Test 1 Study Guide Chapter 1 – Introduction
... iii. Chemiosmosis – production of ATP by a proton (H+) gradient. (Fig. 5.15) 1. Protons have been pumped into inter/outer-membrane space. High concentration drives movement of protons back across membrane. 2. ATP synthase: force of proton movement turns powers ATP synthesis. (Fig. 5.16) 3. Electrons ...
... iii. Chemiosmosis – production of ATP by a proton (H+) gradient. (Fig. 5.15) 1. Protons have been pumped into inter/outer-membrane space. High concentration drives movement of protons back across membrane. 2. ATP synthase: force of proton movement turns powers ATP synthesis. (Fig. 5.16) 3. Electrons ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... iii. Chemiosmosis – production of ATP by a proton (H+) gradient. (Fig. 5.15) 1. Protons have been pumped into inter/outer-membrane space. High concentration drives movement of protons back across membrane. 2. ATP synthase: force of proton movement turns powers ATP synthesis. (Fig. 5.16) 3. Electrons ...
... iii. Chemiosmosis – production of ATP by a proton (H+) gradient. (Fig. 5.15) 1. Protons have been pumped into inter/outer-membrane space. High concentration drives movement of protons back across membrane. 2. ATP synthase: force of proton movement turns powers ATP synthesis. (Fig. 5.16) 3. Electrons ...
Anaerobically functioning mitochondria
... until oxygen levels are sufficient to resume aerobic respiration followed by enzymatic oxidation to release pyruvate as an essential TCA cycle substrate (Grieshaber et al., 1994) (Fig. 1). The amino acids used in the biosynthesis of opines are alanine, arginine or glycine (Fields et al., 1980, Siegm ...
... until oxygen levels are sufficient to resume aerobic respiration followed by enzymatic oxidation to release pyruvate as an essential TCA cycle substrate (Grieshaber et al., 1994) (Fig. 1). The amino acids used in the biosynthesis of opines are alanine, arginine or glycine (Fields et al., 1980, Siegm ...
Electron transport chain…
... PMF drives ATP synthesis • diffusion of protons back across membrane (down gradient) drives formation of ATP • ATP synthase ...
... PMF drives ATP synthesis • diffusion of protons back across membrane (down gradient) drives formation of ATP • ATP synthase ...
Chapter 8 Your Body`s Metabolism
... Electrons from hydrogen atoms in coenzymes enter the electron transport chain ...
... Electrons from hydrogen atoms in coenzymes enter the electron transport chain ...
File
... Succinyl-CoA Synthetase Key points: • Substrate level phosphorylation • Energy of thioester allows for incorporation of inorganic phosphate • Goes through a phospho-enzyme intermediate • Produces GTP, which can be converted to ATP • Slightly thermodynamically favorable/reversible – Product concentr ...
... Succinyl-CoA Synthetase Key points: • Substrate level phosphorylation • Energy of thioester allows for incorporation of inorganic phosphate • Goes through a phospho-enzyme intermediate • Produces GTP, which can be converted to ATP • Slightly thermodynamically favorable/reversible – Product concentr ...
Document
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space H then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H to drive phosphorylation of ...
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space H then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H to drive phosphorylation of ...
Properties of ATP - BioWiki
... Phosphorylation reactions using ATP are really nucleophilic substitution reactions which proceed through a pentavalent intermediate. The rest of the ATP molecule is then considered the leaving group, which could be theoretically ADP or AMP as well. If water is the nucleophile, the reaction is also a ...
... Phosphorylation reactions using ATP are really nucleophilic substitution reactions which proceed through a pentavalent intermediate. The rest of the ATP molecule is then considered the leaving group, which could be theoretically ADP or AMP as well. If water is the nucleophile, the reaction is also a ...
Nutrient cycles - VBIOLOGY
... coenzyme A to produce acetylcoenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
... coenzyme A to produce acetylcoenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
Oxidation of Fatty Acids Is the Source of Increased
... change in mitochondrial content in kidney tubules. Substrate processing rather than the mitochondrial ETC is changed in kidney tubules in diabetes. Diabetic tubule kidney mitochondria oxidizing glutamate have higher state 3 respiratory rates compared with the control (Table 2). The ADP-to-oxygen rat ...
... change in mitochondrial content in kidney tubules. Substrate processing rather than the mitochondrial ETC is changed in kidney tubules in diabetes. Diabetic tubule kidney mitochondria oxidizing glutamate have higher state 3 respiratory rates compared with the control (Table 2). The ADP-to-oxygen rat ...
Muscle Metabolism lecture teacher
... This is okay, because your body will repair this damage and your muscles will actually become stronger because of it. However, it can be uncomfortable for some people -- especially if you aren't well-conditioned. 2. There is also a theory that waste products -- particularly lactic acid -- that are c ...
... This is okay, because your body will repair this damage and your muscles will actually become stronger because of it. However, it can be uncomfortable for some people -- especially if you aren't well-conditioned. 2. There is also a theory that waste products -- particularly lactic acid -- that are c ...
BIO 16l EXAM2 SUMMER6WKKey
... a. depends on unusual amino acids not common in proteins. b. has a certaifi unique amino acid to fit each substrate. C. is shaped to fit a certain substrate molecule. d. is lined with glycolipids and glycoproteins. e. passes electrons from one part ofthe substrate to another. ...
... a. depends on unusual amino acids not common in proteins. b. has a certaifi unique amino acid to fit each substrate. C. is shaped to fit a certain substrate molecule. d. is lined with glycolipids and glycoproteins. e. passes electrons from one part ofthe substrate to another. ...
Chapter 11
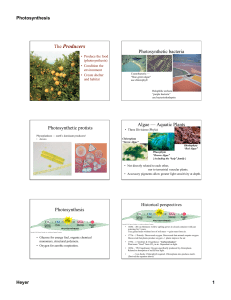
... • Energy carried by photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength • Pigment – light absorbing molecule ...
... • Energy carried by photon is inversely proportional to the wavelength • Pigment – light absorbing molecule ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... Completion of the TCA Cycle – Oxidation of Succinate to Oxaloacetate • This process involves a series of three reactions • These reactions include: – Oxidation of a single bond to a double bond (FAD/FADH2) – Hydration reaction – Oxidation of the resulting alcohol to a ketone (NAD+/NADH) • These rea ...
... Completion of the TCA Cycle – Oxidation of Succinate to Oxaloacetate • This process involves a series of three reactions • These reactions include: – Oxidation of a single bond to a double bond (FAD/FADH2) – Hydration reaction – Oxidation of the resulting alcohol to a ketone (NAD+/NADH) • These rea ...
Fall 2011 Prelim 1 BioG 1440 Introduction to Comparative
... Cellular respiration consists of three groups of reactions: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These three groups of reactions are not independent of each other but are coupled together by several different compounds. As a consequence of this coupling, 8) under anaerob ...
... Cellular respiration consists of three groups of reactions: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These three groups of reactions are not independent of each other but are coupled together by several different compounds. As a consequence of this coupling, 8) under anaerob ...
Problem Set 8 Key
... For glycerol-3-phosphate backbone: DHAP glycerol-3-phosphate: 1 NADH used, Sacrificed: 5 NADH, 1 FADH, 3 ATP Total of 19.5 ATP sacrificed Palmitic acid is 16 carbons, so 8 Acetyl CoA are required. Each Acetyl-CoA would normally go into the TCA cycle and generate 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 ATP total ...
... For glycerol-3-phosphate backbone: DHAP glycerol-3-phosphate: 1 NADH used, Sacrificed: 5 NADH, 1 FADH, 3 ATP Total of 19.5 ATP sacrificed Palmitic acid is 16 carbons, so 8 Acetyl CoA are required. Each Acetyl-CoA would normally go into the TCA cycle and generate 3 NADH + 1 FADH2 + 1 ATP total ...
2 H+
... § Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space § H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase § ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation ...
... § Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space § H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase § ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation ...
2 - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space H then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H to drive phosphorylation of ...
... Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space H then moves back across the membrane, passing through the protein complex, ATP synthase ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H to drive phosphorylation of ...
ENERGY-PRODUCING ABILITY OF BACTERIA
... used as a common means of producing ATP through photophosphorylation. Once the amount of NADPH exceeds the level of NADP+, normal ATP production is often slow down or halted. NADP+ must be available as a reducing cofactor for the reaction and its decrease leads to a concomitant reduction of photopho ...
... used as a common means of producing ATP through photophosphorylation. Once the amount of NADPH exceeds the level of NADP+, normal ATP production is often slow down or halted. NADP+ must be available as a reducing cofactor for the reaction and its decrease leads to a concomitant reduction of photopho ...
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of compounds that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. This creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis, or the generation of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The final acceptor of electrons in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen.Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy via redox reactions from sunlight in photosynthesis or, such as in the case of the oxidation of sugars, cellular respiration. In eukaryotes, an important electron transport chain is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane where it serves as the site of oxidative phosphorylation through the use of ATP synthase. It is also found in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast in photosynthetic eukaryotes. In bacteria, the electron transport chain is located in their cell membrane.In chloroplasts, light drives the conversion of water to oxygen and NADP+ to NADPH with transfer of H+ ions across chloroplast membranes. In mitochondria, it is the conversion of oxygen to water, NADH to NAD+ and succinate to fumarate that are required to generate the proton gradient. Electron transport chains are major sites of premature electron leakage to oxygen, generating superoxide and potentially resulting in increased oxidative stress.