CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST
... CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST In order to do well on the test the following is a list of what you will need to know: I. II. ...
... CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST In order to do well on the test the following is a list of what you will need to know: I. II. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
unit 4 overview
... reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. b. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (includi ...
... reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. b. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (includi ...
Cell parts practice
... ______ Phospholipid bilayer that controls what enters and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
... ______ Phospholipid bilayer that controls what enters and leaves the cell ______ Found outside of the cell membrane in plants & bacteria; provides support & protection ...
Cell Structure
... 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
LTM-1000 Powerpoint Presentation
... Injection into the female gametophyte of plant *Whereas the damage and sample escape appear by the conventional method, LTM-1000 ensures no damage and continuous injections without sample escape by using a fine tip capillary. ...
... Injection into the female gametophyte of plant *Whereas the damage and sample escape appear by the conventional method, LTM-1000 ensures no damage and continuous injections without sample escape by using a fine tip capillary. ...
Definitions of Cell Structures and Their Functions Instructions for
... -Cell wall: Non-living structure surrounding plant cell; provides shape and support -Cell membrane: Enclosed the cell, controlling the inward and outward flow of materials -Chloroplasts: Contain chlorophyll, used by plants to make food -Cytoplasm: Jelly-like material where chemical processes take pl ...
... -Cell wall: Non-living structure surrounding plant cell; provides shape and support -Cell membrane: Enclosed the cell, controlling the inward and outward flow of materials -Chloroplasts: Contain chlorophyll, used by plants to make food -Cytoplasm: Jelly-like material where chemical processes take pl ...
Ch 3 Notes Outline
... Micrographs are: The transmission electron microscope: The scanning electron microscope: 3.2 How Cells are Organized Biologists classify cells into two broad categories: Both have: Internal Structure of Eukaryotic Cells: Evolutionary History of the Animal Cell The first cells to arise were: ________ ...
... Micrographs are: The transmission electron microscope: The scanning electron microscope: 3.2 How Cells are Organized Biologists classify cells into two broad categories: Both have: Internal Structure of Eukaryotic Cells: Evolutionary History of the Animal Cell The first cells to arise were: ________ ...
CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONS
... hormones), releases calcium RER: produces phospholipids and proteins Contain digestive enzymes that break ...
... hormones), releases calcium RER: produces phospholipids and proteins Contain digestive enzymes that break ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... Surrounded by a __________________ and contain __________________-bound organelles that perform _______________ functions The organelles are _______________ in the cytoplasm by the _________________ – a network of protein fibers Role: ______________ support and to help move _________________ – micro ...
... Surrounded by a __________________ and contain __________________-bound organelles that perform _______________ functions The organelles are _______________ in the cytoplasm by the _________________ – a network of protein fibers Role: ______________ support and to help move _________________ – micro ...
12/10/09
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
... To understand the functions carried on by the different parts of the cell, you must first understand why these parts are even needed. The easiest analogy is to compare a cell to a factory. ...
Cell Notes
... 2. Connects the cell to its surroundings by controlling what enters and leaves the cells ...
... 2. Connects the cell to its surroundings by controlling what enters and leaves the cells ...
5.2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major
... • The cell is the smallest unit of living material having major structures within it allowing it to live. • Some kinds of organisms are just one cell. This single cell is the organism’s entire body. • Many organisms are made of more than one cell. ...
... • The cell is the smallest unit of living material having major structures within it allowing it to live. • Some kinds of organisms are just one cell. This single cell is the organism’s entire body. • Many organisms are made of more than one cell. ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... Mitochondria have a large surface area. A folded inner membrane of the mitochondria is where production of ATP occurs. ...
... Mitochondria have a large surface area. A folded inner membrane of the mitochondria is where production of ATP occurs. ...
Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
... – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
... – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ______________. 5. What do mitochondria produce? What do they use to produce it? 6. What does every cell hold in its nucleus? 7 ...
... them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ______________. 5. What do mitochondria produce? What do they use to produce it? 6. What does every cell hold in its nucleus? 7 ...
1.2 Notes
... Protects cell by controlling what goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
... Protects cell by controlling what goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material ...
Cell City Analogy
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
The Cell Theory
... Margulis proposed endosymbiont hypothesis: that organelles derived from ancient colonization of large bacteria (became the eucaryotic cell) by smaller bacteria (became the mitochondria, chloroplast, etc.) Symbiosis = "living together". *Mitochondria & Chloroplasts have their own DNA ...
... Margulis proposed endosymbiont hypothesis: that organelles derived from ancient colonization of large bacteria (became the eucaryotic cell) by smaller bacteria (became the mitochondria, chloroplast, etc.) Symbiosis = "living together". *Mitochondria & Chloroplasts have their own DNA ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
designing a cell city - Milton
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. 2. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible envelope that surrounds the cell. It allows the cell to change shape and controls what goes into and out ...
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. 2. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible envelope that surrounds the cell. It allows the cell to change shape and controls what goes into and out ...
Avery Owen I have shrunken to microscopic size, and am now
... I am now seeing the Ribosomes everywhere. The Ribosomes are small, round structures that make proteins for things inside the cell. They are protein factories, like meat that you eat, which gives you protein. ...
... I am now seeing the Ribosomes everywhere. The Ribosomes are small, round structures that make proteins for things inside the cell. They are protein factories, like meat that you eat, which gives you protein. ...
The cytoskeleton The cell surface and junctions
... (b) Motor molecules can also attach to receptors on organelles such as vesicles and enable the organelles to "walk" along microtubules of the cytoskeleton. For example, vesicles containing neurotransmitters migrate to the tips of axons, the long extensions of nerve cells that release transmitter mol ...
... (b) Motor molecules can also attach to receptors on organelles such as vesicles and enable the organelles to "walk" along microtubules of the cytoskeleton. For example, vesicles containing neurotransmitters migrate to the tips of axons, the long extensions of nerve cells that release transmitter mol ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... carbohydrates, & proteins into particles usable by rest of cell. b.) Also function to break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. This helps prevent “junk” from cluttering up cell. ...
... carbohydrates, & proteins into particles usable by rest of cell. b.) Also function to break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. This helps prevent “junk” from cluttering up cell. ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... This is a typical prokaryotic bacterial cell and shows the following features all of which are mentioned in the monograph P2 ...
... This is a typical prokaryotic bacterial cell and shows the following features all of which are mentioned in the monograph P2 ...
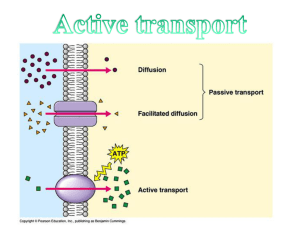
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑