Galaxies
... • Extends 50,000 light years beyond the central bulge • Forms spiral arms that contain a lot of gas and dust • Population I stars are found in the spiral arms – these are young O and B main-sequence stars – they are often found in open clusters ...
... • Extends 50,000 light years beyond the central bulge • Forms spiral arms that contain a lot of gas and dust • Population I stars are found in the spiral arms – these are young O and B main-sequence stars – they are often found in open clusters ...
Click here
... galaxy groups. The Local Group - ________________ million light years in diameter. This is a group of over 50 galaxies. The Milky Way Galaxy - 100,000 light years in diameter o Our Solar System - the Sun's gravity extends out to around 2 light years. So it is about 4 light years in diameter. E ...
... galaxy groups. The Local Group - ________________ million light years in diameter. This is a group of over 50 galaxies. The Milky Way Galaxy - 100,000 light years in diameter o Our Solar System - the Sun's gravity extends out to around 2 light years. So it is about 4 light years in diameter. E ...
Telephone Quizzes for ASTR 200 1999 Revision
... is the same as that of the Sun as mass does not affect the lifetime of a star. is shorter than that of the Sun since there is less fuel to burn. is longer than that of the Sun because the star generates energy (uses fuel) at a very slow rate. cannot be discussed as such a star is too small to genera ...
... is the same as that of the Sun as mass does not affect the lifetime of a star. is shorter than that of the Sun since there is less fuel to burn. is longer than that of the Sun because the star generates energy (uses fuel) at a very slow rate. cannot be discussed as such a star is too small to genera ...
Consider Average Stars
... Look to the western horizon, with the sun still up in the sky. Then move your cursor to the time display at the top left, and advance the minutes quickly by holding down the arrow key on your keyboard. This makes the sun set rapidly – and you can watch the stars come out! ...
... Look to the western horizon, with the sun still up in the sky. Then move your cursor to the time display at the top left, and advance the minutes quickly by holding down the arrow key on your keyboard. This makes the sun set rapidly – and you can watch the stars come out! ...
Handout from Allaire Star Party
... Open clusters are also clusters of stars, but they are much smaller and younger than globular clusters. A typical open cluster might contain anywhere from less than 10 to more than 10,000 stars in an area about 50-100 light years across. When comparing these to globular clusters, which can have over ...
... Open clusters are also clusters of stars, but they are much smaller and younger than globular clusters. A typical open cluster might contain anywhere from less than 10 to more than 10,000 stars in an area about 50-100 light years across. When comparing these to globular clusters, which can have over ...
Planetarium Key Points
... Constellation shape change with epoch and observer position; shape is not for ever becouse of star’s proper motion, but no detectable change during human life at naked eye Constellations and asterisms; we use structures invented by assirian priests in XII century BC: Orion, Ursa Major, Ursa Mino ...
... Constellation shape change with epoch and observer position; shape is not for ever becouse of star’s proper motion, but no detectable change during human life at naked eye Constellations and asterisms; we use structures invented by assirian priests in XII century BC: Orion, Ursa Major, Ursa Mino ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... What is a comet nucleus made of? How about the tail? What are meteors? What is the Titius-Bode Law (aka Bode’s Law)? What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1 ...
... What is a comet nucleus made of? How about the tail? What are meteors? What is the Titius-Bode Law (aka Bode’s Law)? What is a dwarf planet? The destructive power of a collision with an asteroid or comet nucleus comes from the kinetic energy of the object hitting the Earth. Since kinetic energy is 1 ...
june 2011 - Holt Planetarium
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
june 2011 - Holt Planetarium
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
... and mantle, leaving behind its core and not much else. This spectacular view of the crater Degas was obtained as a highresolution targeted observation (90 m/pixel). Impact melt coats its floor, and as the melt cooled and shrank, it formed the cracks observed across the crater. For context, Mariner 1 ...
red shift blue shift
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
Create a HR Diagram - EarthSpaceScience
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
... Use that Table of stars and plot them on the Empty H-R diagram based on Luminosity and Spectral Class. Use circles or shading to correctly label the Main Sequence, Giants, and Dwarfs. Then use your diagram to answer the questions. Stars: Star Name ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... the K5 giant to be more luminous, it must have more square meters; i.e, it must have a larger surface area, thus a larger radius. 5. The B0 I star is farthest away, as it is the most luminous among the stars listed. The white dwarf is nearest, as it has the lowest luminosity among the stars listed. ...
... the K5 giant to be more luminous, it must have more square meters; i.e, it must have a larger surface area, thus a larger radius. 5. The B0 I star is farthest away, as it is the most luminous among the stars listed. The white dwarf is nearest, as it has the lowest luminosity among the stars listed. ...
Chapter14- Our Galaxy - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... In 1917 Harlow Shapley discovered that the globular clusters form a huge spherical system that is not centered on the Earth. ...
... In 1917 Harlow Shapley discovered that the globular clusters form a huge spherical system that is not centered on the Earth. ...
overview - Butlins
... - a collection of stars that make a shape normally named a er mythological characters, people, animals and things – Ursa Major, Orion, the Northern Cross etc ...
... - a collection of stars that make a shape normally named a er mythological characters, people, animals and things – Ursa Major, Orion, the Northern Cross etc ...
Measuring Distance in our Universe. Due Tue 1 Dec 2009 Imagine
... Imagine that you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. It would take 8 minutes to get to the Sun from Earth. To get to the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, it would take 4.2 years traveling at the speed of light. Distances on earth are often measured in kilometers but distances to the ...
... Imagine that you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. It would take 8 minutes to get to the Sun from Earth. To get to the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, it would take 4.2 years traveling at the speed of light. Distances on earth are often measured in kilometers but distances to the ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
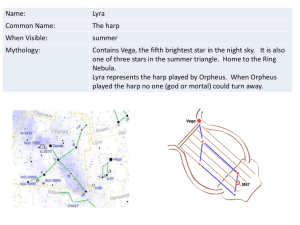
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.