SOMBRERO, BEARSKIN1, and BEARSKIN2 Regulate Root Cap
... SND1 proteins form another small subgroup and together with the SMB/BRN1/BRN2 subgroup make up one branch of the Class IIB family. The other branch contains the seven VND proteins, which are also separated into two distinct subgroups. SMB Controls LRC Maturation In light of its relationship to NAC-d ...
... SND1 proteins form another small subgroup and together with the SMB/BRN1/BRN2 subgroup make up one branch of the Class IIB family. The other branch contains the seven VND proteins, which are also separated into two distinct subgroups. SMB Controls LRC Maturation In light of its relationship to NAC-d ...
Access Presentation
... This result confirms the experimental observations that (1) de-phosphorylation of cdc-2 (k4) and (2) degradation of cyclin (k6), are the two key steps ...
... This result confirms the experimental observations that (1) de-phosphorylation of cdc-2 (k4) and (2) degradation of cyclin (k6), are the two key steps ...
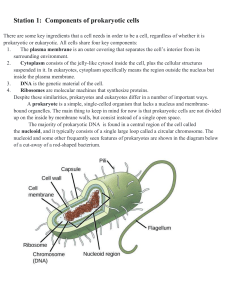
Station 1: Components of prokaryotic cells
... Bacteria exist as a single cell and there are thousands of species. The diet of bacteria is generally determined by their metabolic category. The process of bacteria breaking down food to get energy is called respiration. Phototrophic bacteria get their energy directly from the sun. Some bacteria fe ...
... Bacteria exist as a single cell and there are thousands of species. The diet of bacteria is generally determined by their metabolic category. The process of bacteria breaking down food to get energy is called respiration. Phototrophic bacteria get their energy directly from the sun. Some bacteria fe ...
Links between genome replication and chromatin landscapes
... requires thousands of cell divisions to transform the unicellular zygote into the adult body. This is particularly relevant in the case of plants, in which organogenesis occurs entirely in a post-embryonic manner. Remarkably, the integrity of the genetic material of every cell must be maintained thr ...
... requires thousands of cell divisions to transform the unicellular zygote into the adult body. This is particularly relevant in the case of plants, in which organogenesis occurs entirely in a post-embryonic manner. Remarkably, the integrity of the genetic material of every cell must be maintained thr ...
regulates cortical cell migration out of the
... into isotropic, orthogonal arrays and increases the viscosity and stiffness of the F-actin network18,21–24. Filamin A is essential for radial cell migration, but its expression from the intermediate zone to the cortical plate, both in migratory and post-migratory neurons of the developing neocortex2 ...
... into isotropic, orthogonal arrays and increases the viscosity and stiffness of the F-actin network18,21–24. Filamin A is essential for radial cell migration, but its expression from the intermediate zone to the cortical plate, both in migratory and post-migratory neurons of the developing neocortex2 ...
Calcium-Dependent Prevention of Neuronal Apoptosis by Lithium Ion
... Increase in [Ca2ⴙ]i Mediates the Antiapoptotic Action of Liⴙ. We next studied upstream mechanisms underlying the antiapoptosis action of Li⫹. In light of ideas that neurons can be rescued from apoptosis or programmed cell ...
... Increase in [Ca2ⴙ]i Mediates the Antiapoptotic Action of Liⴙ. We next studied upstream mechanisms underlying the antiapoptosis action of Li⫹. In light of ideas that neurons can be rescued from apoptosis or programmed cell ...
characterisation of amino acid transport in red blood cells of a
... lOmmoll" 1 Mops/Tris, pH7.5). Cl~ determinations of plasma or red cells prewashed four times with an excess of ice-cold CP-free solution (SOOmmolP1 sodium methylsulphate buffered with lOmmolF 1 Mops/Tris, pH7.5) were carried out by coulometric titration using a Corning model 920M chloride meter. ...
... lOmmoll" 1 Mops/Tris, pH7.5). Cl~ determinations of plasma or red cells prewashed four times with an excess of ice-cold CP-free solution (SOOmmolP1 sodium methylsulphate buffered with lOmmolF 1 Mops/Tris, pH7.5) were carried out by coulometric titration using a Corning model 920M chloride meter. ...
Control of convergent yolk syncytial layer nuclear movement in
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
Control of convergent yolk syncytial layer nuclear movement in
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
... Up⬇1 μm/minute is the speed with which the progenitor patch moves. Since the time scale for cortical flow is much longer than that for elastic relaxation, the cortex may be described as an incompressible viscous fluid for the present purpose. In general, the flow profile is a function of the Reynold ...
Cell Processes: Nernst Potential
... lots of ions: there are many different ions inside and outside your cells (usually we talk about K+, Na+, Cl-, and then lump the rest together as anonymous anions, or A-). Each of these ions can (under certain circumstances) affect the diffusion-voltage equilibrium. And they are all operating at the ...
... lots of ions: there are many different ions inside and outside your cells (usually we talk about K+, Na+, Cl-, and then lump the rest together as anonymous anions, or A-). Each of these ions can (under certain circumstances) affect the diffusion-voltage equilibrium. And they are all operating at the ...
Oriented cell motility and division underlie early limb bud
... conferred by Wnt5a, is likely to underlie these oriented cell behaviours. ...
... conferred by Wnt5a, is likely to underlie these oriented cell behaviours. ...
immunodetection of arabinogalactan proteins in different types of
... Fig. 1. Galanthus nivalis ovule 24 h after pollination, labelled with JIM 13 Mab. × 200. Figs. 2, 3. Micropylar part of Galanthus nivalis ovules 24 h after pollination, with strong fluorescence visible inside the micropylar canal. Fig. 2. Labelled with JIM 13 Mab. × 330. Fig. 3. Labelled with JIM 8 ...
... Fig. 1. Galanthus nivalis ovule 24 h after pollination, labelled with JIM 13 Mab. × 200. Figs. 2, 3. Micropylar part of Galanthus nivalis ovules 24 h after pollination, with strong fluorescence visible inside the micropylar canal. Fig. 2. Labelled with JIM 13 Mab. × 330. Fig. 3. Labelled with JIM 8 ...
Role of Topoisomerase II@3in the Resistance of 9-OH
... tion (3). Two distinct forms of topoisomerase II exist in mammals, designated topoisomerase !!a (l70-kDa form) and topoisomerase I!@ (l80-kDa form; Ref. 4). These enzymes are encoded by two separate genes with distinct but related sequences that, in human cells, are located on chromosomes 17 and 3 f ...
... tion (3). Two distinct forms of topoisomerase II exist in mammals, designated topoisomerase !!a (l70-kDa form) and topoisomerase I!@ (l80-kDa form; Ref. 4). These enzymes are encoded by two separate genes with distinct but related sequences that, in human cells, are located on chromosomes 17 and 3 f ...
COUP-TFI and COUP-TFII regulate expression of the NHE through a
... A series of vectors were engineered using various fragments of the 21085/2800-nt element fused to the plasmid pGL-SV40MP-luc. These vectors were: pGL 21058/2857SV40MP-luc, pGL 2858/2800-SV40MP-luc, pGL 21085/2916-SV40MP-luc, pGL 2918/2824-SV40MPluc, pGL 21085/2924-SV40, pGL 2923/2800-SV40 and pGL 28 ...
... A series of vectors were engineered using various fragments of the 21085/2800-nt element fused to the plasmid pGL-SV40MP-luc. These vectors were: pGL 21058/2857SV40MP-luc, pGL 2858/2800-SV40MP-luc, pGL 21085/2916-SV40MP-luc, pGL 2918/2824-SV40MPluc, pGL 21085/2924-SV40, pGL 2923/2800-SV40 and pGL 28 ...
An Ancient Yeast for Young Geneticists: A Primer on the
... S. cerevisiae has been a companion to humans since the invention of bread making and brewing. In contrast, apart from the relatively minor applications mentioned earlier, S. pombe has not historically had many practical applications. This difference has influenced the ways in which these two model or ...
... S. cerevisiae has been a companion to humans since the invention of bread making and brewing. In contrast, apart from the relatively minor applications mentioned earlier, S. pombe has not historically had many practical applications. This difference has influenced the ways in which these two model or ...
PDF + SI - Development - The Company of Biologists
... be functionally similar to that mediated by ZOU. More detailed biophysical analysis as well as detailed cell structure analysis will help to clarify whether molecular pathways are shared between these processes and with other dPCD events in plants, but may be hampered by the relative ...
... be functionally similar to that mediated by ZOU. More detailed biophysical analysis as well as detailed cell structure analysis will help to clarify whether molecular pathways are shared between these processes and with other dPCD events in plants, but may be hampered by the relative ...
Mapping the route from naive pluripotency to lineage specification
... mixed population of lineage progenitors cells along with pluripotent precursors [44]. EpiSCs can also be generated from ESCs by differentiation in the continuous presence of activin and Fgf2 [45]. However, stable EpiSC cultures are obtained only after passaging and the process is accompanied by hete ...
... mixed population of lineage progenitors cells along with pluripotent precursors [44]. EpiSCs can also be generated from ESCs by differentiation in the continuous presence of activin and Fgf2 [45]. However, stable EpiSC cultures are obtained only after passaging and the process is accompanied by hete ...
Calcium-Containing Organelles Display Unique Reactivity to
... Solutions and drugs. The recording medium contained (in mM): 129 NaCl, 4 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 4.2 glucose, and 10 HEPES, along with 0.5 mM tetrodotoxin. pH was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH, and osmolarity to 320 mOsm by addition of sucrose. In Mn21-containing solutions, CaCl2 was replaced by MnCl2. I ...
... Solutions and drugs. The recording medium contained (in mM): 129 NaCl, 4 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 4.2 glucose, and 10 HEPES, along with 0.5 mM tetrodotoxin. pH was adjusted to 7.4 with NaOH, and osmolarity to 320 mOsm by addition of sucrose. In Mn21-containing solutions, CaCl2 was replaced by MnCl2. I ...
c-Jun Reprograms Schwann Cells of Injured Nerves to Generate a
... was excised from almost all Schwann cells (Parkinson et al., 2008), c-Jun expression in neurons, macrophages, and fibroblasts was normal, and the rate of axonal disintegration after cut was similar in WT and mutants (Figures S2 and S3). The close similarity between WT and mutant nerves was confirmed ...
... was excised from almost all Schwann cells (Parkinson et al., 2008), c-Jun expression in neurons, macrophages, and fibroblasts was normal, and the rate of axonal disintegration after cut was similar in WT and mutants (Figures S2 and S3). The close similarity between WT and mutant nerves was confirmed ...
Document
... a definite method of "sectioning" the material has been followed. It is customary to begin filming at the upper left hand corner of a large sheet and to continue from left to right in equal sections with small overlaps. If necessary, sectioning is continued again—beginning below the first row and co ...
... a definite method of "sectioning" the material has been followed. It is customary to begin filming at the upper left hand corner of a large sheet and to continue from left to right in equal sections with small overlaps. If necessary, sectioning is continued again—beginning below the first row and co ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.