Stars and Constellations
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
... how stars evolve. Lead students to understand the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Showing a flashlight at varying distances is a concrete means of demonstrating the difference. 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protr ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... Russell first had the idea of plotting the absolute magnitude of a star against its spectral type. This type of diagram is known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Since the original diagram was produced other quantities, the surface temperature and the luminosity compared with the Sun, have been add ...
... Russell first had the idea of plotting the absolute magnitude of a star against its spectral type. This type of diagram is known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Since the original diagram was produced other quantities, the surface temperature and the luminosity compared with the Sun, have been add ...
Day 1: How to Describe the Sky The Motions of the Stars
... • The angle an object appears to span in your field of view. • Depends on: • Actual size of object • Distance from us to the object ...
... • The angle an object appears to span in your field of view. • Depends on: • Actual size of object • Distance from us to the object ...
M13 – The Great Hercules Cluster
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
The Milky Way
... • We define our age by trips around the Sun. • How many trips of Sun around Milky Way? R = 8.5 kpc V = 220km/s P = 2.5x108 yrs ...
... • We define our age by trips around the Sun. • How many trips of Sun around Milky Way? R = 8.5 kpc V = 220km/s P = 2.5x108 yrs ...
Universe and Galaxy Short Study Guide
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. inflationary universe e. steady-state theory b. cosmology f. Hubble constant c. Big Bang theory g. active galactic nucleus d. cosmic background radiation h. superclusters ____ 7. Core of a galaxy in which highly energetic objects or activities are ...
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. inflationary universe e. steady-state theory b. cosmology f. Hubble constant c. Big Bang theory g. active galactic nucleus d. cosmic background radiation h. superclusters ____ 7. Core of a galaxy in which highly energetic objects or activities are ...
Blowing Bubbles in Space: The Birth and Death of Practically
... • Eta Carinae was observed by Hubble in September 1995 with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). Images taken through red and near-ultraviolet filters were subsequently combined to produce the color image shown. A sequence of eight exposures was necessary to cover the object's huge dynamic ran ...
... • Eta Carinae was observed by Hubble in September 1995 with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). Images taken through red and near-ultraviolet filters were subsequently combined to produce the color image shown. A sequence of eight exposures was necessary to cover the object's huge dynamic ran ...
TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES
... 14. A navigational instrument made from a quarter (1/4) circle protractor is a _________. 15. A ___________measures altitude from ___° at the _______ to ___ ° at the _______. 16. The vertical angle of an object from the horizon is the ____________. 17. The horizontal angle of an object clockwise fro ...
... 14. A navigational instrument made from a quarter (1/4) circle protractor is a _________. 15. A ___________measures altitude from ___° at the _______ to ___ ° at the _______. 16. The vertical angle of an object from the horizon is the ____________. 17. The horizontal angle of an object clockwise fro ...
Earth Science Chapter Two: What Makes Up the Solar System
... Multiple Choice Lesson One: Investigation-No test questions from this lesson Lesson Two: Stars and Galaxies 1. What is formed from a huge cloud of dust and gas called a nebula? 2. How long does the average star live? 3. The sun is part of a galaxy. How would you describe a galaxy? Lesson Three: Cons ...
... Multiple Choice Lesson One: Investigation-No test questions from this lesson Lesson Two: Stars and Galaxies 1. What is formed from a huge cloud of dust and gas called a nebula? 2. How long does the average star live? 3. The sun is part of a galaxy. How would you describe a galaxy? Lesson Three: Cons ...
neutron star - Livonia Public Schools
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and coll ...
... All stars, regardless of their size, eventually run out of fuel and collapse due to gravity. Death of Low-Mass Stars • Stars less than one-half the mass of the sun never evolve to the red giant stage but remain in the stable main-sequence stage until they consume all their hydrogen fuel and coll ...
Navigation Methods
... • GPS uses these "man-made stars" as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. In fact, with advanced forms of GPS you can make measurements to better than a ...
... • GPS uses these "man-made stars" as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. In fact, with advanced forms of GPS you can make measurements to better than a ...
Chapter 17 and 18 Vocabulary Quist
... 42. Dark cooler areas of the Sun’s surface are called __________________ 43. A very high energy object in space that is very far away is called a _____________________ 44. Our Sun is considered to be a star of this color ______________________ 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone ______ ...
... 42. Dark cooler areas of the Sun’s surface are called __________________ 43. A very high energy object in space that is very far away is called a _____________________ 44. Our Sun is considered to be a star of this color ______________________ 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone ______ ...
Planisphere Exercise
... daylight savings time is observed locally. Which famous asterism is located high in the south at chart time? ...
... daylight savings time is observed locally. Which famous asterism is located high in the south at chart time? ...
Space Science Unit - World of Teaching
... other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
... other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
Phobos
... Monthly Highlights: The first total eclipse of the Moon since 2004 occurs on the night of March 3rd-4th. Also, several bright planets are favourably placed for viewing this month. At dusk Venus is fairly high in the west and Saturn in the east-southeast. Jupiter doesn’t rise until the middle of the ...
... Monthly Highlights: The first total eclipse of the Moon since 2004 occurs on the night of March 3rd-4th. Also, several bright planets are favourably placed for viewing this month. At dusk Venus is fairly high in the west and Saturn in the east-southeast. Jupiter doesn’t rise until the middle of the ...
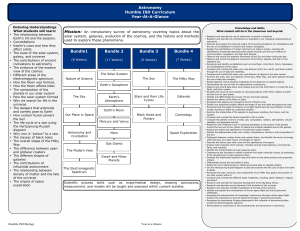
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Compare and contrast the factors essential to life on Earth. • Compare the planets in terms of orbit, size, composition, rotation, atmosphere, natural satellites, and geological activity. • Relate the role of Newton's law of universal gravitation to the motion of the planets around the Sun and to ...
... • Compare and contrast the factors essential to life on Earth. • Compare the planets in terms of orbit, size, composition, rotation, atmosphere, natural satellites, and geological activity. • Relate the role of Newton's law of universal gravitation to the motion of the planets around the Sun and to ...
Space Science Unit
... other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
... other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). They make up 90% of the stars in our sky. These stars are the diagonal strip running through the middle of the chart. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.