PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... Prerequisite: An appropriate Mathematics Placement test result, or MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolutio ...
... Prerequisite: An appropriate Mathematics Placement test result, or MA045 Basic Math Skills, or MA050 Introductory Mathematics This course covers these topics: the sun and other stars, multiple star systems, the Milky Way and other galaxies, nebulae, intergalactic material, cosmology and the evolutio ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
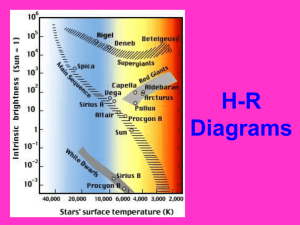
... brightness with all stars placed at same distance ...
... brightness with all stars placed at same distance ...
PEGASUS, THE FLYING HORSE Pegasus is a constellation in the
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
Extra Credit
... Something disturbs the comet's orbit -- like the gravity of a passing star -- starting it on a long fall toward the Sun. As a comet approaches the Sun, some of its ice vaporizes, freeing particles of rock as well. This material forms a bright cloud around the comet. And some of the material is pushe ...
... Something disturbs the comet's orbit -- like the gravity of a passing star -- starting it on a long fall toward the Sun. As a comet approaches the Sun, some of its ice vaporizes, freeing particles of rock as well. This material forms a bright cloud around the comet. And some of the material is pushe ...
Star Vocabulary
... Star Vocabulary 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4 ...
... Star Vocabulary 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4 ...
HERE
... b. Fuse hydrogen into carbon c. Form planetary nebula d. Form supernovas 51. Which of the following is not an inner planet? ...
... b. Fuse hydrogen into carbon c. Form planetary nebula d. Form supernovas 51. Which of the following is not an inner planet? ...
The Evolution of Massive Stars
... debris from a supernova in about 1680: today the brightest radio source in the sky ...
... debris from a supernova in about 1680: today the brightest radio source in the sky ...
Adventurer Pathfinder
... Light-Year: The distance light travels in one year. Milky Way: The galaxy in which our solar system is found. Moon: The satellite that moves around the earth once each month and reflects light from the sun. Planet: One of the nine large heavenly bodies circling the sun. Star: A ball of burning gases ...
... Light-Year: The distance light travels in one year. Milky Way: The galaxy in which our solar system is found. Moon: The satellite that moves around the earth once each month and reflects light from the sun. Planet: One of the nine large heavenly bodies circling the sun. Star: A ball of burning gases ...
I : Internal structure of main sequence stars
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
... The luminosity L The efficiency of the fusion η The mass of the star M The fraction of the stellar mass that can participate in the fusion reactions f ...
31_Finding Earths
... one can measure the brightness very accurately and can observer all the time. A large optical telescope with a coronagraph or an infrared interferometer could actually see earth like planets around nearby stars! ...
... one can measure the brightness very accurately and can observer all the time. A large optical telescope with a coronagraph or an infrared interferometer could actually see earth like planets around nearby stars! ...
Volume 20 Number 4 March 2012 - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... ―Zodiacal Light‖. It is the cone-shaped glow of meteoric dust that appears above the western horizon as twilight fades to darkness, and when there is no or very little moonlight – the days before and after the 22nd.. ...
... ―Zodiacal Light‖. It is the cone-shaped glow of meteoric dust that appears above the western horizon as twilight fades to darkness, and when there is no or very little moonlight – the days before and after the 22nd.. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.