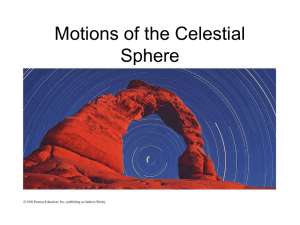
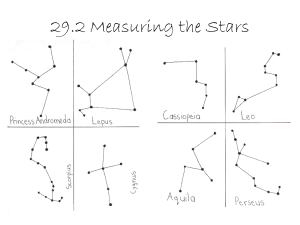
Constellations and Distances to Stars
... • When scientists discovered how far apart stars actually are, they realized that a new unit of measure was needed to record their differences. Measuring star distances in kilometers would be like measuring city distances in millimeters. • Distances in space are often measured in light years. A li ...
... • When scientists discovered how far apart stars actually are, they realized that a new unit of measure was needed to record their differences. Measuring star distances in kilometers would be like measuring city distances in millimeters. • Distances in space are often measured in light years. A li ...
Name Date ______ Period _____ Earth Science Chapter 25 Study
... Stars that radiate short pulses of radio energy are called ____________________. The most dense stars known to exist are called ___________. The average star spends ____________________ percent of its life as a hydrogen-burning, main-sequence star. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of ...
... Stars that radiate short pulses of radio energy are called ____________________. The most dense stars known to exist are called ___________. The average star spends ____________________ percent of its life as a hydrogen-burning, main-sequence star. The sun is positioned about ____________________ of ...
Stars and Galaxies
... The mass of a tremendously big supernova core can collapse to a point, forming a black hole Gravity is so strong not even light can escape Beyond a black hole’s event horizon gravity operates as it would before the mass collapsed Matter emitted by a star over its life time is recycled and can ...
... The mass of a tremendously big supernova core can collapse to a point, forming a black hole Gravity is so strong not even light can escape Beyond a black hole’s event horizon gravity operates as it would before the mass collapsed Matter emitted by a star over its life time is recycled and can ...
Name ______KEY Date Core ______ Study Guide Galaxies and the
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
... When did the Big Bang happen and what has happened since? The big bang theory is theorized to have happened 14 billion years ago when the universe suddenly began to expand from one merged mass of matter or substance. At that time, all matter was dense and hot and the universe developed in less than ...
Document
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
8-3-Star_Classification STUDENT
... Of course not. All you could do is look out the windows and get some view of part of the building. If you looked out enough windows you might get a general idea but you could never know for sure if you were right about all its features. ...
... Of course not. All you could do is look out the windows and get some view of part of the building. If you looked out enough windows you might get a general idea but you could never know for sure if you were right about all its features. ...
coSmoS in youR PockET
... Inspired by The 826 Pocket Activity Book: Illustrated by Irene Cecile: Funded by: ...
... Inspired by The 826 Pocket Activity Book: Illustrated by Irene Cecile: Funded by: ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... A scatter scatter graph that shows the relationship between star’s absolute magnitudes and temperature of the stars. *** Known as a H-R Diagram ...
... A scatter scatter graph that shows the relationship between star’s absolute magnitudes and temperature of the stars. *** Known as a H-R Diagram ...
Relative sizes of astronomical objects
... Viewed in comparison to the Sun, Earth dwindles to a speck. Our sun is classified as an unremarkable yellow dwarf main sequence star – one of over 100 million such stars in our galaxy. However, it alone accounts for 99.9% of the mass of our solar system, including all the planets, satellites (moons) ...
... Viewed in comparison to the Sun, Earth dwindles to a speck. Our sun is classified as an unremarkable yellow dwarf main sequence star – one of over 100 million such stars in our galaxy. However, it alone accounts for 99.9% of the mass of our solar system, including all the planets, satellites (moons) ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... 1. Spica (dimmer and hotter) and Polaris (brighter and cooler) 2. Betelgeuse (brighter and same cool temperature) and Bernard’s star (dimmer and same cool temp.) 3. Sirius B (brighter and hotter) and Procyon B (dimmer and cooler) 4. Sun (dimmer and cooler) and Vega (brighter and hotter) 5. Alpha Cen ...
... 1. Spica (dimmer and hotter) and Polaris (brighter and cooler) 2. Betelgeuse (brighter and same cool temperature) and Bernard’s star (dimmer and same cool temp.) 3. Sirius B (brighter and hotter) and Procyon B (dimmer and cooler) 4. Sun (dimmer and cooler) and Vega (brighter and hotter) 5. Alpha Cen ...
August Skies
... The source of the Perseid meteor shower is actually debris from the comet SwiftTuttle. Every year, the earth passes through the debris stream left by the comet and the earth's atmosphere incinerates the particles into the glowing embers called meteors or “falling stars”. The shower peaks early after ...
... The source of the Perseid meteor shower is actually debris from the comet SwiftTuttle. Every year, the earth passes through the debris stream left by the comet and the earth's atmosphere incinerates the particles into the glowing embers called meteors or “falling stars”. The shower peaks early after ...
Astronomy 2
... Average to small stars collapse again after C fuel is used up → white dwarf (Earth size) Large stars (at least 7 times our sun) when fusion (of carbon) stops, a central iron core is left, intense gravitational energy causes further collapse, creates heavier elements → explosion causes loss of ½ the ...
... Average to small stars collapse again after C fuel is used up → white dwarf (Earth size) Large stars (at least 7 times our sun) when fusion (of carbon) stops, a central iron core is left, intense gravitational energy causes further collapse, creates heavier elements → explosion causes loss of ½ the ...
doc - IAC
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
Planets and Stars Study Guide Test Date: ______ Vocabulary to
... 5. What are Ursa Major, The Big Dipper, and Orion? ...
... 5. What are Ursa Major, The Big Dipper, and Orion? ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Cassiopeia (KAS-ee-uh-PEE-uh), the Queen. Is one of the so-called circumpolar constellations, which means that it may be observed on any evening of the year. Look for the obvious letter M, or W, floating opposite the Big Dipper, with Polaris in between. Here we will find a beautiful, true binary sta ...
... Cassiopeia (KAS-ee-uh-PEE-uh), the Queen. Is one of the so-called circumpolar constellations, which means that it may be observed on any evening of the year. Look for the obvious letter M, or W, floating opposite the Big Dipper, with Polaris in between. Here we will find a beautiful, true binary sta ...
Review Guide
... 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appear redder than they should? 10. What are 2 pieces of eviden ...
... 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appear redder than they should? 10. What are 2 pieces of eviden ...
Document
... • People in years past used the constellations to know when to prepare for planting, harvest and ritual celebrations ...
... • People in years past used the constellations to know when to prepare for planting, harvest and ritual celebrations ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
... average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Because they are very large. 8) Why do white dwarf stars appear so dim, when they ...
Society News - Bristol Astronomical Society
... number of galaxies that are located with its boundaries including 5 that made it into Messiers list of nebulous objects. The bright stars form a reasonable outline of a prone lion, the brightest member of Leo, alpha (α) Leonis, has the proper name Regulus and shines at magnitude +1.35. it marks one ...
... number of galaxies that are located with its boundaries including 5 that made it into Messiers list of nebulous objects. The bright stars form a reasonable outline of a prone lion, the brightest member of Leo, alpha (α) Leonis, has the proper name Regulus and shines at magnitude +1.35. it marks one ...
The 22 First Magnitude Stars
... • Only the brightest stars have proper names in common use • Multiple stars have suffix A, B, C, etc. applied to components in order of apparent brightness ...
... • Only the brightest stars have proper names in common use • Multiple stars have suffix A, B, C, etc. applied to components in order of apparent brightness ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.