Trends in Biotechnology
... The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
... The cell does not have many big spaces in it. The cell is really very crowded. ...
Inside Cells
... worn out parts so they can be recycled into new stuff. They go around “eating” stuff like pac man. (Why do you think the name LYSOL was chosen?) ...
... worn out parts so they can be recycled into new stuff. They go around “eating” stuff like pac man. (Why do you think the name LYSOL was chosen?) ...
The Cell
... Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. What are eukaryotes? Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, but they all have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. ...
... Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. What are eukaryotes? Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular, but they all have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. ...
Cell Size and Shape
... Each cell membrane is a boundary (lipid bilayer) that controls the flow of substances across it Fluid mosaic model • Membrane is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and other components • Phospholipids drift within the bilayer ...
... Each cell membrane is a boundary (lipid bilayer) that controls the flow of substances across it Fluid mosaic model • Membrane is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and other components • Phospholipids drift within the bilayer ...
Cell Organelles
... found on the surface of many bacteria. • Cilia like structures that help bacteria attach to other cells • They help disease causing bacteria attach to their hosts. They are like teeth. ...
... found on the surface of many bacteria. • Cilia like structures that help bacteria attach to other cells • They help disease causing bacteria attach to their hosts. They are like teeth. ...
Cell Organelle: Analogy To A Football Team
... How are Organelle and analogous parts similar? Example today: The New England Patriots! ...
... How are Organelle and analogous parts similar? Example today: The New England Patriots! ...
Plants and Animal Cells Under the Light Microscope
... nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane cell wall ...
... nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane cell wall ...
Document
... This organelle is only found in the plant cell – and provides support for the cell. ...
... This organelle is only found in the plant cell – and provides support for the cell. ...
Section 2 cont.
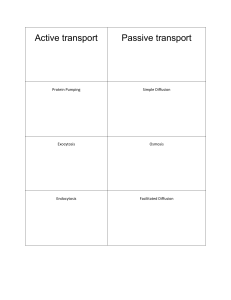
... A type of passive transport that is used for 1) molecules too large to pass through the cell membrane 2) molecules that do not dissolve in lipids ...
... A type of passive transport that is used for 1) molecules too large to pass through the cell membrane 2) molecules that do not dissolve in lipids ...
Cell Organelles - Fulton County Schools
... Garbage disposal of the cell Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes ...
... Garbage disposal of the cell Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes ...
1. Distinguish between magnification and resolving
... Nucleus – membrane-bound cellular organelle in eukaryotes • Contains most of the genes that control the entire cell mRNA transcribed in nucleus from DNA passes through nuclear pores to cytoplasm attaches to ribosomes where the genetic message is translated into primary protein structure ...
... Nucleus – membrane-bound cellular organelle in eukaryotes • Contains most of the genes that control the entire cell mRNA transcribed in nucleus from DNA passes through nuclear pores to cytoplasm attaches to ribosomes where the genetic message is translated into primary protein structure ...
Revision Poster
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
Biology: Cell Test
... What are the threadlike structures that contain genetic information called? Ribosomes Lysosomes Chromosomes None of the above What do the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria have in common? They are all organelles They are all found in the nucleus They are all ribosomes What are ...
... What are the threadlike structures that contain genetic information called? Ribosomes Lysosomes Chromosomes None of the above What do the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and mitochondria have in common? They are all organelles They are all found in the nucleus They are all ribosomes What are ...
eukaryote: cell that has a membrane
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
... Nervous tissue composed of nerve cells called neurons. Nucleus: contains the cell's genetic information that is passed on to future generations. It controls the activities of the cell. May contain nucleoli, which function in protein synthesis. Mitochondrion: supply energy to the cell by the process ...
1-2: What are the properties of matter?
... contains the protons and neutrons; in cells, structure that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities – CYTOPLASM: material inside the cell membrane—not including the nucleus ...
... contains the protons and neutrons; in cells, structure that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities – CYTOPLASM: material inside the cell membrane—not including the nucleus ...
Notes on Unit 7A Cells
... might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cells. ...
... might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cells. ...
3-D Cell Model - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... You must identify all the organelles listed below for whichever cell you choose. The type of cell, your name and class must be identified somehow on the model and on the typed report. DO NOT label the organelles on the model, use ID numbers. The key will identify which organelle is represented by ea ...
... You must identify all the organelles listed below for whichever cell you choose. The type of cell, your name and class must be identified somehow on the model and on the typed report. DO NOT label the organelles on the model, use ID numbers. The key will identify which organelle is represented by ea ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑