ATP is made during this process. Pyruvate marks the end of glycolysis, the first stage of respiration. Pyruvate can also be turned back into glucose by reversing glycolysis, and this is called gluconeogenesis. 6. ...
CH3 Test_answers_2011
... events that occur in a chloroplast during photosynthesis it is reasonable to claim that A. oxygen is an input to reactions at P. B. carbon dioxide is an input to reactions at Q. C. chlorophyll is essential for reactions that occur at Q. D. ADP produced during the events at P is used by events at Q. ...
... events that occur in a chloroplast during photosynthesis it is reasonable to claim that A. oxygen is an input to reactions at P. B. carbon dioxide is an input to reactions at Q. C. chlorophyll is essential for reactions that occur at Q. D. ADP produced during the events at P is used by events at Q. ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.