Macromolecules I PPT
... Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together. Macromolecules are large molecules composed of smaller molecules, and they can be very complex in structure. ...
... Another level in the hierarchy of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together. Macromolecules are large molecules composed of smaller molecules, and they can be very complex in structure. ...
Chapter 4 The Importance of Carbon
... Requires input of energy to assemble Reaction carried out by enzymes Hydrolysis reaction Molecule of water added as subunits are broken apart Reactions disassemble molecules to subunits, energy released CARBOHYDRATES Sugars Are Simple Carbohydrates Contain C, H, O in 1:2:1 ratio Function in energy s ...
... Requires input of energy to assemble Reaction carried out by enzymes Hydrolysis reaction Molecule of water added as subunits are broken apart Reactions disassemble molecules to subunits, energy released CARBOHYDRATES Sugars Are Simple Carbohydrates Contain C, H, O in 1:2:1 ratio Function in energy s ...
Constructing Models of Carbodydrates
... organisms. This lab will focus on the chemical structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Most organic compounds are large polymers constructed by linking smaller monomers together with the removal of water in a process called dehydration synthesis. Each class of organic compound has is own po ...
... organisms. This lab will focus on the chemical structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Most organic compounds are large polymers constructed by linking smaller monomers together with the removal of water in a process called dehydration synthesis. Each class of organic compound has is own po ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 2. Astronauts and backpackers often bring dehydrated food. What do you think dehydrated food is? __________________________________________________________________ Gizmo Warm-up What do rice, potatoes, and sugar have in common? They are all foods rich in carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are an important ...
... 2. Astronauts and backpackers often bring dehydrated food. What do you think dehydrated food is? __________________________________________________________________ Gizmo Warm-up What do rice, potatoes, and sugar have in common? They are all foods rich in carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are an important ...
lecture 2 - carbohydrates
... – Important acids in animals – D-glucuronic acid and its epimer L-iduronic acid – In liver cells glucuronic acid combines with steroids, certain drugs, and bilirubin to improve water solubility therby helping the removal of waste products from the body – These acids are abundant in the connective ti ...
... – Important acids in animals – D-glucuronic acid and its epimer L-iduronic acid – In liver cells glucuronic acid combines with steroids, certain drugs, and bilirubin to improve water solubility therby helping the removal of waste products from the body – These acids are abundant in the connective ti ...
lecture 2 - carbohydrates
... – Important acids in animals – D-glucuronic acid and its epimer L-iduronic acid – In liver cells glucuronic acid combines with steroids, certain drugs, and bilirubin to improve water solubility therby helping the removal of waste products from the body – These acids are abundant in the connective ti ...
... – Important acids in animals – D-glucuronic acid and its epimer L-iduronic acid – In liver cells glucuronic acid combines with steroids, certain drugs, and bilirubin to improve water solubility therby helping the removal of waste products from the body – These acids are abundant in the connective ti ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 5e (Campbell) Chapter 3: The
... E) the addition of a phosphate group. 7) Many names for sugars end in the suffix A) -acid. B) -ose. C) -hyde. D) -ase. E) -ing. 8) Sucrose is formed A) from two glucose molecules. B) from two monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis. C) when ionic bonds link two monosaccharides. D) when water molec ...
... E) the addition of a phosphate group. 7) Many names for sugars end in the suffix A) -acid. B) -ose. C) -hyde. D) -ase. E) -ing. 8) Sucrose is formed A) from two glucose molecules. B) from two monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis. C) when ionic bonds link two monosaccharides. D) when water molec ...
Chapter 9
... Reproduction: making new cells or organisms Regulations: responding to changes in the surroundings Metabolism: breathing, digesting, eliminating waste Synthesis: directing cell activities to create needed substances ...
... Reproduction: making new cells or organisms Regulations: responding to changes in the surroundings Metabolism: breathing, digesting, eliminating waste Synthesis: directing cell activities to create needed substances ...
Sugar
... Nucleic Acids ● Include DNA and RNA Information storage molecules They provide the directions for building proteins ...
... Nucleic Acids ● Include DNA and RNA Information storage molecules They provide the directions for building proteins ...
nutrition study guide
... 17. Oxygen is the gas that is inhaled when you breathe. 18. Carbon dioxide is the gas that is exhaled when you breathe. 19. What do lungs look like when they’ve been damaged from smoking? Gray with black spots 20. Give 2 examples of Carbohydrates: ...
... 17. Oxygen is the gas that is inhaled when you breathe. 18. Carbon dioxide is the gas that is exhaled when you breathe. 19. What do lungs look like when they’ve been damaged from smoking? Gray with black spots 20. Give 2 examples of Carbohydrates: ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
... in place by hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) between different parts of the polypeptide chain. ...
Low FODMAP Diet and IBD
... include abdominal bloating, excessive gas, chronic diarrhoea or constipation. Such patients, particularly those with unexplained chronic diarrhoea or bloating, should considered reducing their dietary intake of FODMAPs, but total exclusion is rarely necessary. ...
... include abdominal bloating, excessive gas, chronic diarrhoea or constipation. Such patients, particularly those with unexplained chronic diarrhoea or bloating, should considered reducing their dietary intake of FODMAPs, but total exclusion is rarely necessary. ...
this lecture as PDF here
... A. Isomerism In organic chemistry, isomerism is defined as the existence of more than one compound with the same molecular formula. A close observation of the structure of monosaccharides (hexoses) indicate that they possess same molecular formula (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) but with different physical and chem ...
... A. Isomerism In organic chemistry, isomerism is defined as the existence of more than one compound with the same molecular formula. A close observation of the structure of monosaccharides (hexoses) indicate that they possess same molecular formula (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) but with different physical and chem ...
Chemistry of Molecules
... Monomer = 1 unit, glucose, amino acids Dimer = 2 units – maltose have 2 glucose units and a dipeptide has 2 amino acids. Polymer = many units, Starch has hundreds / thousands of glucose units a protein has hundreds of amino acids and a nucleic acid has thousands to millions of units. Carbohydrates M ...
... Monomer = 1 unit, glucose, amino acids Dimer = 2 units – maltose have 2 glucose units and a dipeptide has 2 amino acids. Polymer = many units, Starch has hundreds / thousands of glucose units a protein has hundreds of amino acids and a nucleic acid has thousands to millions of units. Carbohydrates M ...
Organic Chemistry - Holding
... – Make up 15% of your body mass (10,000 different proteins in a single cell!) – Involved in almost every function of your body • Structural support • Cellular transport ...
... – Make up 15% of your body mass (10,000 different proteins in a single cell!) – Involved in almost every function of your body • Structural support • Cellular transport ...
3_carbohydrate - WordPress.com
... carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone derivatives of polyhydroxy alcohol or their condensatio ...
... carbohydrates. Animal tissues contain glycogen (animal starch). They are the major sources of energy and play key role in many biochemical processes including energy generation. DEFINITION Chemically all the carbohydrates are aldehyde or ketone derivatives of polyhydroxy alcohol or their condensatio ...
Macromolecules,Carbs - Ms. Nakamura`s Biology Class Wiki
... Root Word – COGN (To Know) Why is carbon important to the human ...
... Root Word – COGN (To Know) Why is carbon important to the human ...
dehydration synthesis
... Many Sugars a) the form in which living things store excess sugar long-term energy b) 3 forms of polysaccharides 1) Starch - Most important found in: plants & animals 2) Glycogen - excess sugar stored in this molecule found in: plant & animals forms: fat molecules 3) Cellulose - major component of w ...
... Many Sugars a) the form in which living things store excess sugar long-term energy b) 3 forms of polysaccharides 1) Starch - Most important found in: plants & animals 2) Glycogen - excess sugar stored in this molecule found in: plant & animals forms: fat molecules 3) Cellulose - major component of w ...
Carbohydrates
... In this example, 3 condensation reactions have produced 3 water molecules to produce the polysaccharide. A HYDROLYSIS reaction (addition of water) reverses the reaction and splits the polysaccharide releasing 3 monosaccharide molecules. ...
... In this example, 3 condensation reactions have produced 3 water molecules to produce the polysaccharide. A HYDROLYSIS reaction (addition of water) reverses the reaction and splits the polysaccharide releasing 3 monosaccharide molecules. ...
Carbohydrates
... Recognition/binding of CHO moieties of glycoproteins, glycolipids & proteoglycans by animal lectins is a factor in: ...
... Recognition/binding of CHO moieties of glycoproteins, glycolipids & proteoglycans by animal lectins is a factor in: ...
1. 4-methyl-4-octanol oxidizes to form a) 4-methyl-4
... 9. What determines if a molecule is a reducing sugar? a) It has an anomeric –OH available b) It is a monosaccharide c) It is a disaccharide d) It must be a beta linkage 10. What is the name of the enzyme that cleaves the glycosidic bond in lactose? a) lactese b) lactase c) sucrose d) galactase 11. S ...
... 9. What determines if a molecule is a reducing sugar? a) It has an anomeric –OH available b) It is a monosaccharide c) It is a disaccharide d) It must be a beta linkage 10. What is the name of the enzyme that cleaves the glycosidic bond in lactose? a) lactese b) lactase c) sucrose d) galactase 11. S ...
biochem notes CP Edited
... oxygen in a ratio of 1C:2H:1O, Serve as a source of energy or used for structural materials Monosaccharides- a monomer of a carbohydrate (glucose, fructose and galactose) Disaccharides- two monosaccharides or a double sugar (glucose + fructose = sucrose) Polysaccharides- three or more monosacc ...
... oxygen in a ratio of 1C:2H:1O, Serve as a source of energy or used for structural materials Monosaccharides- a monomer of a carbohydrate (glucose, fructose and galactose) Disaccharides- two monosaccharides or a double sugar (glucose + fructose = sucrose) Polysaccharides- three or more monosacc ...
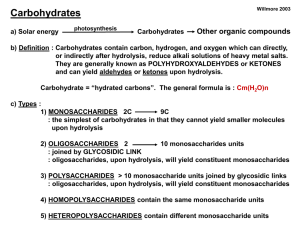
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. In general, the monosaccharides and disaccharides, which are smaller (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning ""sugar."" While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose (see illustration).Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).