II. Chemistry of Sugars
... organic compound on this planet; about 50% of organic mass is cellulose. Cotton is pure cellulose. The β glycosidic link forces each glucose to be flipped 180o with respect to the preceding but the overall chain is essentially linear. Chains then assemble first into 2D sheets which can stack into th ...
... organic compound on this planet; about 50% of organic mass is cellulose. Cotton is pure cellulose. The β glycosidic link forces each glucose to be flipped 180o with respect to the preceding but the overall chain is essentially linear. Chains then assemble first into 2D sheets which can stack into th ...
Glossary Digestion
... maltase an enzyme that hydrolyzes maltose maltose a disaccharide composed of two glucose units; sometimes known as malt sugar. monosaccharides carbohydrates of the general formula CnH2nOn that typically form a single ring. phytic acid a nonnutrient component of plant seeds which occurs in the husks ...
... maltase an enzyme that hydrolyzes maltose maltose a disaccharide composed of two glucose units; sometimes known as malt sugar. monosaccharides carbohydrates of the general formula CnH2nOn that typically form a single ring. phytic acid a nonnutrient component of plant seeds which occurs in the husks ...
File
... Atom -the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element ...
... Atom -the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element ...
Sugars and Sweeteners - Southern University Ag Center
... cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. All educational programs conducted by the Southern University Agricultural Research and Extension Center are provided to all persons regardless of race, national origin, or disability. © 2008 SU Ag Center. ...
... cooperation with the U.S. Department of Agriculture. All educational programs conducted by the Southern University Agricultural Research and Extension Center are provided to all persons regardless of race, national origin, or disability. © 2008 SU Ag Center. ...
Study Guide
... 1 carbon with hydrogens on each of the 4 valance sites is called methane: METH=1 and alkANE = single bonds. 2 carbons with a double bond is ethane: ETH=2, alkENE = double bonds. See the table in the TeacherNotes. Each compound has different characteristics. Propane (3 carbons, single bonds) is grill ...
... 1 carbon with hydrogens on each of the 4 valance sites is called methane: METH=1 and alkANE = single bonds. 2 carbons with a double bond is ethane: ETH=2, alkENE = double bonds. See the table in the TeacherNotes. Each compound has different characteristics. Propane (3 carbons, single bonds) is grill ...
21.5 Some Important Monosaccharides
... possible stereoisomers, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms. D and L enantiomers differ in the orientation of the —OH group on the chiral carbon atom farthest from the carbonyl. In Fischer projections, D sugars have the —OH on the right and L sugars have the —OH on the left. D-Glucose (and ...
... possible stereoisomers, where n is the number of chiral carbon atoms. D and L enantiomers differ in the orientation of the —OH group on the chiral carbon atom farthest from the carbonyl. In Fischer projections, D sugars have the —OH on the right and L sugars have the —OH on the left. D-Glucose (and ...
Chapter 14. CARBOHYDRATES
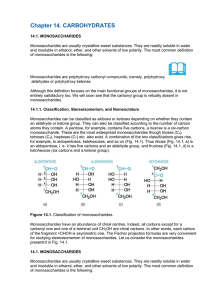
... Only a few monosaccharides from Fig. 14.2 are virtually important, and their structures should be remembered. These are aldohexoses d-glucose, d-galactose, and d-mannose due to their wide occurrence in nature. The structures of the latter two sugars are easy to memorize once the structure of glucose ...
... Only a few monosaccharides from Fig. 14.2 are virtually important, and their structures should be remembered. These are aldohexoses d-glucose, d-galactose, and d-mannose due to their wide occurrence in nature. The structures of the latter two sugars are easy to memorize once the structure of glucose ...
Chapter 3 – Molecules of Cells
... The name carbohydrate refers to a class of molecules that range from small sugar molecules to long polymers of sugar monomers So carbohydrates are formed from “sugar” monomers A. Monosaccharides (simple sugars) Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas that are some multiple of CH2O e.g., gl ...
... The name carbohydrate refers to a class of molecules that range from small sugar molecules to long polymers of sugar monomers So carbohydrates are formed from “sugar” monomers A. Monosaccharides (simple sugars) Monosaccharides generally have molecular formulas that are some multiple of CH2O e.g., gl ...
PowerPoint 簡報 - Solon City Schools
... Aldehyde groups, where the C=O group is at the end of an organic molecule. A hydrogen atom is also located on the same carbon atom. Keto groups, where the C=O group is located within an organic molecule. All sugars have either a keto or an aldehyde group. An aldehyde and a ketone may be structural i ...
... Aldehyde groups, where the C=O group is at the end of an organic molecule. A hydrogen atom is also located on the same carbon atom. Keto groups, where the C=O group is located within an organic molecule. All sugars have either a keto or an aldehyde group. An aldehyde and a ketone may be structural i ...
organic chemistry
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
Carbohydrate Structure
... • Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers. • The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides or simple sugars. • Disaccharides, double sugars, consist of two monosaccharides joined by a condensation reaction. • Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides. ...
... • Carbohydrates include both sugars and polymers. • The simplest carbohydrates are monosaccharides or simple sugars. • Disaccharides, double sugars, consist of two monosaccharides joined by a condensation reaction. • Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides. ...
organic chemistry-1
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
Chapter 14 - "Organic Chemistry"
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
... • When plants photosynthesize the use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen. – Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate used by animals. – Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is used in plant cell walls to maintain their structure. ...
Slide 1
... POLYHYDRIC ALCOHOLS (1) Monosaccharides are those carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates: They may be classified as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, or heptoses, depending upon the number of carbon atoms; and as aldoses or ketoses depending upon whether they have an ...
... POLYHYDRIC ALCOHOLS (1) Monosaccharides are those carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler carbohydrates: They may be classified as trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, or heptoses, depending upon the number of carbon atoms; and as aldoses or ketoses depending upon whether they have an ...
the chemistry of life - bio-ib-basu
... They are relatively insoluble in water Its property depends on the number and types of monomer it contains Polysaccharides can combine with lipid forming glycolipid or with protein called glycoprotein Types and Function: Starch ...
... They are relatively insoluble in water Its property depends on the number and types of monomer it contains Polysaccharides can combine with lipid forming glycolipid or with protein called glycoprotein Types and Function: Starch ...
The Chemicals of Life Properties of Organic Compounds Organic
... It has a high electronegativity, so it pulls electrons away from the carbon atom It is important in carbohydrates, pyruvic acid (used in respiration), glycerol (a component of fats), and alcohols Alcohols are compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (OH-) attached to the carbon, and can easily dissol ...
... It has a high electronegativity, so it pulls electrons away from the carbon atom It is important in carbohydrates, pyruvic acid (used in respiration), glycerol (a component of fats), and alcohols Alcohols are compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (OH-) attached to the carbon, and can easily dissol ...
Important Basics Food Charts with Carbs - Dia
... which give sweetness to ripe fruits. In contrast to sugars, starch is often accompanied by significant amounts of other nutrients including dietary fibre. Starch has the same energy value as sugars. Health authorities are in agreement that we should increase our consumption of foods containing starc ...
... which give sweetness to ripe fruits. In contrast to sugars, starch is often accompanied by significant amounts of other nutrients including dietary fibre. Starch has the same energy value as sugars. Health authorities are in agreement that we should increase our consumption of foods containing starc ...
Unit 2A Organic Chem. Intro
... Think about it this way… The hydrocarbon is like your last name- most everyone ...
... Think about it this way… The hydrocarbon is like your last name- most everyone ...
• Life`s diversity results from the variety of molecules in cells • A
... • Many monosaccharides form rings, as shown here for glucose ...
... • Many monosaccharides form rings, as shown here for glucose ...
How to make a Biomolecules booklet
... Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together Single sugar carbohydrates are called monosaccharides (mono- “one”) Two single sugars bonded together are called a disaccharide. (di- “two”) ...
... Carbohydrates are compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together Single sugar carbohydrates are called monosaccharides (mono- “one”) Two single sugars bonded together are called a disaccharide. (di- “two”) ...
Organic compounds
... dehydration synthesis) Dehydration synthesis- chemical reaction in which one monomer donates a hydroxyl (OH-) and the other monomer donates a hydrogen (H) forming water (H2O) ...
... dehydration synthesis) Dehydration synthesis- chemical reaction in which one monomer donates a hydroxyl (OH-) and the other monomer donates a hydrogen (H) forming water (H2O) ...
SBI 4U biochem 1
... • contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • It is the sequence of the amino acid that forms the primary structure of proteins. • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the midd ...
... • contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • It is the sequence of the amino acid that forms the primary structure of proteins. • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the midd ...
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. In general, the monosaccharides and disaccharides, which are smaller (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning ""sugar."" While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose (see illustration).Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).