Handout 3 1-2 ppt
... Fifty thousand years ago, a giant fireball streaked across the North American sky. It struck the earth in what is now northern Arizona, exploding with the force of 2 ½ million tons of TNT. ...
... Fifty thousand years ago, a giant fireball streaked across the North American sky. It struck the earth in what is now northern Arizona, exploding with the force of 2 ½ million tons of TNT. ...
Specific Word Instruction Possible Sentences
... Read the Selection Studying the Sky stronomy is the study of the planets, stars, and galaxies. People have been watching the movement of the sun, moon, planets, and stars since ancient times. So astronomy is a very, very old science. From early times, people tried to make models of the universe. For ...
... Read the Selection Studying the Sky stronomy is the study of the planets, stars, and galaxies. People have been watching the movement of the sun, moon, planets, and stars since ancient times. So astronomy is a very, very old science. From early times, people tried to make models of the universe. For ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
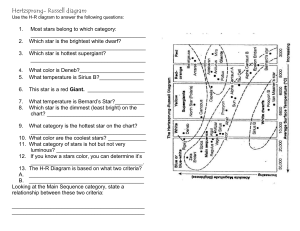
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
2007-8 Astronomy Outline
... **Night Sky Journal Entry 1 Example** Date: Time: (try to go out around the same time each night) Light Conditions: (here is where you state how dark it is; cloud cover; how much light is coming in from other houses aka light pollution) Location: where you are and the direction you are facing Observ ...
... **Night Sky Journal Entry 1 Example** Date: Time: (try to go out around the same time each night) Light Conditions: (here is where you state how dark it is; cloud cover; how much light is coming in from other houses aka light pollution) Location: where you are and the direction you are facing Observ ...
Binocular Universe: Bikini Bottom
... circled by a close-set pair of stars. The more massive of those two is a blue star, but little is known about its companion apart from it taking only 8.7 days to orbit. The two are separated from each other by only one-third Mercury's distance from the Sun. Our last stop within Capricornus is the c ...
... circled by a close-set pair of stars. The more massive of those two is a blue star, but little is known about its companion apart from it taking only 8.7 days to orbit. The two are separated from each other by only one-third Mercury's distance from the Sun. Our last stop within Capricornus is the c ...
Document
... • Visible Light: light we see coming from the sun or the stars. But there is still radiation, and other waves we can not see from space. Special telescopes have been developed to detect the different types of invisible radiation. • Keck I and Keck II largest telescopes in the world. • Hubble Telesco ...
... • Visible Light: light we see coming from the sun or the stars. But there is still radiation, and other waves we can not see from space. Special telescopes have been developed to detect the different types of invisible radiation. • Keck I and Keck II largest telescopes in the world. • Hubble Telesco ...
Jeopardy Questions
... Q: What is the difference between a nova, a core-collapse supernova, and a Type Ia supernova? A: Nova – Material falls on WD, fuses in small burst of energy. Type Ia Supernova – Material falls on WD, builds up until Chandrasekhar limit, and then everything explodes. Core-collapse Supernova – Massive ...
... Q: What is the difference between a nova, a core-collapse supernova, and a Type Ia supernova? A: Nova – Material falls on WD, fuses in small burst of energy. Type Ia Supernova – Material falls on WD, builds up until Chandrasekhar limit, and then everything explodes. Core-collapse Supernova – Massive ...
Quiz #4 – The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Stars
... Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies – Study Guide Name _______________________ ...
... Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies – Study Guide Name _______________________ ...
The Planet with Three Suns
... Imagine a world where each season lasts over 100 years and you have three shadows at once. Now meet HD 131399ab, a newly discovered exo-planet with these exact quirks! (An exo-planet is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. T ...
... Imagine a world where each season lasts over 100 years and you have three shadows at once. Now meet HD 131399ab, a newly discovered exo-planet with these exact quirks! (An exo-planet is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. T ...
Topic E: Astrophysics E1 Introduction to the Universe.
... if the gas has time to _________________ into a disk before it is all used up, then you get a spiral galaxy. Or perhaps some of the elliptical galaxies are made from merging of other types of galaxies. Observations of distant galaxies indicates that spiral galaxies were more common in the past ...
... if the gas has time to _________________ into a disk before it is all used up, then you get a spiral galaxy. Or perhaps some of the elliptical galaxies are made from merging of other types of galaxies. Observations of distant galaxies indicates that spiral galaxies were more common in the past ...
Notes: Astronomy and Groups of Stars
... Oval shaped, Extremely bright, Older stars No regular shape, Very low mass Made of gas and dust, Least common Looks like a wheel with arm extensions Most common type Arms consist of younger stars, gas/dust. - our galaxy -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our ...
... Oval shaped, Extremely bright, Older stars No regular shape, Very low mass Made of gas and dust, Least common Looks like a wheel with arm extensions Most common type Arms consist of younger stars, gas/dust. - our galaxy -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our ...
The Earth`s Orbit and Season Demonstration
... summer. Rotate the earth on its axis until North America is directly opposite the sun, midnight. Notice the constellation directly in front of North America, Sagittarius Winter Solstice. In six months the Earth will travel around the sun to the other side and the Sun will appears in the constellatio ...
... summer. Rotate the earth on its axis until North America is directly opposite the sun, midnight. Notice the constellation directly in front of North America, Sagittarius Winter Solstice. In six months the Earth will travel around the sun to the other side and the Sun will appears in the constellatio ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.