NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... star formation and is also called a starburst galaxy. It’s also sometimes called The Cigar Galaxy because it’s seen almost edge-on. They’re both about 12 million ly away, and easily glimpsed together in 10x50 binoculars. M51 lies under the end of the “handle” of the Big Dipper. To find it, imagine a ...
... star formation and is also called a starburst galaxy. It’s also sometimes called The Cigar Galaxy because it’s seen almost edge-on. They’re both about 12 million ly away, and easily glimpsed together in 10x50 binoculars. M51 lies under the end of the “handle” of the Big Dipper. To find it, imagine a ...
proposed october viewing list
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
Dark Sky Scotland - Constellation Project
... constellations to work with. Finding the distance to stars in Light Years will be a key challenge for pupils or teachers. You can find this information on the web (see below) and you will need to understand some scientific conventions and complexities to collate this information: ...
... constellations to work with. Finding the distance to stars in Light Years will be a key challenge for pupils or teachers. You can find this information on the web (see below) and you will need to understand some scientific conventions and complexities to collate this information: ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
March
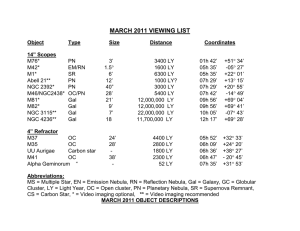
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
Chapter 25 - OG
... Red Supergiant - core contracts – causes temp to increase then COOLS Supernova : outer portion of star explodes (def = huge explosion that destroys a star) ▪ Neutron Star – consists only of Neutrons in dense core ▪ Black Hole – core collapses until there is no volume – gravity so great nothing c ...
... Red Supergiant - core contracts – causes temp to increase then COOLS Supernova : outer portion of star explodes (def = huge explosion that destroys a star) ▪ Neutron Star – consists only of Neutrons in dense core ▪ Black Hole – core collapses until there is no volume – gravity so great nothing c ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 5
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
Nov13Guide - East-View
... and Pegasus. Although Andromeda is one of the largest constellations in the sky, none of its stars is particularly bright and I find it difficult to see any meaningful shape in the arrangement of stars. It is worth scanning eastwards from Alpheratz with binoculars and you are sure to locate the Andr ...
... and Pegasus. Although Andromeda is one of the largest constellations in the sky, none of its stars is particularly bright and I find it difficult to see any meaningful shape in the arrangement of stars. It is worth scanning eastwards from Alpheratz with binoculars and you are sure to locate the Andr ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... Familiar winter constellations like Orion begin to set in the west with the onset of darkness, bringing the spring constellations of Leo, Virgo, Coma Bernices and Ursa Major into prominence. It is within these that hosts of galaxies reside. The North Galactic Pole, the point in the sky directly over ...
... Familiar winter constellations like Orion begin to set in the west with the onset of darkness, bringing the spring constellations of Leo, Virgo, Coma Bernices and Ursa Major into prominence. It is within these that hosts of galaxies reside. The North Galactic Pole, the point in the sky directly over ...
Chapter 30.1
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its brightest stars form a V shape along with the brighter red giant Aldebaran, which is not p ...
... away and thus, one of the beststudied of all star clusters. It consists of hundreds of stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its brightest stars form a V shape along with the brighter red giant Aldebaran, which is not p ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Andromeda is like a larger version of our own Milky Way galaxy. It’s a flat disk that spans more than a quarter-million light-years. Its brightest stars form spiral arms that make the galaxy look like a pinwheel. Yet the galaxy is so far away that its structure is visible only through telescopes. Th ...
... Andromeda is like a larger version of our own Milky Way galaxy. It’s a flat disk that spans more than a quarter-million light-years. Its brightest stars form spiral arms that make the galaxy look like a pinwheel. Yet the galaxy is so far away that its structure is visible only through telescopes. Th ...
- ALMA Observatory
... as it aged. It grew a lot, but as it produced no extra heat, it went cold. As its temperature dropped, the star turned redder. This may seem odd, given that in our daily lives we usually associate the color red with hot ...
... as it aged. It grew a lot, but as it produced no extra heat, it went cold. As its temperature dropped, the star turned redder. This may seem odd, given that in our daily lives we usually associate the color red with hot ...
answers
... 18. What is the special name for 2 suns that orbit each other? [Binary system] 19. Name 3 castles in the UK.. ...
... 18. What is the special name for 2 suns that orbit each other? [Binary system] 19. Name 3 castles in the UK.. ...
changing constellations
... s three month is found low in the west set, the Southern Looking south after sun in the sky in h hig ud, Cross stands pro near the horizon n dow ide ups is winter, but during summer. positions So, what is going on? The ause each day bec r yea the ing change dur n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha ...
... s three month is found low in the west set, the Southern Looking south after sun in the sky in h hig ud, Cross stands pro near the horizon n dow ide ups is winter, but during summer. positions So, what is going on? The ause each day bec r yea the ing change dur n 2.5 million the Earth moves more tha ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.