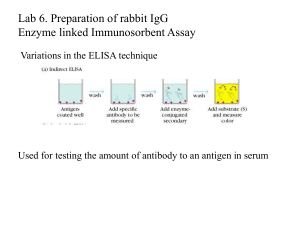
Lecture 6
... All molecules will travel in the same direction Each additional nucleoside confers an additional charge, so charge is directly proportional to size. All molecules will have the same e The solution is to use a gel which consists of pores surrounded by cross-linked fibers This will make e dependent ...
... All molecules will travel in the same direction Each additional nucleoside confers an additional charge, so charge is directly proportional to size. All molecules will have the same e The solution is to use a gel which consists of pores surrounded by cross-linked fibers This will make e dependent ...
Electrophoretic techniques : general principles , supporting
... Not required but they are recommended solid knowledges of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, General and Organic Chemistry, as well as some principles of physics in order to reaching a comprehensive understanding of the proposed topics ...
... Not required but they are recommended solid knowledges of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, General and Organic Chemistry, as well as some principles of physics in order to reaching a comprehensive understanding of the proposed topics ...
1 kb ladder.eng Ed.08. March 14
... 5- Visualise DNA by staining with ethidium bromide or with SYBR® Green I. *The mixture should be scaled up or down, depending on the width of the agarose gel. Use 0.1µg of DNA ladder/mm of lane. The 1kb DNA Ladder was not designed for precise quantification of DNA mass, but can be used for semi-quan ...
... 5- Visualise DNA by staining with ethidium bromide or with SYBR® Green I. *The mixture should be scaled up or down, depending on the width of the agarose gel. Use 0.1µg of DNA ladder/mm of lane. The 1kb DNA Ladder was not designed for precise quantification of DNA mass, but can be used for semi-quan ...
20X Speed Buffer for DNA gel electrophoresis
... 20X Speed Buffer 0.2 M NaOH stir in boric acid until pH is 8.0 Store at room temp. Pouring an agarose gel for DNA gel electrophoresis Make 1 liter of 1x buffer: Measure 50 ml of 20X Speed buffer into 1 liter graduated cylinder Add water from distilled water tap to 1 liter Transfer the buffer t ...
... 20X Speed Buffer 0.2 M NaOH stir in boric acid until pH is 8.0 Store at room temp. Pouring an agarose gel for DNA gel electrophoresis Make 1 liter of 1x buffer: Measure 50 ml of 20X Speed buffer into 1 liter graduated cylinder Add water from distilled water tap to 1 liter Transfer the buffer t ...
Electrophoresis, Blotting and Immunodetection Gel
... Extract DNA from agarose gels in a single 10min spin with this easy-to-use kit. A gel nebuliser converts agarose to a spray from which DNA is separated (via a 0.45µm Ultrafree-MC filter). Prepares gel-purified PCR products for sequencing or cloning without need for further purification. Device volum ...
... Extract DNA from agarose gels in a single 10min spin with this easy-to-use kit. A gel nebuliser converts agarose to a spray from which DNA is separated (via a 0.45µm Ultrafree-MC filter). Prepares gel-purified PCR products for sequencing or cloning without need for further purification. Device volum ...
The Mechanical and Electrical Dynamics of Gel
... proportional to its mass. Mobility in free solution would then be the same for molecules of the same charge to mass ratio. Stokes' law, however, is not sufficient to describe the frictional force within a gel matrix. In addition to the viscosity of the medium, also determining frictional resistance ...
... proportional to its mass. Mobility in free solution would then be the same for molecules of the same charge to mass ratio. Stokes' law, however, is not sufficient to describe the frictional force within a gel matrix. In addition to the viscosity of the medium, also determining frictional resistance ...
Introduction to gel electrophoresis
... • DNA fragments can be separated by size when applied to an electric field. • DNA molecules migrate toward the anode (+). ...
... • DNA fragments can be separated by size when applied to an electric field. • DNA molecules migrate toward the anode (+). ...
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and/or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving.Proteins are separated by charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for separation of nanoparticles.Gel electrophoresis uses a gel as an anticonvective medium and/or sieving medium during electrophoresis, the movement of a charged particle in an electrical field. Gels suppress the thermal convection caused by application of the electric field, and can also act as a sieving medium, retarding the passage of molecules; gels can also simply serve to maintain the finished separation, so that a post electrophoresis stain can be applied. DNA Gel electrophoresis is usually performed for analytical purposes, often after amplification of DNA via PCR, but may be used as a preparative technique prior to use of other methods such as mass spectrometry, RFLP, PCR, cloning, DNA sequencing, or Southern blotting for further characterization.