DNA_LAdders_files/StoS 100bp DNA Ladder flyer new
... A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 11 fragments suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-1,500 bp. The 500 and 1,500 bp ban ...
... A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 11 fragments suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-1,500 bp. The 500 and 1,500 bp ban ...
Plasmid
... Using the 100 bp DNA ladder in the first line as a guide, determine the size of your GCK4 and HNF1A gene fragments from PCR, and the size of recombinant OX2R from plasmid ...
... Using the 100 bp DNA ladder in the first line as a guide, determine the size of your GCK4 and HNF1A gene fragments from PCR, and the size of recombinant OX2R from plasmid ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH13.QXD
... 1. In _______________________ , only animals with desired characteristics are allowed to produce the next generation. 2. Crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both Organisms is called ________________________ . 3. The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteris ...
... 1. In _______________________ , only animals with desired characteristics are allowed to produce the next generation. 2. Crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both Organisms is called ________________________ . 3. The continued breeding of individuals with similar characteris ...
Protein Electrophoresis
... to accurately separate proteins by molecular weight and not by shape or charge, the secondary structure of the protein is unfolded using the anionic detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and a reducing agent. The SDS molecules form a complex with the protein, negating its inherent charge. The reduc ...
... to accurately separate proteins by molecular weight and not by shape or charge, the secondary structure of the protein is unfolded using the anionic detergent sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and a reducing agent. The SDS molecules form a complex with the protein, negating its inherent charge. The reduc ...
Biotechnological Tools and Techniques
... • a method of separating molecules based on size • DNA migrates through the gel towards a positive electrode • smaller fragments move faster through the gel, causing separation by size • DNA fragments can be seen by using a stain such as ethidium bromide ...
... • a method of separating molecules based on size • DNA migrates through the gel towards a positive electrode • smaller fragments move faster through the gel, causing separation by size • DNA fragments can be seen by using a stain such as ethidium bromide ...
Mass Spectrometers - Porto Conte Ricerche
... MALDI (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization) source provides accurate information on the structure and molecular weight of biomolecules such as peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides and carbohydrates, as well as synthetic polymers. Furthermore, through the PMF (Peptide MassFingerprinting) tech ...
... MALDI (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization) source provides accurate information on the structure and molecular weight of biomolecules such as peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides and carbohydrates, as well as synthetic polymers. Furthermore, through the PMF (Peptide MassFingerprinting) tech ...
“In-Gel” Digestion of Proteins in SDS-Page Gel - QB3
... We recommend Gelcode Blue® Coomassie stain (Pierce) for detecting bands. This technique works for any band that can be seen by this stain. 0.1 to 0.2 micrograms of protein is ideal. Use a new scalpel or razor blade to cut out each band. Mince each band into < 1mm2 pieces and transfer to a clean micr ...
... We recommend Gelcode Blue® Coomassie stain (Pierce) for detecting bands. This technique works for any band that can be seen by this stain. 0.1 to 0.2 micrograms of protein is ideal. Use a new scalpel or razor blade to cut out each band. Mince each band into < 1mm2 pieces and transfer to a clean micr ...
Science and Society: Unit 2 Review Packet Directions: Use your
... therefore the amino acid sequence of the protein coded for by this gene. DNA TTAAGCCCTGGGCAATAG mRNA ________________________________________________________ amino acids ________________________________________________________ ...
... therefore the amino acid sequence of the protein coded for by this gene. DNA TTAAGCCCTGGGCAATAG mRNA ________________________________________________________ amino acids ________________________________________________________ ...
Gel electrophoresis
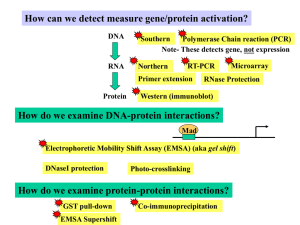
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and/or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving.Proteins are separated by charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for separation of nanoparticles.Gel electrophoresis uses a gel as an anticonvective medium and/or sieving medium during electrophoresis, the movement of a charged particle in an electrical field. Gels suppress the thermal convection caused by application of the electric field, and can also act as a sieving medium, retarding the passage of molecules; gels can also simply serve to maintain the finished separation, so that a post electrophoresis stain can be applied. DNA Gel electrophoresis is usually performed for analytical purposes, often after amplification of DNA via PCR, but may be used as a preparative technique prior to use of other methods such as mass spectrometry, RFLP, PCR, cloning, DNA sequencing, or Southern blotting for further characterization.