SNC 1D Astonomy
... Apparent Magnitude • Star maps show constellations and individual stars. • The larger the dot on the map, the larger the star appears to us on Earth. • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as seen from Earth ...
... Apparent Magnitude • Star maps show constellations and individual stars. • The larger the dot on the map, the larger the star appears to us on Earth. • Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as seen from Earth ...
Chapter 7 Review Answers
... The CBR found fits with the predictions consistent with the BBT, supporting the BBT. 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies ...
... The CBR found fits with the predictions consistent with the BBT, supporting the BBT. 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
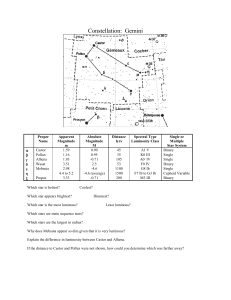
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
Sample Assessment Items
... a. Mars is farther away than the stars. b. Mars is moving much faster than the stars. c. The stars are much farther away than Mars, so they appear not to move. d. Earth and the stars move in one direction, and Mars moves in the other. Answer: The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly mov ...
... a. Mars is farther away than the stars. b. Mars is moving much faster than the stars. c. The stars are much farther away than Mars, so they appear not to move. d. Earth and the stars move in one direction, and Mars moves in the other. Answer: The stars in the night sky look as if they are slowly mov ...
Name____________________________________________
... 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. 6. Our Solar System is a single star system, but is located in the Milky Way Galaxy which contains other single stars, double stars, star systems, and dust & gas. 7. How do the planets stay in orbit around the sun? Gravity ...
... 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. 6. Our Solar System is a single star system, but is located in the Milky Way Galaxy which contains other single stars, double stars, star systems, and dust & gas. 7. How do the planets stay in orbit around the sun? Gravity ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Galaxies, spiral, irregular, and elliptical; the Milky Way Star clusters, open and globular Galaxy clusters Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence tha ...
... Galaxies, spiral, irregular, and elliptical; the Milky Way Star clusters, open and globular Galaxy clusters Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence tha ...
Week 5 (10/16) – Quiz #11
... A gravitational force and a strong nuclear force are canceling each other ...
... A gravitational force and a strong nuclear force are canceling each other ...
Homework 7
... Homework 7 Due Friday, November 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. How does solar nebula theory explain the dramatic density difference between the terrestrial and Jovian planets? ...
... Homework 7 Due Friday, November 22, 2013 at 5 p.m., either electronically or on paper. 1. How does solar nebula theory explain the dramatic density difference between the terrestrial and Jovian planets? ...
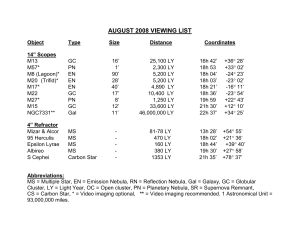
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
... supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
Physical properties of stars
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
solar system
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
Geography
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... In February bright stars are nearly overhead. Sirius, the brightest star, is north of the zenith. Canopus, the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's ...
... In February bright stars are nearly overhead. Sirius, the brightest star, is north of the zenith. Canopus, the second brightest star, is south of the zenith. Below and left of Sirius are Orion's bright stars: bluish Rigel and reddish Betelgeuse. Between them is the line of three stars making Orion's ...
Constellation Packet - Mr. Jenkins` Classroom
... Draco livd many years ago in the beautiful garden of hesperides. He grew to be a large strong dragon. He required no sleep and was always awake and moving around. The gods thought he would make an excellent guard. The gods gave him the duty of defending the garden of hesperides. Hercules lived far a ...
... Draco livd many years ago in the beautiful garden of hesperides. He grew to be a large strong dragon. He required no sleep and was always awake and moving around. The gods thought he would make an excellent guard. The gods gave him the duty of defending the garden of hesperides. Hercules lived far a ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.