Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
... and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, these objects appeared to move with respect to the __________________________. 10. Because of the ___________________________ and its __________ around the Sun, it is convenient to divide the constell ...
Star Quiz - Sue Ryder
... Sue Ryder is a charity registered in England and Wales (1052076) and in Scotland (SC039578). Ref. No. 01696 © Sue Ryder. April 2013 ...
... Sue Ryder is a charity registered in England and Wales (1052076) and in Scotland (SC039578). Ref. No. 01696 © Sue Ryder. April 2013 ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
... Most stars are made of H, He, Fe, Na, Ca Color indicates surface temp of star: – Blue = hotter (30,000 C) – Red = cooler (3,500 C) ...
Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star – Polaris - which seems to st ...
... whole night they appear to move from east to west (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s rotation causes the illusion of movement. The stars appear to rotate around a single point in the sky – the North Star – Polaris - which seems to st ...
Constellation Part II readingConstellation Part II reading(es)
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
... The stars are distant objects. Their distances vary, but they are all very far away. Excluding our Sun, the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is more than 4 light years away. As Earth spins on its axis, we, as Earth-bound observers, spin past this background of distant stars. As Earth spins, the stars ...
ch. 5 study guide
... o What is the closest star to Earth? The Sun is the closest star to Earth. o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book includ ...
... o What is the closest star to Earth? The Sun is the closest star to Earth. o Why do we see different stars during different seasons? As Earth revolves around the Sun, it passes different groups of stars. o What is one constellation from our science book? The constellations in our science book includ ...
18 Throughout history people around the world have looked up at
... story originated in Canada, so observers at lower latitudes will not perceive exactly the same effect described in the story because some of the stars represented in the Bear Hunt will dip below the horizon during the winter; however, the general sequence of events will remain the same. Share other ...
... story originated in Canada, so observers at lower latitudes will not perceive exactly the same effect described in the story because some of the stars represented in the Bear Hunt will dip below the horizon during the winter; however, the general sequence of events will remain the same. Share other ...
Gr9_unit1_ch10_notes-2015
... Chapter 10 Notes Observing Celestial Bodies Celestial Bodies are natural objects found in space. They include Moon Sun Planets Comets Asteroids Constellations are a distinctive pattern in the night sky formed by groups of stars. Many are named after Greek and Roman mythology characters. ...
... Chapter 10 Notes Observing Celestial Bodies Celestial Bodies are natural objects found in space. They include Moon Sun Planets Comets Asteroids Constellations are a distinctive pattern in the night sky formed by groups of stars. Many are named after Greek and Roman mythology characters. ...
1 - Pitt County Schools
... What can astronomers learn by studying a star’s color? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. How does distance affect parallax? _______________________________________________________ ...
... What can astronomers learn by studying a star’s color? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 2. How does distance affect parallax? _______________________________________________________ ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... Towards the north of the constellation are globular clusters NGC 5824 and NGC 5986, and close by the dark nebula B 228. To the south are two open clusters, NGC 5822 and NGC 5749, as well as globular cluster NGC 5927 on the eastern border with Norma. On the western border are two spiral galaxies and ...
... Towards the north of the constellation are globular clusters NGC 5824 and NGC 5986, and close by the dark nebula B 228. To the south are two open clusters, NGC 5822 and NGC 5749, as well as globular cluster NGC 5927 on the eastern border with Norma. On the western border are two spiral galaxies and ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
... runs a distinctive line of three stars comprising Orion’s Belt. To the top right of Orion lies another prominent star, Alderbaran, which represents the eye of Taurus. Continue the line from Orion through Aldebaran brings you to the Pleiades, a star cluster. ...
Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
File
... • 2. Greek letter (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, . . .) • Labeled in an approximate order of decreasing brightness for stars in the constellation. ...
... • 2. Greek letter (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, . . .) • Labeled in an approximate order of decreasing brightness for stars in the constellation. ...
Astronomy Exam review
... 17.On what date will someone in the northern hemisphere have the greatest amount of sunlight? 18.On June 21 the Sun will rise and set perpendicular to the horizon at the 19.At what latitude will the Sun be seen overhead on September 23? 20.What is the latitude of the tropic of Cancer? 21.How many st ...
... 17.On what date will someone in the northern hemisphere have the greatest amount of sunlight? 18.On June 21 the Sun will rise and set perpendicular to the horizon at the 19.At what latitude will the Sun be seen overhead on September 23? 20.What is the latitude of the tropic of Cancer? 21.How many st ...
Chapter 16 Lesson 2: What is a Star
... than the Milky Way. d. Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the ...
... than the Milky Way. d. Some galaxies are called irregular because they are not spiral or elliptical and do not have a definite shape. 1. Irregular galaxies are probably young galaxies with their stars are still forming. Constellations a. Ursa Major is a constellation, an area of the sky and all the ...
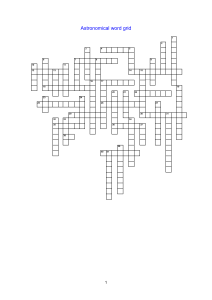
Astronomy word grid
... Astronomical wordgrid Across 4. The distance of an object with a parallax of one second 7. The plane of our galaxy visible as a pale band of stars 12. The shape of a planet’s orbit 14. Name given to the line between day and night on the Moon 17. The brightest star in the northern sky 18. The appare ...
... Astronomical wordgrid Across 4. The distance of an object with a parallax of one second 7. The plane of our galaxy visible as a pale band of stars 12. The shape of a planet’s orbit 14. Name given to the line between day and night on the Moon 17. The brightest star in the northern sky 18. The appare ...
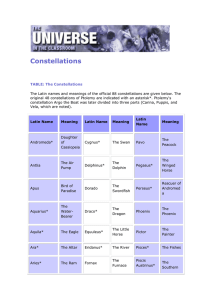
Constellations
... A natural human tendency is to see patterns and relationships between objects even when no true connection exists. Long ago, people connected the brightest stars into configurations called constellations, which ancient astronomers named after mythological beings, heroes, and animals—whatever was imp ...
... A natural human tendency is to see patterns and relationships between objects even when no true connection exists. Long ago, people connected the brightest stars into configurations called constellations, which ancient astronomers named after mythological beings, heroes, and animals—whatever was imp ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- A METEOROID THAT HITS THE EARTH’S SURFACE. 19. What force pulls together matter in stars? GRAVITY 20. If you look at an ...
... 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- A METEOROID THAT HITS THE EARTH’S SURFACE. 19. What force pulls together matter in stars? GRAVITY 20. If you look at an ...
J S U N I L T U... 2011 “Chase Excellence- Success Will Follow” ll Follow”
... (b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is __Mars__. (c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a __constellation__. (d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a satellite_. (e) Shooting stars are actually not stars __. (Shooting stars are no ...
... (b) The planet which appears reddish in colour is __Mars__. (c) A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky is known as a __constellation__. (d) A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as a satellite_. (e) Shooting stars are actually not stars __. (Shooting stars are no ...
Constellation
... pressures. An Binary Star is a stellar system consisting of two stars orbiting about a common center of mass and often appearing as a single visual or telescopic object . In this constellation, and every single other constellation it has stars aligned in a shape. ...
... pressures. An Binary Star is a stellar system consisting of two stars orbiting about a common center of mass and often appearing as a single visual or telescopic object . In this constellation, and every single other constellation it has stars aligned in a shape. ...
Virtual Sky II (Rev 10/11)
... (DST on or off depending on date). Pick one of these constellations depending on when you are doing this: Spring Semester-Canis Major, Summer Semester-Bootes, Fall Semester-Lyra. Use View>Constellations menu to find constellations. Name of brightest star _______________ (Size of star on chart relate ...
... (DST on or off depending on date). Pick one of these constellations depending on when you are doing this: Spring Semester-Canis Major, Summer Semester-Bootes, Fall Semester-Lyra. Use View>Constellations menu to find constellations. Name of brightest star _______________ (Size of star on chart relate ...
StarFlight - Center for the Presentation of Science
... constellation as a subjective shape, whose ascription from view on earth does not align with the actual position of the stars in space. For example, Figure 2 shows the constellation Scorpius as it is seen from earth and Figure 3 shows this same constellation as it is viewed from the side, 293 light- ...
... constellation as a subjective shape, whose ascription from view on earth does not align with the actual position of the stars in space. For example, Figure 2 shows the constellation Scorpius as it is seen from earth and Figure 3 shows this same constellation as it is viewed from the side, 293 light- ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.