Kuever et al_final.p
... from a freshwater ditch and is of interest because it can grow with a large variety of organic substrates, in particular several aromatic compounds, short-chain and mediumchain fatty acids, which are degraded completely to carbon dioxide coupled to the reduction of sulfate. It can grow autotrophical ...
... from a freshwater ditch and is of interest because it can grow with a large variety of organic substrates, in particular several aromatic compounds, short-chain and mediumchain fatty acids, which are degraded completely to carbon dioxide coupled to the reduction of sulfate. It can grow autotrophical ...
Eukaryote-to-eukaryote gene transfer events revealed by the
... several of these genes (e.g., HXT16, PAU21, and SOR1) are known to vary in copy number between strains (7, 12, 14). A large 17-kb telomeric region on chromosome VI encompassing YFL052W to YFL058W was absent in EC1118. Nontelomeric genes (21 genes) were also found absent from EC1118. They consist mai ...
... several of these genes (e.g., HXT16, PAU21, and SOR1) are known to vary in copy number between strains (7, 12, 14). A large 17-kb telomeric region on chromosome VI encompassing YFL052W to YFL058W was absent in EC1118. Nontelomeric genes (21 genes) were also found absent from EC1118. They consist mai ...
The role of variable DNA tandem repeats in bacterial adaptation
... with their role in phase variation (Power et al., 2009). An interesting situation exists in the mycoplasmas, where long trinucleotide repeats are overrepresented in Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, but occur mainly in intergenic regions in the former two ...
... with their role in phase variation (Power et al., 2009). An interesting situation exists in the mycoplasmas, where long trinucleotide repeats are overrepresented in Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, but occur mainly in intergenic regions in the former two ...
Homology - a persona..
... If there is more than one ortholog, which one is ‘correct’? There is a tendency to wish that there could be only one ortholog in an organism. This is frequently not the case. Figure 1 shows a gene tree. The A1 gene has three orthologs in species C. The nature of the subtype relationship depends sole ...
... If there is more than one ortholog, which one is ‘correct’? There is a tendency to wish that there could be only one ortholog in an organism. This is frequently not the case. Figure 1 shows a gene tree. The A1 gene has three orthologs in species C. The nature of the subtype relationship depends sole ...
ashgPoster2011ver3.pdf
... catalog. This catalog contains SNPs that are associated genetically with phenotypes; they are tag SNPS, but not necessarily the functional SNP. However, a subset of them could actually be functional, and we will search for these to illustrate the power of Galaxy tools for finding candidate functiona ...
... catalog. This catalog contains SNPs that are associated genetically with phenotypes; they are tag SNPS, but not necessarily the functional SNP. However, a subset of them could actually be functional, and we will search for these to illustrate the power of Galaxy tools for finding candidate functiona ...
The UCSC Known Genes
... 74 290 entries. Each Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL protein may cross-reference multiple mRNAs as its supporting evidence. We tried to pick the best mRNA among all those referenced as the representative mRNA and designate it as a Known Gene. The protein and mRNA sequences in each protein–mRNA pair are aligned us ...
... 74 290 entries. Each Swiss-Prot/TrEMBL protein may cross-reference multiple mRNAs as its supporting evidence. We tried to pick the best mRNA among all those referenced as the representative mRNA and designate it as a Known Gene. The protein and mRNA sequences in each protein–mRNA pair are aligned us ...
Inheritance of Red Green - Department Of Biological Sciences
... variants, available evidence points to allelism of those traits that affect a given cone type. However, a true complementation test (requiring expression of both alleles in the same cell) is not possible because each cell in a female expresses only one of her two X chromosomes (6). The evidence for ...
... variants, available evidence points to allelism of those traits that affect a given cone type. However, a true complementation test (requiring expression of both alleles in the same cell) is not possible because each cell in a female expresses only one of her two X chromosomes (6). The evidence for ...
Comparative analysis of peanut NBS‐LRR gene clusters suggests
... was also found to have three RGAs (Mt7g088460.1, Mt7g088470.1, Mt7g099490.1) that shared high homology to the peanut RGAs. These two regions (BAC AC169666 and AC149204) are separated by c. 250 kb on Medicago chromosome 7. This finding indicates that disease resistance genes were present in this regi ...
... was also found to have three RGAs (Mt7g088460.1, Mt7g088470.1, Mt7g099490.1) that shared high homology to the peanut RGAs. These two regions (BAC AC169666 and AC149204) are separated by c. 250 kb on Medicago chromosome 7. This finding indicates that disease resistance genes were present in this regi ...
key
... (c) (2 pts) What does this predict about the fertility of the animal in part (b)? Will it be higher, lower, or the same as in part (a)? The (b) animal will have reduced fertility. Whenever a crossover occurs anywhere between loci D and F, two of the resulting gametes will be inviable due to chromoso ...
... (c) (2 pts) What does this predict about the fertility of the animal in part (b)? Will it be higher, lower, or the same as in part (a)? The (b) animal will have reduced fertility. Whenever a crossover occurs anywhere between loci D and F, two of the resulting gametes will be inviable due to chromoso ...
Replicational and transcriptional selection on codon usage in
... level of replication. An organism that can replicate more quickly could have a selective advantage over one whose replication is retarded. It was pointed out by Fraser et al. (7) that approximately two-thirds of the genes on the B. burgdorferi genome were transcribed away from the origin of replicat ...
... level of replication. An organism that can replicate more quickly could have a selective advantage over one whose replication is retarded. It was pointed out by Fraser et al. (7) that approximately two-thirds of the genes on the B. burgdorferi genome were transcribed away from the origin of replicat ...
bioinformatics
... distantly related organisms, the most commonly used features for comparative maps are protein coding genes, both because of their ubiquity and because of the ability of local alignment search tools to detect the relationship among highly diverged protein sequences. When multiple pairs of homologous ...
... distantly related organisms, the most commonly used features for comparative maps are protein coding genes, both because of their ubiquity and because of the ability of local alignment search tools to detect the relationship among highly diverged protein sequences. When multiple pairs of homologous ...
Conspiracy of silence among repeated transgenes
... would pair more easily than looped structures. That this variegation was indeed caused by heterochromatin formation was confirmed by showing suppression of silencing by suppressors of PEV, and more recent work has demonstrated additional heterochromatic properties of mini-white repeat arrays.(10) He ...
... would pair more easily than looped structures. That this variegation was indeed caused by heterochromatin formation was confirmed by showing suppression of silencing by suppressors of PEV, and more recent work has demonstrated additional heterochromatic properties of mini-white repeat arrays.(10) He ...
Operon Control of Gene Expression - Glebe
... are switched on and off together, as a unit. It is not the proteins that are produced that define an operon, an operon is a mechanism of control. An operon always contains several structural genes, an operator, and a promoter. ...
... are switched on and off together, as a unit. It is not the proteins that are produced that define an operon, an operon is a mechanism of control. An operon always contains several structural genes, an operator, and a promoter. ...
PDF - Blood Journal
... indicated the pufferfish (Fugu rubripes and the closely related Spheroides nephelus) as an ideal species for just this task because it has a relatively compact genome of 400 Mb, approximately 7.5 times smaller than the human genome.1,2 Nevertheless, the Fugu genome contains a complement of genes sim ...
... indicated the pufferfish (Fugu rubripes and the closely related Spheroides nephelus) as an ideal species for just this task because it has a relatively compact genome of 400 Mb, approximately 7.5 times smaller than the human genome.1,2 Nevertheless, the Fugu genome contains a complement of genes sim ...
LightCycler® 480 System - Gene Scanning
... 2. Temperature shifting: the temperature axis of the normalized melting curves is shifted to the point where the entire double-stranded DNA is completely denatured. Samples with heterozygous SNPs can then be easily be distinguished from the wild type by the different shapes of their melting curves. ...
... 2. Temperature shifting: the temperature axis of the normalized melting curves is shifted to the point where the entire double-stranded DNA is completely denatured. Samples with heterozygous SNPs can then be easily be distinguished from the wild type by the different shapes of their melting curves. ...
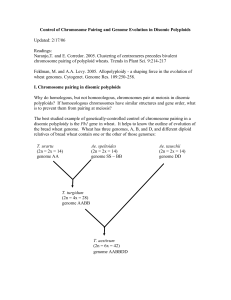
Control of Chromosome Pairing and Genome Evolution in Disomic
... Another control population is made from the cross of DSCnn1A to Chinese Spring (CS). DSCnn1A is identical to Chinese Spring except its chromosome 1A pair is from the cultivar Cheyenne. This allows measurement of recombination between homologous chromosomes 1A in the presence of Ph1. To study the eff ...
... Another control population is made from the cross of DSCnn1A to Chinese Spring (CS). DSCnn1A is identical to Chinese Spring except its chromosome 1A pair is from the cultivar Cheyenne. This allows measurement of recombination between homologous chromosomes 1A in the presence of Ph1. To study the eff ...
Supplemental File S9. Homologous Chromosomes
... Question 1-3: Why do you think there are so many more transcripts that align on the chromosome compared to the number of genes on the chromosome? Answer 1-3: Though the process of alternative splicing, many different transcripts can be produced from a single genomic locus. Thus, the number of transc ...
... Question 1-3: Why do you think there are so many more transcripts that align on the chromosome compared to the number of genes on the chromosome? Answer 1-3: Though the process of alternative splicing, many different transcripts can be produced from a single genomic locus. Thus, the number of transc ...
II. Purpose of Meiosis #1
... This outline is the same as is found in your Lecture Guide. In order to obtain an overview of the material in the Lecture Guide and to be able to see the ‘big’ picture while you study, fill in the missing components of the following outline from the Lecture Guide. ...
... This outline is the same as is found in your Lecture Guide. In order to obtain an overview of the material in the Lecture Guide and to be able to see the ‘big’ picture while you study, fill in the missing components of the following outline from the Lecture Guide. ...
Gene Duplication, Gene Conversion and the Evolution of
... both gene conversion and crossing over on the Y, recombination can be viewed as a factor that either constrains (via gene conversion) or promotes (via crossing over) Y chromosome degeneration. These observations concerning Y chromosome gene content and recombination raise interesting questions that ...
... both gene conversion and crossing over on the Y, recombination can be viewed as a factor that either constrains (via gene conversion) or promotes (via crossing over) Y chromosome degeneration. These observations concerning Y chromosome gene content and recombination raise interesting questions that ...
exercises - Evolutionary Genomics Group
... genome atlas is a visual representation of genome properties, genes/proteins and patterns in DNA associated with DNA structures, helix, repeats and so on. A genome atlas can be made from a GenBank file and uses the gene/protein annotations published with the genome DNA sequence. It is important to h ...
... genome atlas is a visual representation of genome properties, genes/proteins and patterns in DNA associated with DNA structures, helix, repeats and so on. A genome atlas can be made from a GenBank file and uses the gene/protein annotations published with the genome DNA sequence. It is important to h ...
Construction of consecutive deletions of the Escherichia
... found to contain essential gene(s), whereas 2 regions had no essential genes and were deleted without complementing plasmids. The other two regions (OCL30 and OCL34) did not contain any essential genes, but these regions were essential and therefore were not deleted without the complementing plasmid ...
... found to contain essential gene(s), whereas 2 regions had no essential genes and were deleted without complementing plasmids. The other two regions (OCL30 and OCL34) did not contain any essential genes, but these regions were essential and therefore were not deleted without the complementing plasmid ...
Copy-number variation

Copy-number variations (CNVs)—a form of structural variation—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal or, for certain genes, a normal variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of ""C"") or A-B-D (a deletion of ""C"").This variation accounts for roughly 13% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.