SigAssignment
... That is about a total distance of 728,933,977,000,000 miles away from us! Yet on a clear night, we are still able to see it in the sky. This star is in the Red Giant stage so when compared to the size of our Sun, which is in the main sequence stage, it is believed to be 5 billion years ahead in its ...
... That is about a total distance of 728,933,977,000,000 miles away from us! Yet on a clear night, we are still able to see it in the sky. This star is in the Red Giant stage so when compared to the size of our Sun, which is in the main sequence stage, it is believed to be 5 billion years ahead in its ...
Dubhe
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s centennial. (shgresources.com) It is also one of the seven brightest stars. ...
... On January 22,1996 the star dubhe was named the state centennial star because the light emitted from the star takes 100 years to reach us, of course, 1996 was Utah’s centennial. (shgresources.com) It is also one of the seven brightest stars. ...
New Directions in Star Cluster Research
... (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - internally supplied radiation (exhaustion nuclear fuel) ...
... (a) Violation of first condition - self gravity (breakup of star scattering material into space) (b) Violation second condition - internally supplied radiation (exhaustion nuclear fuel) ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
Stars
... • Watch the Video Field Trip about Stars. • Discuss the following questions with the person in front of you. – How does mass affect the life of a star? – Why do stars die? ...
... • Watch the Video Field Trip about Stars. • Discuss the following questions with the person in front of you. – How does mass affect the life of a star? – Why do stars die? ...
RFS_315_answers
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
Patterns in the Sky
... 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some celestial objects can be seen with the unaided eye and can be identified by their motion. 4. The Sun emits light and other forms of ...
... 1. Careful observation of the night sky can offer clues about the motion of celestial objects. 2. Celestial objects in the Solar System have unique properties. 3. Some celestial objects can be seen with the unaided eye and can be identified by their motion. 4. The Sun emits light and other forms of ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... conditions, M1 can be a tough quarry. Ursa Major (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 32) The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint ...
... conditions, M1 can be a tough quarry. Ursa Major (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 32) The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint ...
Groups of Stars
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... - Double star, Alcore and Mizar, middle star in dipper handle used by Roman Army as a test of eyesight. - American Indian story, the changing of leaves in fall - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetar ...
... - Double star, Alcore and Mizar, middle star in dipper handle used by Roman Army as a test of eyesight. - American Indian story, the changing of leaves in fall - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetar ...
Grade 6 Standard 4 - Murray School District
... objects, movement, and apparent motion (due to Earth’s rotation) of objects in the universe and how cultures have understood, related to and used these objects in the night sky. Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how var ...
... objects, movement, and apparent motion (due to Earth’s rotation) of objects in the universe and how cultures have understood, related to and used these objects in the night sky. Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how var ...
Review_game_and_answers
... formed, the planets that lost most of their gases became the what? The rocky inner planets ...
... formed, the planets that lost most of their gases became the what? The rocky inner planets ...
For each statement or question, select the word or expression that
... ____ 9. The constellation that contains the "pointer stars" used to locate Polaris is A. Canis Major B. Cassiopeia C. Orion D. Ursa Major ____ 10. An example of a winter constellation is A. Lyra B. Orion C. Cygnus D. Cassiopeia ____ 11. A light-year measures A. time B. distance C. speed D. energy _ ...
... ____ 9. The constellation that contains the "pointer stars" used to locate Polaris is A. Canis Major B. Cassiopeia C. Orion D. Ursa Major ____ 10. An example of a winter constellation is A. Lyra B. Orion C. Cygnus D. Cassiopeia ____ 11. A light-year measures A. time B. distance C. speed D. energy _ ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... star hop will be different, but here's one that works for me (and yes, I field tested it this time). Start with Orion, one of the most recognizable winter constellations. It'll be reasonably high in the south or southeast in the evening this month. My next step is to look past Orion's right shoulder ...
... star hop will be different, but here's one that works for me (and yes, I field tested it this time). Start with Orion, one of the most recognizable winter constellations. It'll be reasonably high in the south or southeast in the evening this month. My next step is to look past Orion's right shoulder ...
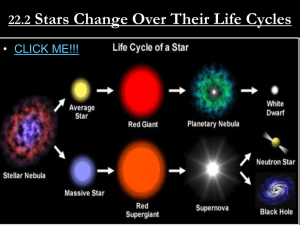
22.2 Stars Change Over Their Life Cycles
... position of an object when viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
... position of an object when viewed from different locations. • Try this! Close one eye at a time and focus on a single object. Blink back and forth quickly. What happens!? Does the object appear to move? ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.