Renaturation of telomere-binding proteins after the fractionation by
... 0.1mM EDTA). This denaturation/renaturation method usually results in low recoveries of active DNA-binding proteins, and becomes unpractical if large number of gel slices have to be handled. However, there is a simpler method, described by Ossipow et al. (1993), which is based on the observation th ...
... 0.1mM EDTA). This denaturation/renaturation method usually results in low recoveries of active DNA-binding proteins, and becomes unpractical if large number of gel slices have to be handled. However, there is a simpler method, described by Ossipow et al. (1993), which is based on the observation th ...
Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis - Bio-Rad
... High resolution of DNA fragments up to 250 kb can be achieved by using high-voltage gradients at 9 V/cm. This voltage can be combined with a narrow angle of electrophoresis to resolve samples in very short run times, 4 hr or less. ...
... High resolution of DNA fragments up to 250 kb can be achieved by using high-voltage gradients at 9 V/cm. This voltage can be combined with a narrow angle of electrophoresis to resolve samples in very short run times, 4 hr or less. ...
Biochem Option (D)
... 1.00 g of cereal raises the temperature of 400. cm3 of water in an insulated food calorimeter from 23.7̊C to 33.4̊C. Calculate the energy value per gram of the cereal, assuming the heat capacity of a calorimeter is negligible and given the specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g ̊C. ...
... 1.00 g of cereal raises the temperature of 400. cm3 of water in an insulated food calorimeter from 23.7̊C to 33.4̊C. Calculate the energy value per gram of the cereal, assuming the heat capacity of a calorimeter is negligible and given the specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g ̊C. ...
Lab 4 Restriction Enzyme Digestions and Mapping
... Add 1X TBE buffer to submerge the gel. Load 10 l of the molecular weight markers provided and 20 l of the samples. Run the gel at 100 V until the bromophenol blue is about 3/4 through the gel (approx. 1 h). ...
... Add 1X TBE buffer to submerge the gel. Load 10 l of the molecular weight markers provided and 20 l of the samples. Run the gel at 100 V until the bromophenol blue is about 3/4 through the gel (approx. 1 h). ...
Finding genes and detecting mutations
... heterozygous for a mutation, the product will contain fragments that are different at a single position in the sequence • If they are denatured and renatured, they will form either perfectlymatched double stranded DNA, or "heteroduplex" DNA in which one strand is from the normal and the other from t ...
... heterozygous for a mutation, the product will contain fragments that are different at a single position in the sequence • If they are denatured and renatured, they will form either perfectlymatched double stranded DNA, or "heteroduplex" DNA in which one strand is from the normal and the other from t ...
Field Analyzer
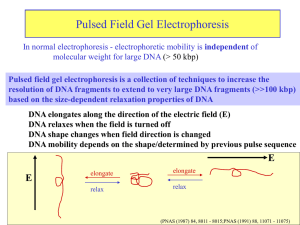
... Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a collection of techniques to increase the resolution of DNA fragments to extend to very large DNA fragments (>>100 kbp) based on the size-dependent relaxation properties of DNA DNA elongates along the direction of the electric field (E) DNA relaxes when the field ...
... Pulsed field gel electrophoresis is a collection of techniques to increase the resolution of DNA fragments to extend to very large DNA fragments (>>100 kbp) based on the size-dependent relaxation properties of DNA DNA elongates along the direction of the electric field (E) DNA relaxes when the field ...
1. Small Scale Expression of Tagged Recombinant Proteins
... 1. Select 3 colonies/ recombinant plasmid and one for empty vector. Grow 5ml cultures of LB with 100µg/mL Carbenicillin or Ampicillin to an A600 of 0.8 (3-5h) with vigorous agitation at 37ºC. Store 2.5mL of this cells as un-induced sample (store in ice). 2. Induce fusion protein expression by adding ...
... 1. Select 3 colonies/ recombinant plasmid and one for empty vector. Grow 5ml cultures of LB with 100µg/mL Carbenicillin or Ampicillin to an A600 of 0.8 (3-5h) with vigorous agitation at 37ºC. Store 2.5mL of this cells as un-induced sample (store in ice). 2. Induce fusion protein expression by adding ...
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge and/or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge.Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving.Proteins are separated by charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for separation of nanoparticles.Gel electrophoresis uses a gel as an anticonvective medium and/or sieving medium during electrophoresis, the movement of a charged particle in an electrical field. Gels suppress the thermal convection caused by application of the electric field, and can also act as a sieving medium, retarding the passage of molecules; gels can also simply serve to maintain the finished separation, so that a post electrophoresis stain can be applied. DNA Gel electrophoresis is usually performed for analytical purposes, often after amplification of DNA via PCR, but may be used as a preparative technique prior to use of other methods such as mass spectrometry, RFLP, PCR, cloning, DNA sequencing, or Southern blotting for further characterization.