Cell membrane
... All other cells are eukaryotic cells. These include protists, fungi, plants, and animals. The diagram below shows link between bacteria, archaea, and the four other kingdoms. ...
... All other cells are eukaryotic cells. These include protists, fungi, plants, and animals. The diagram below shows link between bacteria, archaea, and the four other kingdoms. ...
Topic 1
... Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): for studying the internal structure of cells ...
... Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): for studying the internal structure of cells ...
cell division
... – To grow and develop – To replace cells that die • Why do unicellular organisms do mitosis (eukaryotes) or binary fission (prokaryotes)? – To reproduce asexually (cloning) • Why do multicellular organisms for meiosis? – To reproduce sexually ...
... – To grow and develop – To replace cells that die • Why do unicellular organisms do mitosis (eukaryotes) or binary fission (prokaryotes)? – To reproduce asexually (cloning) • Why do multicellular organisms for meiosis? – To reproduce sexually ...
VCE Biology: Sample teaching plan
... topic area? Which local issues lend themselves to debate and investigation? Which experiments can students complete within the resource limitations of their learning environments? Week ...
... topic area? Which local issues lend themselves to debate and investigation? Which experiments can students complete within the resource limitations of their learning environments? Week ...
Morphology of Prokaryotic Cells
... referred to as a capsule. 2. Thin lay er, unorga nized, loose ly held to the cell wall it is referred to as a slime layer. B. Function: 1. attachment, Allows the bacteria to attach to surfaces in its natu ral en viron me nt. 2. protect against dehydration, ...
... referred to as a capsule. 2. Thin lay er, unorga nized, loose ly held to the cell wall it is referred to as a slime layer. B. Function: 1. attachment, Allows the bacteria to attach to surfaces in its natu ral en viron me nt. 2. protect against dehydration, ...
Project Title: Functional characterisation of centrosome proteins in
... Many stem cells divide asymmetrically thereby generating mother and daughter cells with distinct cell fates. The differential distribution of cell fate determinants and/or cellular components depends on the correct orientation of the mitotic spindle accordingly to the cell polarity axis. The centros ...
... Many stem cells divide asymmetrically thereby generating mother and daughter cells with distinct cell fates. The differential distribution of cell fate determinants and/or cellular components depends on the correct orientation of the mitotic spindle accordingly to the cell polarity axis. The centros ...
Project Cellular Structures and Functions
... Part Five. Intercellular junctions [p73-75]: Neighboring cells often adhere, interact, and communicate through special patches of direct physical contact called intercellular junctions. For the cell type that your chose for your project (either animal or plant), create a short story concerning the i ...
... Part Five. Intercellular junctions [p73-75]: Neighboring cells often adhere, interact, and communicate through special patches of direct physical contact called intercellular junctions. For the cell type that your chose for your project (either animal or plant), create a short story concerning the i ...
common formative assessment planning template
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
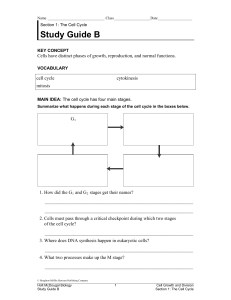
Study Guide B
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ Class___________________Date__________________ ...
1. Cells PPT
... Our cells are surrounded by extracellular fluid frequently called interstitial fluid ...
... Our cells are surrounded by extracellular fluid frequently called interstitial fluid ...
Cell Organelles BioH
... Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually one per cell ...
... Nucleus Control center of the cell Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually one per cell ...
Cell Test Review Key2
... Directions: Define the following terms listed below. Use a separate sheet of paper if you can’t fit them in the space provided. Take this home and study. ...
... Directions: Define the following terms listed below. Use a separate sheet of paper if you can’t fit them in the space provided. Take this home and study. ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... of organisms: 1) Bacteria (prokaryote kingdom) 2)The fungi (yeasts and molds) (eukaryotes) 3) Protozoa (protists) Helminths (worms) (animal kingdom) Viruses (acellular) ...
... of organisms: 1) Bacteria (prokaryote kingdom) 2)The fungi (yeasts and molds) (eukaryotes) 3) Protozoa (protists) Helminths (worms) (animal kingdom) Viruses (acellular) ...
Cells
... Question: How do plant and animal cells differ? Hypothesis: If we study a plant cell and an animal cell, then we will see that they are different from each other because______ _________________________________________________ Materials: light microscope, 2 glass slides, 2 coverslips, dropper, Methyl ...
... Question: How do plant and animal cells differ? Hypothesis: If we study a plant cell and an animal cell, then we will see that they are different from each other because______ _________________________________________________ Materials: light microscope, 2 glass slides, 2 coverslips, dropper, Methyl ...
Chap 7 HW Biology Due Date: Please compl
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
... 1. What are the two major parts of the cell? 2. What is the difference between the smooth ER and rough ER? 3. What is the function of the mitochondria? 4. You examine an unknown cell under a microscope and discover that the cell contains chloroplasts. From what type of organism does the cell li ...
Which cell structure contains the cell`s genetic material and controls
... cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? nucleus Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they ...
... cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? nucleus Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they ...
Diffusion Prelab - Science With Miss F
... Pre Lab Assessment 1. What is kinetic energy and how does it differ from potential energy? 2. What environmental factors affect kinetic energy and diffusion? 3. Why do these factors alter diffusion rates? How do they affect rates? 4. How are gradients important in diffusion and osmosis? 5. What is t ...
... Pre Lab Assessment 1. What is kinetic energy and how does it differ from potential energy? 2. What environmental factors affect kinetic energy and diffusion? 3. Why do these factors alter diffusion rates? How do they affect rates? 4. How are gradients important in diffusion and osmosis? 5. What is t ...
Chapter 4
... Cells must respond to important information and filter out unimportant information. Cell membranes contain specialized proteins, receptor proteins that bind signal molecules and enable the cell to respond to the signal. 25. Describe two ways that the binding of a signal molecule to a receptor protei ...
... Cells must respond to important information and filter out unimportant information. Cell membranes contain specialized proteins, receptor proteins that bind signal molecules and enable the cell to respond to the signal. 25. Describe two ways that the binding of a signal molecule to a receptor protei ...
Document
... 2. All living things are made up of one or more cells 3. All cells come from preexisting cells? ...
... 2. All living things are made up of one or more cells 3. All cells come from preexisting cells? ...
Cellular Components - holyoke
... Overview of Cell Structure Cells vary in size, shape and function Control center of the cell – Nucleus Cell contains fluid filled cytoplasm Cell is surrounded by a membrane ...
... Overview of Cell Structure Cells vary in size, shape and function Control center of the cell – Nucleus Cell contains fluid filled cytoplasm Cell is surrounded by a membrane ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
... Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Anatomy of the Cell Cells are not all the same All cells share general structures Cells are organized into three main regions Nucleus Cytoplasm Plasma membrane ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.