Stars - BrainBytes
... The closest star to Earth, besides the sun is Proxima Centauri – located 4.2 light years away ...
... The closest star to Earth, besides the sun is Proxima Centauri – located 4.2 light years away ...
Name Period ______ Astronomy Unit Study Guide 1. _____
... G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. Greek astronomer who developed a geocentric model of planetary motion I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
... G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. Greek astronomer who developed a geocentric model of planetary motion I. the idea that the earth is the center of the universe J. he developed a law that other galaxies are moving away from us ...
11.3.1 Grade 6 Standard 4 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1
... It takes up over half of the known universe. It cannot be measured or compared. It is very small when compared to the universe ...
... It takes up over half of the known universe. It cannot be measured or compared. It is very small when compared to the universe ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... Due to the equation of time the latest sunrise of the year occurs around the 2nd January; the mornings lighten. The Sun moves from Sagittarius to Capricornus on the 20th of the month. It is also beginning its journey towards more northerly latitudes once more, and will eventually become better place ...
... Due to the equation of time the latest sunrise of the year occurs around the 2nd January; the mornings lighten. The Sun moves from Sagittarius to Capricornus on the 20th of the month. It is also beginning its journey towards more northerly latitudes once more, and will eventually become better place ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
Earth in the Solar System - San Diego Unified School District
... d. ____________________ are the source of ______________________ for all bright objects in outer space and that the ____________________ and _________________ shine by _________________________________, NOT their own _________________. ...
... d. ____________________ are the source of ______________________ for all bright objects in outer space and that the ____________________ and _________________ shine by _________________________________, NOT their own _________________. ...
Unit 1 Cutouts
... 4(B) research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy, including Ptolemy, Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, Neawton, Einstein, and Hubble, and the contribution of women astronaomers, including Maria Mitchell and ...
... 4(B) research and describe the contributions of scientists to our changing understanding of astronomy, including Ptolemy, Copernicus, Tycho Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, Neawton, Einstein, and Hubble, and the contribution of women astronaomers, including Maria Mitchell and ...
Main Sequence Stars
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
Mountain Skies
... its orbit. In April, we get a chance at both views. Tonight, as the sky darkens, it is in the west below Mars. But, recall that Mercury, because it is so close to the sun, moves very rapidly. Thus, we will have a favorable vie ...
... its orbit. In April, we get a chance at both views. Tonight, as the sky darkens, it is in the west below Mars. But, recall that Mercury, because it is so close to the sun, moves very rapidly. Thus, we will have a favorable vie ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
A Star’s Life
... 1. Read the two life cycle assignments (part I and II). 2. Create a graphic organizer that summarizes what you are reading. 3. Check your answers to the questions of part I (summary questions at the end) and part II (sections 1, 2, 4 and 5) in schoology. Note: the true/false section (Those A-Maz-Ing ...
... 1. Read the two life cycle assignments (part I and II). 2. Create a graphic organizer that summarizes what you are reading. 3. Check your answers to the questions of part I (summary questions at the end) and part II (sections 1, 2, 4 and 5) in schoology. Note: the true/false section (Those A-Maz-Ing ...
Chapter 17 Science Class 8
... 4. The Moon and Venus appear to change phases, because from Earth only part of the reflected sunlight can be seen as these two move in their orbit. The Earth has many man made or artificial satellites that are nearer than the Moon , and therefore, do not reflect sunlight regularly. They can seen for ...
... 4. The Moon and Venus appear to change phases, because from Earth only part of the reflected sunlight can be seen as these two move in their orbit. The Earth has many man made or artificial satellites that are nearer than the Moon , and therefore, do not reflect sunlight regularly. They can seen for ...
Stars
... Stars have different sizes. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be wider than 300 million miles. That is more than one thousand times the distance from Earth to the Moon. Stars can be different colors such as blue, yellow, orange, red, white, and black. ...
... Stars have different sizes. White dwarf stars are about the size of Earth. Supergiant stars can be wider than 300 million miles. That is more than one thousand times the distance from Earth to the Moon. Stars can be different colors such as blue, yellow, orange, red, white, and black. ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Draw lines on the diagram to show the evolutionary paths of stars X and Y. ...
... Draw lines on the diagram to show the evolutionary paths of stars X and Y. ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky H. Variable Stars 1. Some st ...
... 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appear in the nighttime sky H. Variable Stars 1. Some st ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
... • Absolute Luminosity (brightness)Measures how bright a star is in relation to the sun, if all the stars were the same distance from the Earth. ...
Solar System Project
... You are to build a 3-D model (not a poster or diorama) of the Life Cycle of Stars. Your project includes the 3-D model, a report including citing your sources, and an oral presentation. You are to include the following in your model of the Life Cycle of a Star: a) Life cycle- stages, colors, tempera ...
... You are to build a 3-D model (not a poster or diorama) of the Life Cycle of Stars. Your project includes the 3-D model, a report including citing your sources, and an oral presentation. You are to include the following in your model of the Life Cycle of a Star: a) Life cycle- stages, colors, tempera ...
Lecture 19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... - Contains most GMCs, so most star formation takes place in disk - Contains all open clusters, a few million to a billion years old - By proportion, the disk is thinner than a pizza crust (not deep dish!) ...
... - Contains most GMCs, so most star formation takes place in disk - Contains all open clusters, a few million to a billion years old - By proportion, the disk is thinner than a pizza crust (not deep dish!) ...
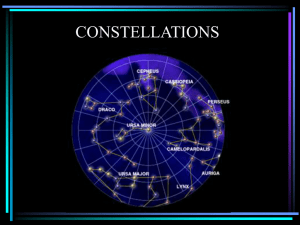
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.