Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide ...
... Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide ...
Solar System - Physics Rocks!
... Most of the objects in the solar system follow a nearly circular orbit—but are still ellipses ...
... Most of the objects in the solar system follow a nearly circular orbit—but are still ellipses ...
Skywatch Astro Ed Dec13
... of other stars, then hurled into space as the stars died, where they could be incorporated into new stars. Population II stars formed when there were almost no heavier elements around, so they have only tiny amounts of them. But Population I stars, like the Sun, are younger, so they have higher prop ...
... of other stars, then hurled into space as the stars died, where they could be incorporated into new stars. Population II stars formed when there were almost no heavier elements around, so they have only tiny amounts of them. But Population I stars, like the Sun, are younger, so they have higher prop ...
STARS - AN INTRODUCTION
... They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
... They give off light and heat. The Sun is a medium sized star. It is bigger than all eight planets combined! However, there are stars a lot bigger than the Sun! The largest stars are called ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
... is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and so they named it. This allowed them to map the movement of the stars throughout the seasons, which helped the d ...
The night sky - Mr. Champion
... • Even before the advent of telescopes, humans took note of star formations and have been influenced by them. • As we often do, some claimed through patterns they could see objects or people “hidden” there. • These objects are what’s known as constellations. • They aren’t necessarily found in the sa ...
... • Even before the advent of telescopes, humans took note of star formations and have been influenced by them. • As we often do, some claimed through patterns they could see objects or people “hidden” there. • These objects are what’s known as constellations. • They aren’t necessarily found in the sa ...
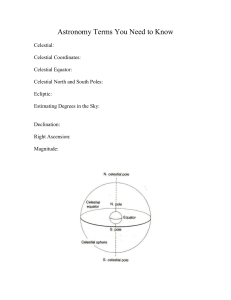
Astronomy Terms You Need to Know
... The Leonids are best known for producing great meteor storms in the years of 1833, 1866, 1966, and 2001. These outbursts of meteor activity are best seen when the parent object, comet 55P/Tempel-Tuttle, is near perihelion (closest approach to the sun). Yet it is not the fresh material we see from th ...
... The Leonids are best known for producing great meteor storms in the years of 1833, 1866, 1966, and 2001. These outbursts of meteor activity are best seen when the parent object, comet 55P/Tempel-Tuttle, is near perihelion (closest approach to the sun). Yet it is not the fresh material we see from th ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #20 Key
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
Stars
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
... • As Earth rotates, Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and other constellations in the northern sky circle around Polaris • Because of this, they are called circumpolar constellations. • It appears that the constellations complete one full circle in the sky in about 24 hr. as Earth rotates on its axis. ...
Earth`s Motions
... - For the most part, celestial objects appear to move from east to west in the sky. They rotate counterclockwise around Polaris (North Star) at about 15o/hour (or 360o in 24 hours). This is because Polaris is directly above Earth’s axis of rotation so it appears not to move in night sky. ...
... - For the most part, celestial objects appear to move from east to west in the sky. They rotate counterclockwise around Polaris (North Star) at about 15o/hour (or 360o in 24 hours). This is because Polaris is directly above Earth’s axis of rotation so it appears not to move in night sky. ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... To talk about space we need to come up with distance units a little more appropriate than just miles. Otherwise it would be like measuring from here to New York in inches! ...
... To talk about space we need to come up with distance units a little more appropriate than just miles. Otherwise it would be like measuring from here to New York in inches! ...
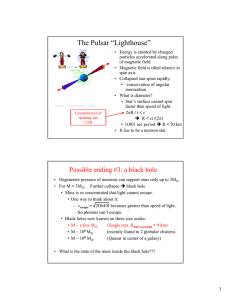
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known on three size scales: • M ~ a few M (Single star. RSchwarzschild = 9 km) • M ~ 105 M (recently found in 2 globu ...
... • Mass is so concentrated that light cannot escape. • One way to think about it: – vescape = 2GM/R becomes greater than speed of light. – So photons can’t escape. • Black holes now known on three size scales: • M ~ a few M (Single star. RSchwarzschild = 9 km) • M ~ 105 M (recently found in 2 globu ...
Homework Problems for Quiz 1 – AY 5 – Spring 2013
... 11. Star A has twice the trigonometric parallax angle and twice the luminosity of Star B. (Assume no dust toward either star) a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? ...
... 11. Star A has twice the trigonometric parallax angle and twice the luminosity of Star B. (Assume no dust toward either star) a) What are the relative distances of the two stars? ...
Universe CBA Review - cms16-17
... 33.) What type of EMS wave has the longest wavelength? _____________________ 34.) Does infrared or x-ray waves have a longer wavelength? __________________ 35.) What type of wave has the highest frequency in the EMS? __________________ 36.) Draw and label the visible light spectrum ...
... 33.) What type of EMS wave has the longest wavelength? _____________________ 34.) Does infrared or x-ray waves have a longer wavelength? __________________ 35.) What type of wave has the highest frequency in the EMS? __________________ 36.) Draw and label the visible light spectrum ...
The winter sky over Bosham
... In the southeast sky in the early evening is the hourglass shape of Orion, the hunter, one of the most recognisable constellations in the night sky. Unlike most constellations, which are mostly random groupings of stars that happen to appear together in the sky, the stars of Orion are almost all rel ...
... In the southeast sky in the early evening is the hourglass shape of Orion, the hunter, one of the most recognisable constellations in the night sky. Unlike most constellations, which are mostly random groupings of stars that happen to appear together in the sky, the stars of Orion are almost all rel ...
Stars
... It is about 2,100 times larger than the sun. It would fit about 9,261,000,000 suns in it. The smallest star known is the OGLE-TR-122B it is 12 solar radii. • That is about 167,ooo km (kilometers). ...
... It is about 2,100 times larger than the sun. It would fit about 9,261,000,000 suns in it. The smallest star known is the OGLE-TR-122B it is 12 solar radii. • That is about 167,ooo km (kilometers). ...
Ch.1, Sec.3 - Mapping the Stars
... horizon: the line where the sky and the Earth appear to meet ...
... horizon: the line where the sky and the Earth appear to meet ...
Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What causes the seasons? Why are they opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres? 6. Has the same star always been the North Star? 7. Can we use the rising and setting of the Sun as the basis ...
... What is so special about the North Star? 4. Are the same stars visible from any location on Earth? 5. What causes the seasons? Why are they opposite in the northern and southern hemispheres? 6. Has the same star always been the North Star? 7. Can we use the rising and setting of the Sun as the basis ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.